- 投稿日:2019-03-05T21:15:23+09:00
vimのカラースキームをmolokaiに設定する。
molokaiのダウンロード
vimのカラースキームを入れるディレクトリを用意します。
$ mkdir ~/.vim $ cd ~/.vim $ mkdir colorsgit cloneコマンドでgithubからmolokaiをダウンロードします。
そして、用意したディレクトリにmolokaiを置きます。
$ git clone https://github.com/tomasr/molokai $ mv molokai/colors/molokai.vim ~/.vim/colors/カラースキームの設定
.vimrcファイルを新規作成します。
$ vi ~/.vimrc下記の通り編集し、ファイルを保存します。
syntax on colorscheme molokai set t_Co=256もう一度.vimrcファイルを開くと変更が反映されています。
$ vi ~/.vimrc
- 投稿日:2019-03-05T17:27:19+09:00
「Wireless Hacks」第二版(英語)by Rob Flickengerをハックしたい<書きかけ>
はじめに(introduction)
「Wireless Hacks」by Rob Flickengerをハックしたい
https://qiita.com/kaizen_nagoya/items/df87e75fe9a931fff472を書いていて、リンク切れなどについては、第二版(英語)を参照している。
第二版(英語)を拝見すると、第二版の視点での整理もあるとよいと思い書き始める。
()書きは第一版の対応または関連する章番号
目次(content)
Bluetooth, Mobile Phones, and GPS
Hacks 1-22: Introduction
Hack 1. Set Up Bluetooth on Linux (16)
Hack 2. Set Up Bluetooth on Windows XP
Hack 3. Connect Mac OS X with a Bluetooth Phone
Hack 4. Connect Linux with a Bluetooth Phone
Hack 5. Connect Windows XP with a Bluetooth Phone
Hack 6. Use Your Treo as a Modem
Hack 7. Send SMS from a PowerBook(14)
Hack 8. Remote Control Mac OS X with Bluetooth Phones and PDAs(13)
Hack 9. Remote Control Linux with a Bluetooth Phone(17)
Hack 10. Control XMMS with Bluetooth(19)
Hack 11. Liven Up Parties with a Participatory Slideshow
Hack 12. Send SMS from Linux
Hack 13. Remote Control Windows with Bluetooth Phones and PDAs
Hack 14. Control Your Bluetooth Phone with FMA
Hack 15. Control Your Computer from Your Palm
Hack 16. Control Your Home Theater from Your Palm
Hack 17. Choose a Cellular Data Plan
Hack 18. Blog from Your Mobile Phone
Hack 19. Get Google Maps on Your Mobile Phone
Hack 20. Share Your GPS
Hack 21. Broadcast Your GPS Position
Hack 22. Map Wi-Fi Networks with Kismet and GPSd
Network Discovery and MonitoringHacks 23-39: Introduction
Hack 23. Find All Available Wireless Networks(20)
Hack 24. Discover Networks with NetStumbler(21)
Hack 25. Detect Networks with Handheld PCs(23)
Hack 26. Find and Join Wireless Networks with AP Radar
Hack 27. Detect Networks on Mac OS X(22)
Hack 28. Scan Passively with KisMAC(24)
Hack 29. Detect Networks with Kismet(31)
Hack 30. Monitor Wireless Links in Linux with Wavemon(33)
Hack 31. Analyze Traffic with Ethereal(38)
Hack 32. Track 802.11 Frames in Ethereal(39)
Hack 33. Watch Network Traffic
Hack 34. grep Your Network
Hack 35. Check Wi-Fi Network Performance with Qcheck
Hack 36. Estimate Network Performance
Hack 37. Get Real-Time Network Stats
Hack 38. Graph Your Wireless Performance
Hack 39. Find Radio Manufacturers by MAC(27)
Wireless SecurityHacks 40-51: Introduction
Hack 40. Stop Moochers from Stealing Your Wi-Fi Bandwidth
Hack 41. Visualize a Network
Hack 42. Secure Your Linux Network with WPA
Hack 43. Control Wireless Access by MAC
Hack 44. Authenticate Wireless Users
Hack 45. Forward Ports over SSH
Hack 46. Proxy Web Traffic over SSH
Hack 47. Securely Connect Two Networks
Hack 48. Generate a Tunnel Configuration Automatically
Hack 49. Poll Wireless Clients
Hack 50. Interrogate the Network
Hack 51. Track Wireless Users
Hardware HacksHacks 5262: Introduction
Hack 52. Add an External Antenna(49)
Hack 53. Do-It-Yourself Access Point Hardware(51)
Hack 54. Boot from a Compact Flash Hard Drive(52)
Hack 55. Increase the Range of a PowerBook
Hack 56. Send Power over Your Ethernet
Hack 57. The NoCat Night Light(50)
Hack 58. Upgrade the Linksys WET11(45)
Hack 59. Scan for Wireless Networks Automatically
Hack 60. Backlight Your Zipit
Hack 61. Unwire Your Pistol Mouse
Hack 62. Mobilize Your WRT54G with the WiFiCar
Software HacksHacks 63-82: Introduction
Hack 63. Build Your Own Access Point with Linux
Hack 64. Bridge Your Linux AP
Hack 65. Protect Your Bridge with a Firewall(59)
Hack 66. Filter MAC with HostAP and Madwifi(60)
Hack 67. Upgrade Your Wireless Router
Hack 68. Set Up an OLSR Mesh Network
Hack 69. Extend Your Wireless Network with WDS
Hack 70. Pebble(53)
Hack 71. Wall Off Your Wireless
Hack 72. Run Your Mac as an Access Point
Hack 73. Run Linux on the Zipit Wireless Messenger
Hack 74. Capture Wireless Users with NoCatAuth
Hack 75. Capture Wireless Users on a Small Scale
Hack 76. Build an Online Community in Your Offline Neighborhood
Hack 77. Manage Multiple AirPort Base Stations
Hack 78. Advertise Bonjour Services in Linux
Hack 79. Advertise Any Service with Bonjour in Mac OS X
Hack 80. Redirect Brought to you by Bonjour Ads
Hack 81. Use a Windows-Only Wireless Card in Linux
Hack 82. Use Your Orinoco Card with Hermes AP(62)
Do-It-Yourself AntennasHacks 83-93: Introduction
Hack 83. Make a Deep Dish Cylindrical Parabolic Reflector(70)
Hack 84. Spider Omni Antenna(71)
Hack 85. Pringles Can Waveguide(72)
Hack 86. Pirouette Can Waveguide(73)
Hack 87. Primestar Dish with Waveguide Feed(74)
Hack 88. Primestar Dish with Biquad Feed(75)
Hack 89. Cut a Cable Omni Antenna(76)
Hack 90. Build a Slotted Waveguide Antenna(77)
Hack 91. The Passive Repeater(78)
Hack 92. Determine Your Antenna Gain(79)
Hack 93. Build Cheap, Effective Roof Mounts(69)
Wireless Network DesignHacks 94-100: Introduction
Hack 94. Analyze Elevation Profiles for Better Long-Range Wireless Networking
Hack 95. Build a Wireless Network for the Large House
Hack 96. Establish Line of Sight(80)
Hack 97. Calculate the Link Budget(81)
Hack 98. Align Antennas at Long Distances(82)
Hack 99. Slow Down to Speed Up(83)
Hack 100. Take Advantage of Antenna Polarization(84)
Appendix A. Wireless StandardsAppendix A. Wireless Standards
Section A.1. 802.11: The Mother of All IEEE Wireless Ethernet(1)
Section A.2. 802.11a: The Betamax of the 802.11 Family(2)
Section A.3. 802.11b: The De Facto Standard(3)
Section A.4. 802.11g: Like 802.11b, only Faster(4)
Section A.5. 802.16: WiMAX Long Distance Wireless Infrastructure(5)
Section A.6. Bluetooth: Cable Replacement for Devices(6)
Section A.7. 900 MHz: Low Speed, Better Coverage(7)
Section A.8. CDPD, 1xRTT, and GPRS: Cellular Data Networks(8)
Section A.9. FRS and GMRS: Super Walkie-Talkies(9)
Section A.10. 802.1x: Port Security for Network Communications(10)
Section A.11. WPA & 802.11i
Section A.12. BSS Versus IBSS(12)
Appendix B. Wireless Hardware GuideAppendix B. Wireless Hardware Guide
Section B.1. Microwave Cabling(62)
Section B.2. Microwave Connector Reference(63)
Section B.3. Antenna Guide(64)
Section B.4. Pigtails(66)
Section B.5. 802.11 Hardware Suppliers(67)対応しているのが57項目。第二版は117項目であり、約半分。
わずか2年の間に劇的に変化。
Bluetooth, Mobile Phones, and GPS
Hacks 1-22: Introduction
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hacks_122_introduction.html
Hack 1. Set Up Bluetooth on Linux
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_1_set_up_bluetooth_on_linux.html
(V1:16.LinuxでBluetoothを使う/ Hack 16 Using Bluetooth with Linux) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-2-sect-5.htmlBlueZ-supported hardware
http://www.holtmann.org/linux/bluetooth/devices.html
リンク切れBlueZ Users mailing list,
http://www.bluez.org/lists.htmlHack 2. Set Up Bluetooth on Windows XP
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_2_set_up_bluetooth_on_windows_xp.html
参照
The O'Reilly Wireless web site
http://wireless.oreilly.com
は
https://www.safaribooksonline.com/search/?query=networking
に転送(redirect)Windows XP Unwired by Wei-Meng Lee (O'Reilly)
http://shop.oreilly.com/product/9780596005368.doHack 3. Connect Mac OS X with a Bluetooth Phone
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_3_connect_mac_os_x_with_a_bluetooth_phone.html
Apple maintains a list of phones
http://www.apple.com/macosx/features/isync/devices.html
は
https://support.apple.com/ja-jp/HT2824
に転送(redirect)日本で日本語のブラウザからだから。Ross Barkman
http://www.taniwha.org.ukOpera's site for GSM providers has an excellent list of APNs
http://www.opera.com/products/mobile/docs/connect/
は
https://www.opera.com/ja/mobile/android
に転送(redirect) 日本で日本語のブラウザからだから。Hack 4. Connect Linux with a Bluetooth Phone
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_4_connect_linux_with_a_bluetooth_phone.html
sdptool
Hack 5. Connect Windows XP with a Bluetooth Phone
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_5_connect_windows_xp_with_a_bluetooth_phone.html
Hack 6. Use Your Treo as a Modem
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_6_use_your_treo_as_a_modem.html
Treo 650
http://www.palm.com/us/support/downloads/treo650updater/sprint.html
リンク切れHow to Use the Bluetooth Dial Up Networking Hack
shadowmite patch
http://www.shadowmite.com/HowToDUN.htmlPdaNet application
http://www.junefabrics.comWirelessModem
http://www.notifymail.com/palm/wmodem/Internet on Air
Treo 650 to a Mac using Bluetooth
http://vocaro.com/trevor/treo-dun/Hack 7. Send SMS from a PowerBook
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_7_send_sms_from_a_powerbook.html
(V1:14.本物のキーボードでショートメッセージ作成/ Hack 14 SMS with a Real Keyboard) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-2-sect-3.htmllist of phones supported by Mac OS X
http://www.apple.com/macosx/features/isync/devices.html
は
https://support.apple.com/ja-jp/HT2824
に転送(redirect)Hack 8. Remote Control Mac OS X with Bluetooth Phones and PDAs
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_8_remote_control_mac_os_x_with_bluetooth_phones_and_pdas.html
(V1:13.ソニーエリクソンの携帯でOS Xを操作する/ Hack 13 Remote Control OS X with a Sony Ericsson Phone) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-2-sect-2.htmlPalmOS 4 or 5 devices
http://homepage.mac.com/jonassalling/Shareware/Clicker/faq.html#supported_devices
リンク切れClicker
http://homepage.mac.com/jonassalling/Shareware/Clicker/
検索すると
www.salling.com/clicker/Hack 9. Remote Control Linux with a Bluetooth Phone
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_9_remote_control_linux_with_a_bluetooth_phone.html
(V1:17.LinuxからBluetooth経由でGPRSを使う/ Hack 17 Bluetooth to GPRS in Linux) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-2-sect-6.htmlBluetooth stack and utilities
http://www.geocities.com/saravkrish/progs/bluemote
http://www.geocities.com/saravkrish/progs/bluemote/scripts.tar.gz
リンク切れbluemoteで検索
(Bluemote – remote control of a 8051 robot with bluetooth
https://redacacia.me/2010/09/21/bluemote-remote-control-of-a-8051-robot-with-bluetooth/ )Hack 10. Control XMMS with Bluetooth
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_10_control_xmms_with_bluetooth.html
(V1:19.BluetoothによるXMMSの制御/ Hack 19 Controlling XMMS with Bluetooth) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-2-sect-8.htmlHack 11. Liven Up Parties with a Participatory Slideshow
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_11_liven_up_parties_with_a_participatory_slideshow.html
Ubuntu
http://www.ubuntulinux.org/downloadHack 12. Send SMS from Linux
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_12_send_sms_from_linux.html
gsmsendsms utility from gsmlib
http://www.pxh.de/fs/gsmlib/index.htmlHack 13. Remote Control Windows with Bluetooth Phones and PDAs
PuppetMaster software
http://www.lim.com.au/PuppetMaste
リンク切れHack 14. Control Your Bluetooth Phone with FMA
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_14_control_your_bluetooth_phone_with_fma.html
flOat's Mobile Agent (FMA)
http://fma.sourceforge.netHack 15. Control Your Computer from Your Palm
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_15_control_your_computer_from_your_palm.html
VNC web
http://www.realvnc.comTightVNC
http://www.tightvnc.comUltraVNC
http://www.ultravnc.comOSXvnc
http://www.redstonesoftware.com/vnc.htmlPalmVNC
http://palmvnc2.free.frPebbles Project
http://www.pebbles.hcii.cmu.eduNo-IP.com
http://www.no-ip.comDynu
http://www.dynu.comDynDNS.org
http://www.dyndns.orgMergic VPN
http://www.mergic.com
リンク切れHack 16. Control Your Home Theater from Your Palm
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_16_control_your_home_theater_from_your_palm.html
OmniRemote
http://www.pacificneotek.com
リンク切れNoviiRemote
http://www.novii.tv
未確認RemoteCentral
http://www.remotecentral.comPacific Neo-Tek
http://www.pacificneotek.com
リンク切れHack 17. Choose a Cellular Data Plan
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_17_choose_a_cellular_data_plan.html
company URL AT&T(Cingular) https://www.att.com/wireless/ Orange France https://boutique.orange.fr EE (Orange UK) https://ee.co.uk Rogers https://www.rogers.com/consumer/home Sprint https://www.sprint.com T-Mobile https://www.t-mobile.com Telcel Mexico https://www.telcel.com Verizon Wireless https://www.verizonwireless.com/ Vodafone UK https://www.vodafone.co.uk Hack 18. Blog from Your Mobile Phone
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_18_blog_from_your_mobile_phone.html
Txtsolutions
http://blog.txtsolutions.comBlogger
http://www.blogger.comLiveJournal
http://www.livejournal.comTypePad
http://www.typepad.comRadio UserLand
http://radio.userland.comTextamerica
http://www.textamerica.comFotolog
http://www.fotolog.netFlickr
http://www.flickr.coma little open source J2ME (Java 2 Mobile Edition)
http://sourceforge.net/projects/moblogger2/http://manojtk.blogspot.com/2005/01/smtp-email-attachments-from-nokia-6600.html.
WordPress
http://www.wordpress.org/
http://wordpress.org/docs/installation/5-minute/http://blade.lansmash.com/index.php?cat=5
http://www.vienna360.net/files/wp-mail.phps.
http://your-domain-name/MyMoblog/wp-mail.php.
Cygwin toolkit
http://www.cygwin.com/Hack 19. Get Google Maps on Your Mobile Phone
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_19_get_google_maps_on_your_mobile_phone.html
Hack 20. Share Your GPS
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_20_share_your_gps.html
参考資料
Casey West's O'Reilly Network article on his cross-car road trip network: http://www.oreillynet.com/pub/a/wireless/2002/08/01/highway_lan.htmlHack 21. Broadcast Your GPS Position
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_21_broadcast_your_gps_position.html
NoCat community network
http://nocat.netBurning Man
http://www.burningman.com参考資料
802.11 beacons:
http://www.wi-fiplanet.com/tutorials/article.php/1492071Hack 22. Map Wi-Fi Networks with Kismet and GPSd
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_22_map_wi_fi_networks_with_kismet_and_gpsd.html
Ethereal
http://www.ethereal.com
はwireshark
に改名。
https://www.wireshark.orgNetwork Discovery and Monitoring
Hacks 23-39: Introduction
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hacks_2339_introduction.html
Hack 23. Find All Available Wireless Networks(20)
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_23_find_all_available_wireless_networks.html
(V1:20.すべての利用可能な無線ネットワークを発見する/ Hack 20 Find All Available Wireless Networks) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-2.htmlHack 24. Discover Networks with NetStumbler
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_24_discover_networks_with_netstumbler.html
(V1:21. NetStumblerを用いたネットワークの発見/ Hack 21 Network Discovery Using NetStumbler) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-3.htmlHack 25. Detect Networks with Handheld PCs
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_25_detect_networks_with_handheld_pcs.html
(V1:23.ハンドヘルドPCを使ってネットワークを検出/ Hack 23 Detecting Networks Using Handheld PCs) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-5.htmlHack 26. Find and Join Wireless Networks with AP Radar
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_26_find_and_join_wireless_networks_with_ap_radar.html
Hack 27. Detect Networks on Mac OS X
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_27_detect_networks_on_mac_os_x.html
(V1:22.Mac OS Xでのネットワーク検出/ Hack 22 Network Detection on Mac OS X) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-4.htmlHack 28. Scan Passively with KisMAC
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_28_scan_passively_with_kismac.html
(V1:24.KisMACによるパッシブスキャン/ Hack 24 Passive Scanning with KisMAC) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-6.htmlHack 29. Detect Networks with Kismet
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_29_detect_networks_with_kismet.html
(V1:31.Kismetでネットワークを検出/ Hack 31 Detecting Networks with Kismet) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-13.htmlHack 30. Monitor Wireless Links in Linux with Wavemon
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_30_monitor_wireless_links_in_linux_with_wavemon.html
(V1:33. Wavemonを用いたLinuxでのリンクモニタリング/ Hack 33 Link Monitoring in Linux with Wavemon) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-15.htmlHack 31. Analyze Traffic with Ethereal
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_31_analyze_traffic_with_ethereal.html
(V1:38.Etherealによる視覚的なトラフィック解析/ Hack 38 Visual Traffic Analysis with Ethereal) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-20.htmlHack 32. Track 802.11 Frames in Ethereal
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_32_track_80211_frames_in_ethereal.html
(V1:39.Etherealで802.11フレームを追跡する/ Hack 39 Tracking 802.11 Frames in Ethereal) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-21.htmlHack 33. Watch Network Traffic
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_33_watch_network_traffic.html
Hack 34. grep Your Network
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_34_grep_your_network.html
Hack 35. Check Wi-Fi Network Performance with Qcheck
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_35_check_wi_fi_network_performance_with_qcheck.html
Hack 36. Estimate Network Performance
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_36_estimate_network_performance.html
Hack 37. Get Real-Time Network Stats
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_37_get_real_time_network_stats.html
Hack 38. Graph Your Wireless Performance
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_38_graph_your_wireless_performance.html
Hack 39. Find Radio Manufacturers by MAC
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_39_find_radio_manufacturers_by_mac.html
(V1:27.MACアドレスでカードのメーカーを特定する/ Hack 27 Finding Radio Manufacturers by MAC Address) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-9.htmlWireless Security
Hacks 40-51: Introduction
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hacks_4051_introduction.html
Hack 40. Stop Moochers from Stealing Your Wi-Fi Bandwidth
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_40_stop_moochers_from_stealing_your_wi_fi_bandwidth.html
Hack 41. Visualize a Network
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_41_visualize_a_network.html
Hack 42. Secure Your Linux Network with WPA
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_42_secure_your_linux_network_with_wpa.html
Hack 43. Control Wireless Access by MAC
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_43_control_wireless_access_by_mac.html
Hack 44. Authenticate Wireless Users
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_44_authenticate_wireless_users.html
Hack 45. Forward Ports over SSH
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_45_forward_ports_over_ssh.html
Hack 46. Proxy Web Traffic over SSH
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_46_proxy_web_traffic_over_ssh.html
Hack 47. Securely Connect Two Networks
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_47_securely_connect_two_networks.html
Hack 48. Generate a Tunnel Configuration Automatically
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_48_generate_a_tunnel_configuration_automatically.html
Hack 49. Poll Wireless Clients
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_49_poll_wireless_clients.html
Hack 50. Interrogate the Network
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_50_interrogate_the_network.html
Hack 51. Track Wireless Users
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_51_track_wireless_users.html
Hardware Hacks
Hacks 52-62: Introduction
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hacks_5262_introduction.html
Hack 52. Add an External Antenna
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_52_add_an_external_antenna.html
(V1:49.AirMacベースステーションにアンテナを追加/ Hack 49 Adding an Antenna to the AirPort) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-8.htmlHack 53. Do-It-Yourself Access Point Hardware
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_53_do_it_yourself_access_point_hardware.html
(V1:51.DIYアクセスポイント/ Hack 51 Do-It-Yourself Access Point Hardware) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-10.htmlHack 54. Boot from a Compact Flash Hard Drive
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_54_boot_from_a_compact_flash_hard_drive.html
(V1:52.コンパクトフラッシュハードディスク/ Hack 52 Compact Flash Hard Drive) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-11.htmlHack 55. Increase the Range of a PowerBook
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_55_increase_the_range_of_a_powerbook.html
Hack 56. Send Power over Your Ethernet
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_56_send_power_over_your_ethernet.html
Hack 57. The NoCat Night Light
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_57_the_nocat_night_light.html
(V1:50.NoCat常夜燈/ Hack 50 The NoCat Night Light) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-9.htmlHack 58. Upgrade the Linksys WET11
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_58_upgrade_the_linksys_wet11.html
(V1:45.WET11のアップグレード/ Hack 45 WET11 Upgrades) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-4.htmlHack 59. Scan for Wireless Networks Automatically
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_59_scan_for_wireless_networks_automatically.html
Hack 60. Backlight Your Zipit
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_60_backlight_your_zipit.html
Hack 61. Unwire Your Pistol Mouse
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_61_unwire_your_pistol_mouse.html
Hack 62. Mobilize Your WRT54G with the WiFiCar
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_62_mobilize_your_wrt54g_with_the_wificar.html
Software Hacks
Hacks 63-82: Introduction
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hacks_6382_introduction.html
Hack 63. Build Your Own Access Point with Linux
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_63_build_your_own_access_point_with_linux.html
Hack 64. Bridge Your Linux AP
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_64_bridge_your_linux_ap.html
Hack 65. Protect Your Bridge with a Firewall
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_65_protect_your_bridge_with_a_firewall.html
(V1:59.ファイアウォール付きブリッジ/ Hack 59 Bridging with a Firewall) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-18.htmlHack 66. Filter MAC with HostAP and Madwifi
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_66_filter_mac_with_hostap_and_madwifi.html
(V1:61.Hermes AP/ Hack 61 Hermes AP) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-20.htmlHack 67. Upgrade Your Wireless Router
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_67_upgrade_your_wireless_router.html
Hack 68. Set Up an OLSR Mesh Network
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_68_set_up_an_olsr_mesh_network.html
Hack 69. Extend Your Wireless Network with WDS
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_69_extend_your_wireless_network_with_wds.html
Hack 70. Pebble
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_70_pebble.html
(V1:53.Pebble/ Hack 53 Pebble) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-12.htmlHack 71. Wall Off Your Wireless
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_71_wall_off_your_wireless.html
Hack 72. Run Your Mac as an Access Point
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_72_run_your_mac_as_an_access_point.html
Hack 73. Run Linux on the Zipit Wireless Messenger
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_73_run_linux_on_the_zipit_wireless_messenger.html
Hack 74. Capture Wireless Users with NoCatAuth
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_74_capture_wireless_users_with_nocatauth.html
Hack 75. Capture Wireless Users on a Small Scale
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_75_capture_wireless_users_on_a_small_scale.html
Hack 76. Build an Online Community in Your Offline Neighborhood
Hack 77. Manage Multiple AirPort Base Stations
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_77_manage_multiple_airport_base_stations.html
Hack 78. Advertise Bonjour Services in Linux
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_78_advertise_bonjour_services_in_linux.html
Hack 79. Advertise Any Service with Bonjour in Mac OS X
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_79_advertise_any_service_with_bonjour_in_mac_os_x.html
Hack 80. Redirect Brought to you by Bonjour Ads
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_80_redirect_brought_to_you_by_bonjour_ads.html
Hack 81. Use a Windows-Only Wireless Card in Linux
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_81_use_a_windows_only_wireless_card_in_linux.html
Hack 82. Use Your Orinoco Card with Hermes AP
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_82_use_your_orinoco_card_with_hermes_ap.html
(V1:62.マイクロ波ケーブルガイド: Hack 62 Microwave Cabling Guide) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-21.htmlDo-It-Yourself Antennas
Hacks 83-93: Introduction
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hacks_8393_introduction.html
Hack 83. Make a Deep Dish Cylindrical Parabolic Reflector
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_83_make_a_deep_dish_cylindrical_parabolic_reflector.html
(V1:70.筒状深皿パラボラ反射板/ Hack 70 Deep Dish Cylindrical Parabolic Reflector) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-2.htmlHack 84. Spider Omni Antenna
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_84_spider_omni_antenna.html
(V1:71.スパイダーオムニ/ Hack 71 "Spider" Omni) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-3.htmlHack 85. Pringles Can Waveguide
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_85_pringles_can_waveguide.html
(V1:72.プリングルス缶の導波管/ Hack 72 Pringles Can Waveguide) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-4.htmlHack 86. Pirouette Can Waveguide
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_86_pirouette_can_waveguide.html
(V1:73.ピルエット缶の導波管/ Hack 73 Pirouette Can Waveguide) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-5.htmlHack 87. Primestar Dish with Waveguide Feed
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_87_primestar_dish_with_waveguide_feed.html
(V1:74.導波管付きのPrimestar衛星パラボラ/ Hack 74 Primestar Dish with Waveguide Feed) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-6.htmlHack 88. Primestar Dish with Biquad Feed
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_88_primestar_dish_with_biquad_feed.html
(V1:75.Primestar衛星パラボラ用のBiQuadフィード/ Hack 75 BiQuad Feed for Primestar Dish) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-7.htmlHack 89. Cut a Cable Omni Antenna
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_89_cut_a_cable_omni_antenna.html
(V1:76.カットケーブル・オムニアンテナ/ Hack 76 Cut Cable Omni Antenna) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-8.htmlHack 90. Build a Slotted Waveguide Antenna
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_90_build_a_slotted_waveguide_antenna.html
(V1:77.スロット型導波管/ Hack 77 Slotted Waveguides) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-9.htmlHack 91. The Passive Repeater
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_91_the_passive_repeater.html
(V1:78.パッシブリピータ(受動型中継器)/ Hack 78 The Passive Repeater) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-10.htmlHack 92. Determine Your Antenna Gain
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_92_determine_your_antenna_gain.html
(V1:79.アンテナの利得の測定/ Hack 79 Determining Antenna Gain) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-11.htmlHack 93. Build Cheap, Effective Roof Mounts
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_93_build_cheap_effective_roof_mounts.html
(V1:69.安くて効果的な屋上マウント/ Hack 69 Cheap but Effective Roof Mounts) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-28.htmlWireless Network Design
Hacks 94-100: Introduction
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hacks_94100_introduction.html
Hack 94. Analyze Elevation Profiles for Better Long-Range Wireless Networking
Hack 95. Build a Wireless Network for the Large House
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_95_build_a_wireless_network_for_the_large_house.html
Hack 96. Establish Line of Sight
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_96_establish_line_of_sight.html
(V1:80.見通し線の確保/ Hack 80 Establishing Line of Sight) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-6-sect-2.htmlHack 97. Calculate the Link Budget
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_97_calculate_the_link_budget.html
(V1:81.リンクバジェットの計算/ Hack 81 Calculating the Link Budget) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-6-sect-3.htmlHack 98. Align Antennas at Long Distances
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_98_align_antennas_at_long_distances.html
(V1:82.長距離リンクのためのアンテナ調整法/ Hack 82 Aligning Antennas at Long Distances) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-6-sect-4.htmlHack 99. Slow Down to Speed Up
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_99_slow_down_to_speed_up.html
(V1:83.遅くすれば速くなる/ Hack 83 Slow Down to Speed Up) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-6-sect-5.htmlHack 100. Take Advantage of Antenna Polarization
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_100_take_advantage_of_antenna_polarization.html
(V1:84.アンテナの偏向性を活用する/ Hack 84 Taking Advantage of Antenna Polarization) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-6-sect-6.htmlAppendix A. Wireless Standards
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/appendix_a_wireless_standards.html
Section A.1. 802.11: The Mother of All IEEE Wireless Ethernet
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a1_80211_the_mother_of_all_ieee_wireless_ethernet.html
(V1:1.802.11:すべてのIEEE無線イーサネットの生みの親/ Hack 1 802.11: The Mother of All IEEE Wireless Ethernet) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-2.htmlSection A.2. 802.11a: The Betamax of the 802.11 Family
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a2_80211a_the_betamax_of_the_80211_family.html
(V1:2.802.11a:802.11ファミリーのベータマックス/ Hack 2 802.11a: The Betamax of the 802.11 Family) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-3.htmlget IEEE 802
http://standards.ieee.org/getieee802/The Wi-Fi alliance
http://www.weca.netSection A.3. 802.11b: The De Facto Standard
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a3_80211b_the_de_facto_standard.html
(V1:3.802.11b:デファクトスタンダード/ Hack 3 802.11b: The De Facto Standard) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-4.htmlSection A.4. 802.11g: Like 802.11b, only Faster
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a4_80211g_like_80211b_only_faster.html
(V1:4.802.11g:より高速な802.11b/ Hack 4 802.11g: Like 802.11b, only Faster) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-5.htmlSection A.5. 802.16: WiMAX Long Distance Wireless Infrastructure
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a5_80216_wimax_long_distance_wireless_infrastructure.html
(V1:5. 802.16:長距離無線インフラ/ Hack 5 802.16: Long Distance Wireless Infrastructure) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-6.htmlSection A.6. Bluetooth: Cable Replacement for Devices
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a6_bluetooth_cable_replacement_for_devices.html
(V1:6.Bluetooth:デバイス間のケーブルの置き換え/ Hack 6 Bluetooth: Cable Replacement for Devices) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-7.htmlSection A.7. 900 MHz: Low Speed, Better Coverage
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a7_900_mhz_low_speed_better_coverage.html
(V1:7. 900MHz:低速度、高到達範囲(Hack 7 900 MHz: Low Speed, Better Coverage) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-8.html
Section A.8. CDPD, 1xRTT, and GPRS: Cellular Data Networks
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a8_cdpd_1xrtt_and_gprs_cellular_data_networks.html
(V1:8. CDPD、1xRTT、GPRS:携帯電話データネットワーク/ Hack 8 CDPD, 1xRTT, and GPRS: Cellular Data Networks) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-9.htmlHipTop by Danger
http://www.danger.com/Section A.9. FRS and GMRS: Super Walkie-Talkies
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a9_frs_and_gmrs_super_walkie_talkies.html
(V1:9.FRS、GMRS:スーパートランシーバー/ Hack 9 FRS and GMRS: Super Walkie-Talkies) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-10.htmlUniversal Licensing System
http://wireless.fcc.gov/uls/FCC rule-book
http://www.access.gpo.gov/nara/cfr/waisidx_00/47cfr95_00.htmlPersonal Radio Steering Group http://www.provide.net/~prsg/rules.htm
リンク切れSection A.10. 802.1x: Port Security for Network Communications
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a10_8021x_port_security_for_network_communications.html
(V1:10.802.1x:ネットワーク通信のためのポートセキュリティ/ Hack 10 802.1x: Port Security for Network Communications) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-11.htmlopen source 802.1x supplicant implementation project
http://www.open1x.org/
は
http://open1x.sourceforge.net
に転送(redirect)802.1x security methods and problems online
http://www.sans.org/rr/wireless/802.11.php
リンク切れメニューから選ぶ
https://www.sans.org/reading-room/
登録した。wireless見当たらず。Section A.11. WPA & 802.11i
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a11_wpa_80211i.html
WPA2 supports the more robust AES encryption algorithms to replace TKIP
Section A.12. BSS Versus IBSS
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a12_bss_versus_ibss.html
(V1:12.BSS対IBSS/ Hack 12 BSS Versus IBSS) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-13.htmlAppendix B. Wireless Hardware Guide
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/appendix_b_wireless_hardware_guide.html
Section B.1. Microwave Cabling
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_b1_microwave_cabling.html
(V1:62.マイクロ波ケーブルガイド/ Hack 62 Microwave Cabling Guide) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-21.htmlSection B.2. Microwave Connector Reference
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_b2_microwave_connector_reference.html
(V1:63.マイクロ波コネクタマニュアル/ Hack 63 Microwave Connector Reference) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-22.htmlBNC (Bayonet Neill Concelman)
TNC (threaded version of the BNC)
N (Neill) connector
SMA (Sub-Miniature, variation A)
SMC (very small version of the SMA)
SMB (quick-connect version of the SMC)APC-7 (Amphenol Precision connector 7mm sexless)
Section B.3. Antenna Guide
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_b3_antenna_guide.html
(V1:64.アンテナガイド/ Hack 64 Antenna Guide) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-23.htmlOmni:Omnidirectional antennas
Sector (or Sectoral)
Yagi
Waveguides and "Cantennas"
Parabolic DishesSection B.4. Pigtails
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_b4_pigtails.html
(V1:66.ピグテイルアダプタ/ Hack 66 Pigtails) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-25.htmlSection B.5. 802.11 Hardware Suppliers
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_b5_80211_hardware_suppliers.html
(V1:67.802.11ハードウェアベンダ/ Hack 67 802.11 Hardware Suppliers) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-26.htmlAeralix, Peabody, MA
http://www.aerialix.com
リンク切れAntenna Systems and Supplies, Schaumburg, IL http://www.antennasystems.com
未確認Down East Microwave, Frenchtown, NJ
http://www.downeastmicrowave.com
確認ElectroComm, Denver, CO
http://www.ecommwireless.com
リンク切れFAB Corp, Tampa Bay, FL
http://www.fab-corp.com
確認HD Communications, Ronkonkoma, NY
http://www.hdcom.com
2016Hyperlink Tech, Boca Raton, FL
http://www.hyperlinktech.com
確認Metrix, Seattle, WA
http://metrix.net
未確認NetGate, Spokane, WA
http://www.netgate.com
確認NetNimble, Sacramento, CA
http://www.netnimble.net
リンク切れPasadena Networks, Pasadena, CA
http://www.pasadena.net
未確認Superpass, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada
http://www.superpass.com
2014The RF Connection, Gaithersburg, MD
http://www.therfc.com
未確認参考資料(reference)
「Wireless Hack」by Rob Flickengerをハックしたい
https://qiita.com/kaizen_nagoya/items/df87e75fe9a931fff472文書履歴(document history)
ver. 0.01 初稿 20190305 午後5時
ver. 0.02 追記 20190305 午後6時
ver. 0.03 10章まで 20190305 午後7時
ver. 0.04 Appendix A 追記 20190305 午後8時
ver. 0.05 Appendix B 追記 20190305 午後9時
ver. 0.06 22章まで 20190305 午後10時
ver. 0.07 60章まで英文URL 20190305 午後11時
ver. 0.08 英文URL完了 20190306 午前7時
ver. 0.09 V1 URL追記 20190306 午前8時
ver. 0.10 V1/V2目次比較 20190306 午前9時対比表 初版、2版(英語)
Chapter 1. The Standards ORG 2nd Appendix A. Wireless Standards Section 1.1. Hacks #1-12 Appendix A. Wireless Standards Hack 1. 802.11: The Mother of All IEEE Wireless Ethernet A1 1 Section A.1. 802.11: The Mother of All IEEE Wireless Ethernet Hack 2. 802.11a: The Betamax of the 802.11 Family A2 2 Section A.2. 802.11a: The Betamax of the 802.11 Family Hack 3. 802.11b: The De Facto Standard A3 3 Section A.3. 802.11b: The De Facto Standard Hack 4. 802.11g: Like 802.11b, only Faster A4 4 Section A.4. 802.11g: Like 802.11b, only Faster Hack 5. 802.16: Long Distance Wireless Infrastructure A5 5 Section A.5. 802.16: WiMAX Long Distance Wireless Infrastructure Hack 6. Bluetooth: Cable Replacement for Devices A6 6 Section A.6. Bluetooth: Cable Replacement for Devices Hack 7. 900 MHz: Low Speed, Better Coverage A7 7 Section A.7. 900 MHz: Low Speed, Better Coverage Hack 8. CDPD, 1xRTT, and GPRS: Cellular Data Networks A8 8 Section A.8. CDPD, 1xRTT, and GPRS: Cellular Data Networks Hack 9. FRS and GMRS: Super Walkie-Talkies A9 9 Section A.9. FRS and GMRS: Super Walkie-Talkies Hack 10. 802.1x: Port Security for Network Communications A10 10 Section A.10. 802.1x: Port Security for Network Communications Hack 11. HPNA and Powerline Ethernet Section A.11. WPA & 802.11i Hack 12. BSS Versus IBSS A12 12 Section A.12. BSS Versus IBSS Chapter 2. Bluetooth and Mobile Data Hacks 122: Introduction Section 2.1. Hacks #13-19 16 Hack 1. Set Up Bluetooth on Linux Hack 13. Remote Control OS X with a Sony Ericsson Phone 8 Hack 2. Set Up Bluetooth on Windows XP Hack 14. SMS with a Real Keyboard -7 Hack 3. Connect Mac OS X with a Bluetooth Phone Hack 15. Photo Blog Automatically with the Nokia 3650 Hack 4. Connect Linux with a Bluetooth Phone Hack 16. Using Bluetooth with Linux 1 Hack 5. Connect Windows XP with a Bluetooth Phone Hack 17. Bluetooth to GPRS in Linux -9 Hack 6. Use Your Treo as a Modem Hack 18. Bluetooth File Transfers in Linux -14 Hack 7. Send SMS from a PowerBook Hack 19. Controlling XMMS with Bluetooth 10 13 Hack 8. Remote Control Mac OS X with Bluetooth Phones and PDAs -17 Hack 9. Remote Control Linux with a Bluetooth Phone Chapter 3. Network Monitoring 19 Hack 10. Control XMMS with Bluetooth Section 3.1. Hacks #20-42 Hack 11. Liven Up Parties with a Participatory Slideshow Hack 20. Find All Available Wireless Networks 23 Hack 12. Send SMS from Linux Hack 21. Network Discovery Using NetStumbler 24 Hack 13. Remote Control Windows with Bluetooth Phones and PDAs Hack 22. Network Detection on Mac OS X 27 Hack 14. Control Your Bluetooth Phone with FMA Hack 23. Detecting Networks Using Handheld PCs 25 Hack 15. Control Your Computer from Your Palm Hack 24. Passive Scanning with KisMAC 28 Hack 16. Control Your Home Theater from Your Palm Hack 25. Establishing Connectivity Hack 17. Choose a Cellular Data Plan Hack 26. Quickly Poll Wireless Clients with ping Hack 18. Blog from Your Mobile Phone Hack 27. Finding Radio Manufacturers by MAC Address 39 Hack 19. Get Google Maps on Your Mobile Phone Hack 28. Rendezvous Service Advertisements in Linux Hack 20. Share Your GPS Hack 29. Advertising Arbitrary Rendezvous Services in OS X Hack 21. Broadcast Your GPS Position Hack 30. "Brought to you by" Rendezvous Ad Redirector Hack 22. Map Wi-Fi Networks with Kismet and GPSd Hack 31. Detecting Networks with Kismet 29 Hack 32. Running Kismet on Mac OS X Network Discovery and Monitoring Hack 33. Link Monitoring in Linux with Wavemon 30 Hacks 2339: Introduction Hack 34. Historical Link State Monitoring 20 Hack 23. Find All Available Wireless Networks Hack 35. EtherPEG and DriftNet 21 Hack 24. Discover Networks with NetStumbler Hack 36. Estimating Network Performance 23 Hack 25. Detect Networks with Handheld PCs Hack 37. Watching Traffic with tcpdump Hack 26. Find and Join Wireless Networks with AP Radar Hack 38. Visual Traffic Analysis with Ethereal 31 22 Hack 27. Detect Networks on Mac OS X Hack 39. Tracking 802.11 Frames in Ethereal 32 24 Hack 28. Scan Passively with KisMAC Hack 40. Interrogating the Network with nmap 31 Hack 29. Detect Networks with Kismet Hack 41. Network Monitoring with ngrep 33 Hack 30. Monitor Wireless Links in Linux with Wavemon Hack 42. Running ntop for Real-Time Network Stats 38 Hack 31. Analyze Traffic with Ethereal 39 Hack 32. Track 802.11 Frames in Ethereal Hack 33. Watch Network Traffic Hack 34. grep Your Network Hack 35. Check Wi-Fi Network Performance with Qcheck Hack 36. Estimate Network Performance Hack 37. Get Real-Time Network Stats Hack 38. Graph Your Wireless Performance 27 Hack 39. Find Radio Manufacturers by MAC Chapter 4. Hardware Hacks Hardware Hacks Section 4.1. Hacks #43-69 Hacks 5262: Introduction Hack 43. Add-on Laptop Antennas -49 Hack 52. Add an External Antenna Hack 44. Increasing the Range of a Titanium PowerBook 51 Hack 53. Do-It-Yourself Access Point Hardware Hack 45. WET11 Upgrades 58 52 Hack 54. Boot from a Compact Flash Hard Drive Hack 46. AirPort Linux Hack 55. Increase the Range of a PowerBook Hack 47. Java Configurator for AirPort APs Hack 56. Send Power over Your Ethernet Hack 48. Apple Software Base Station 50 Hack 57. The NoCat Night Light Hack 49. Adding an Antenna to the AirPort -52 45 Hack 58. Upgrade the Linksys WET11 Hack 50. The NoCat Night Light 57 Hack 59. Scan for Wireless Networks Automatically Hack 51. Do-It-Yourself Access Point Hardware 53 Hack 60. Backlight Your Zipit Hack 52. Compact Flash Hard Drive 54 Hack 61. Unwire Your Pistol Mouse Hack 53. Pebble 70 Hack 62. Mobilize Your WRT54G with the WiFiCar Hack 54. Tunneling: IPIP Encapsulation Hack 55. Tunneling: GRE Encapsulation Hack 56. Running Your Own Top-Level Domain Hack 57. Getting Started with Host AP Appendix B. Wireless Hardware Guide Hack 58. Make Host AP a Layer 2 Bridge Appendix B. Wireless Hardware Guide Hack 59. Bridging with a Firewall 65 62 Section B.1. Microwave Cabling Hack 60. MAC Filtering with Host AP 66 63 Section B.2. Microwave Connector Reference Hack 61. Hermes AP 82 64 Section B.3. Antenna Guide Hack 62. Microwave Cabling Guide B1 66 Section B.4. Pigtails Hack 63. Microwave Connector Reference B2 67 Section B.5. 802.11 Hardware Suppliers Hack 64. Antenna Guide B3 Hack 65. Client Capability Reference Chart Software Hacks Hack 66. Pigtails B4 Hacks 6382: Introduction Hack 67. 802.11 Hardware Suppliers B5 Hack 63. Build Your Own Access Point with Linux Hack 68. Home-Brew Power over Ethernet Hack 64. Bridge Your Linux AP Hack 69. Cheap but Effective Roof Mounts 93 59 Hack 65. Protect Your Bridge with a Firewall 60 Hack 66. Filter MAC with HostAP and Madwifi Hack 67. Upgrade Your Wireless Router Hack 68. Set Up an OLSR Mesh Network Hack 69. Extend Your Wireless Network with WDS 53 Hack 70. Pebble Hack 71. Wall Off Your Wireless Hack 72. Run Your Mac as an Access Point Hack 73. Run Linux on the Zipit Wireless Messenger Hack 74. Capture Wireless Users with NoCatAuth Hack 75. Capture Wireless Users on a Small Scale Hack 76. Build an Online Community in Your Offline Neighborhood Hack 77. Manage Multiple AirPort Base Stations Hack 78. Advertise Bonjour Services in Linux Hack 79. Advertise Any Service with Bonjour in Mac OS X Hack 80. Redirect Brought to you by Bonjour Ads Hack 81. Use a Windows-Only Wireless Card in Linux 61 Hack 82. Use Your Orinoco Card with Hermes AP Chapter 5. Do-It-Yourself Antennas Do-It-Yourself Antennas Section 5.1. Hacks #70-79 Hacks 8393: Introduction Hack 70. Deep Dish Cylindrical Parabolic Reflector 83 70 Hack 83. Make a Deep Dish Cylindrical Parabolic Reflector Hack 71. "Spider" Omni 84 71 Hack 84. Spider Omni Antenna Hack 72. Pringles Can Waveguide 85 72 Hack 85. Pringles Can Waveguide Hack 73. Pirouette Can Waveguide 86 73 Hack 86. Pirouette Can Waveguide Hack 74. Primestar Dish with Waveguide Feed 87 74 Hack 87. Primestar Dish with Waveguide Feed Hack 75. BiQuad Feed for Primestar Dish 88 75 Hack 88. Primestar Dish with Biquad Feed Hack 76. Cut Cable Omni Antenna 89 76 Hack 89. Cut a Cable Omni Antenna Hack 77. Slotted Waveguides 90 77 Hack 90. Build a Slotted Waveguide Antenna Hack 78. The Passive Repeater 91 78 Hack 91. The Passive Repeater Hack 79. Determining Antenna Gain 92 79 Hack 92. Determine Your Antenna Gain 69 Hack 93. Build Cheap, Effective Roof Mounts Wireless Network Design Chapter 6. Long Distance Links Hacks 94100: Introduction Section 6.1. Hacks #80-85 Hack 94. Analyze Elevation Profiles for Better Long-Range Wireless Networking Hack 80. Establishing Line of Sight 96 Hack 95. Build a Wireless Network for the Large House Hack 81. Calculating the Link Budget 97 80 Hack 96. Establish Line of Sight Hack 82. Aligning Antennas at Long Distances 98 81 Hack 97. Calculate the Link Budget Hack 83. Slow Down to Speed Up 99 82 Hack 98. Align Antennas at Long Distances Hack 84. Taking Advantage of Antenna Polarization 100 83 Hack 99. Slow Down to Speed Up Hack 85. Map the Wireless Landscape with NoCat Maps 84 Hack 100. Take Advantage of Antenna Polarization Chapter 7. Wireless Security Wireless Security Section 7.1. Hacks #86-100 Hacks 4051: Introduction Hack 86. Making the Best of WEP Hack 40. Stop Moochers from Stealing Your Wi-Fi Bandwidth Hack 87. Dispel the Myth of Wireless Security Hack 41. Visualize a Network Hack 88. Cracking WEP with AirSnort: The Easy Way Hack 42. Secure Your Linux Network with WPA Hack 89. NoCatAuth Captive Portal Hack 43. Control Wireless Access by MAC Hack 90. NoCatSplash and Cheshire Hack 44. Authenticate Wireless Users Hack 91. Squid Proxy over SSH 93 Hack 45. Forward Ports over SSH Hack 92. SSH SOCKS 4 Proxy Hack 46. Proxy Web Traffic over SSH Hack 93. Forwarding Ports over SSH Hack 47. Securely Connect Two Networks Hack 94. Quick Logins with SSH Client Keys Hack 48. Generate a Tunnel Configuration Automatically Hack 95. "Turbo-Mode" SSH Logins Hack 49. Poll Wireless Clients Hack 96. OpenSSH on Windows Using Cygwin Hack 50. Interrogate the Network Hack 97. Location Support for Tunnels in OS X Hack 51. Track Wireless Users Hack 98. Using vtun over SSH Hack 99. Automatic vtund.conf Generator Hack 100. Tracking Wireless Users with arpwatch Appendix A. Deep Dish Parabolic Reflector Template
- 投稿日:2019-03-05T17:27:19+09:00
「Wireless Hacks」第二版(英語)Rob Flickenger, Roger Weeksをハックしたい
はじめに(introduction)
「Wireless Hacks」by Rob Flickengerをハックしたい
https://qiita.com/kaizen_nagoya/items/df87e75fe9a931fff472を書いていて、リンク切れなどについては、第二版(英語)を参照している。
Wireless Hacks, 2nd Edition, February 2005
Tips & Tools for Building, Extending, and Securing Your Network
By Rob Flickenger, Roger Weeks, Orally, ISBN 978-0596101442
http://shop.oreilly.com/product/9780596101442.do第二版(英語)を拝見すると、第二版の視点での整理もあるとよいと思い書き始める。
()書きは第一版の対応または関連する章番号
なお「リンク切れ」と記載した事項で、通信の輻輳、通信設定の誤り、DNSの浸透の遅れなどからたまたまその日だけ接続できなかった可能性があります。うまく接続できたり、適切な場所に転送されている場合には、お知らせいただけると幸いです。
目次(content)
Bluetooth, Mobile Phones, and GPS
Hacks 1-22: Introduction
Hack 1. Set Up Bluetooth on Linux (16)
Hack 2. Set Up Bluetooth on Windows XP
Hack 3. Connect Mac OS X with a Bluetooth Phone
Hack 4. Connect Linux with a Bluetooth Phone
Hack 5. Connect Windows XP with a Bluetooth Phone
Hack 6. Use Your Treo as a Modem
Hack 7. Send SMS from a PowerBook(14)
Hack 8. Remote Control Mac OS X with Bluetooth Phones and PDAs(13)
Hack 9. Remote Control Linux with a Bluetooth Phone(17)
Hack 10. Control XMMS with Bluetooth(19)
Hack 11. Liven Up Parties with a Participatory Slideshow
Hack 12. Send SMS from Linux
Hack 13. Remote Control Windows with Bluetooth Phones and PDAs
Hack 14. Control Your Bluetooth Phone with FMA
Hack 15. Control Your Computer from Your Palm
Hack 16. Control Your Home Theater from Your Palm
Hack 17. Choose a Cellular Data Plan
Hack 18. Blog from Your Mobile Phone
Hack 19. Get Google Maps on Your Mobile Phone
Hack 20. Share Your GPS
Hack 21. Broadcast Your GPS Position
Hack 22. Map Wi-Fi Networks with Kismet and GPSd
Network Discovery and MonitoringHacks 23-39: Introduction
Hack 23. Find All Available Wireless Networks(20)
Hack 24. Discover Networks with NetStumbler(21)
Hack 25. Detect Networks with Handheld PCs(23)
Hack 26. Find and Join Wireless Networks with AP Radar
Hack 27. Detect Networks on Mac OS X(22)
Hack 28. Scan Passively with KisMAC(24)
Hack 29. Detect Networks with Kismet(31)
Hack 30. Monitor Wireless Links in Linux with Wavemon(33)
Hack 31. Analyze Traffic with Ethereal(38)
Hack 32. Track 802.11 Frames in Ethereal(39)
Hack 33. Watch Network Traffic(37)
Hack 34. grep Your Network(41)
Hack 35. Check Wi-Fi Network Performance with Qcheck
Hack 36. Estimate Network Performance(36)
Hack 37. Get Real-Time Network Stats(42)
Hack 38. Graph Your Wireless Performance
Hack 39. Find Radio Manufacturers by MAC(27)
Wireless SecurityHacks 40-51: Introduction
Hack 40. Stop Moochers from Stealing Your Wi-Fi Bandwidth
Hack 41. Visualize a Network(35)
Hack 42. Secure Your Linux Network with WPA(86)
Hack 43. Control Wireless Access by MAC
Hack 44. Authenticate Wireless Users
Hack 45. Forward Ports over SSH(93)
Hack 46. Proxy Web Traffic over SSH(91)
Hack 47. Securely Connect Two Networks(87)
Hack 48. Generate a Tunnel Configuration Automatically(99)
Hack 49. Poll Wireless Clients
Hack 50. Interrogate the Network
Hack 51. Track Wireless Users(100)
Hardware HacksHacks 5262: Introduction
Hack 52. Add an External Antenna(49)
Hack 53. Do-It-Yourself Access Point Hardware(51)
Hack 54. Boot from a Compact Flash Hard Drive(52)
Hack 55. Increase the Range of a PowerBook
Hack 56. Send Power over Your Ethernet
Hack 57. The NoCat Night Light(50)
Hack 58. Upgrade the Linksys WET11(45)
Hack 59. Scan for Wireless Networks Automatically
Hack 60. Backlight Your Zipit
Hack 61. Unwire Your Pistol Mouse
Hack 62. Mobilize Your WRT54G with the WiFiCar
Software HacksHacks 63-82: Introduction
Hack 63. Build Your Own Access Point with Linux
Hack 64. Bridge Your Linux AP
Hack 65. Protect Your Bridge with a Firewall(59)
Hack 66. Filter MAC with HostAP and Madwifi(60)
Hack 67. Upgrade Your Wireless Router
Hack 68. Set Up an OLSR Mesh Network
Hack 69. Extend Your Wireless Network with WDS
Hack 70. Pebble(53)
Hack 71. Wall Off Your Wireless
Hack 72. Run Your Mac as an Access Point
Hack 73. Run Linux on the Zipit Wireless Messenger
Hack 74. Capture Wireless Users with NoCatAuth(89)
Hack 75. Capture Wireless Users on a Small Scale
Hack 76. Build an Online Community in Your Offline Neighborhood
Hack 77. Manage Multiple AirPort Base Stations
Hack 78. Advertise Bonjour Services in Linux
Hack 79. Advertise Any Service with Bonjour in Mac OS X
Hack 80. Redirect Brought to you by Bonjour Ads
Hack 81. Use a Windows-Only Wireless Card in Linux
Hack 82. Use Your Orinoco Card with Hermes AP(61)
Do-It-Yourself AntennasHacks 83-93: Introduction
Hack 83. Make a Deep Dish Cylindrical Parabolic Reflector(70)
Hack 84. Spider Omni Antenna(71)
Hack 85. Pringles Can Waveguide(72)
Hack 86. Pirouette Can Waveguide(73)
Hack 87. Primestar Dish with Waveguide Feed(74)
Hack 88. Primestar Dish with Biquad Feed(75)
Hack 89. Cut a Cable Omni Antenna(76)
Hack 90. Build a Slotted Waveguide Antenna(77)
Hack 91. The Passive Repeater(78)
Hack 92. Determine Your Antenna Gain(79)
Hack 93. Build Cheap, Effective Roof Mounts(69)
Wireless Network DesignHacks 94-100: Introduction
Hack 94. Analyze Elevation Profiles for Better Long-Range Wireless Networking
Hack 95. Build a Wireless Network for the Large House
Hack 96. Establish Line of Sight(80)
Hack 97. Calculate the Link Budget(81)
Hack 98. Align Antennas at Long Distances(82)
Hack 99. Slow Down to Speed Up(83)
Hack 100. Take Advantage of Antenna Polarization(84)
Appendix A. Wireless StandardsAppendix A. Wireless Standards
Section A.1. 802.11: The Mother of All IEEE Wireless Ethernet(1)
Section A.2. 802.11a: The Betamax of the 802.11 Family(2)
Section A.3. 802.11b: The De Facto Standard(3)
Section A.4. 802.11g: Like 802.11b, only Faster(4)
Section A.5. 802.16: WiMAX Long Distance Wireless Infrastructure(5)
Section A.6. Bluetooth: Cable Replacement for Devices(6)
Section A.7. 900 MHz: Low Speed, Better Coverage(7)
Section A.8. CDPD, 1xRTT, and GPRS: Cellular Data Networks(8)
Section A.9. FRS and GMRS: Super Walkie-Talkies(9)
Section A.10. 802.1x: Port Security for Network Communications(10)
Section A.11. WPA & 802.11i
Section A.12. BSS Versus IBSS(12)
Appendix B. Wireless Hardware GuideAppendix B. Wireless Hardware Guide
Section B.1. Microwave Cabling(62)
Section B.2. Microwave Connector Reference(63)
Section B.3. Antenna Guide(64)
Section B.4. Pigtails(66)
Section B.5. 802.11 Hardware Suppliers(67)対応しているのが57項目。第二版は117項目であり、約半分。
その後、URL, コマンドなどの一致するものを整理し、現在約70項目。著者
Marcel Bilal
わずか2年の間に劇的に変化。
Bluetooth, Mobile Phones, and GPS
Hacks 1-22: Introduction
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hacks_122_introduction.html
Hack 1. Set Up Bluetooth on Linux
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_1_set_up_bluetooth_on_linux.html
(V1:16.LinuxでBluetoothを使う/ Hack 16 Using Bluetooth with Linux) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-2-sect-5.htmlBlueZ-supported hardware
http://www.holtmann.org/linux/bluetooth/devices.html
リンク切れBlueZ Users mailing list,
http://www.bluez.org/lists.htmlhcitool scanHack 2. Set Up Bluetooth on Windows XP
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_2_set_up_bluetooth_on_windows_xp.html
参照
The O'Reilly Wireless web site
http://wireless.oreilly.com
は
https://www.safaribooksonline.com/search/?query=networking
に転送(redirect)Windows XP Unwired by Wei-Meng Lee (O'Reilly)
http://shop.oreilly.com/product/9780596005368.doHack 3. Connect Mac OS X with a Bluetooth Phone
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_3_connect_mac_os_x_with_a_bluetooth_phone.html
Apple maintains a list of phones
http://www.apple.com/macosx/features/isync/devices.html
は
https://support.apple.com/ja-jp/HT2824
に転送(redirect)日本で日本語のブラウザからだから。Ross Barkman
http://www.taniwha.org.ukOpera's site for GSM providers has an excellent list of APNs
http://www.opera.com/products/mobile/docs/connect/
は
https://www.opera.com/ja/mobile/android
に転送(redirect) 日本で日本語のブラウザからだから。Hack 4. Connect Linux with a Bluetooth Phone
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_4_connect_linux_with_a_bluetooth_phone.html
sdptool
Hack 5. Connect Windows XP with a Bluetooth Phone
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_5_connect_windows_xp_with_a_bluetooth_phone.html
Hack 6. Use Your Treo as a Modem
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_6_use_your_treo_as_a_modem.html
Treo 650
http://www.palm.com/us/support/downloads/treo650updater/sprint.html
リンク切れHow to Use the Bluetooth Dial Up Networking Hack
shadowmite patch
http://www.shadowmite.com/HowToDUN.htmlPdaNet application
http://www.junefabrics.comWirelessModem
http://www.notifymail.com/palm/wmodem/Internet on Air
Treo 650 to a Mac using Bluetooth
http://vocaro.com/trevor/treo-dun/Hack 7. Send SMS from a PowerBook
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_7_send_sms_from_a_powerbook.html
(V1:14.本物のキーボードでショートメッセージ作成/ Hack 14 SMS with a Real Keyboard) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-2-sect-3.htmllist of phones supported by Mac OS X
http://www.apple.com/macosx/features/isync/devices.html
は
https://support.apple.com/ja-jp/HT2824
に転送(redirect)Hack 8. Remote Control Mac OS X with Bluetooth Phones and PDAs
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_8_remote_control_mac_os_x_with_bluetooth_phones_and_pdas.html
(V1:13.ソニーエリクソンの携帯でOS Xを操作する/ Hack 13 Remote Control OS X with a Sony Ericsson Phone) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-2-sect-2.htmlPalmOS 4 or 5 devices
http://homepage.mac.com/jonassalling/Shareware/Clicker/faq.html#supported_devices
リンク切れClicker
http://homepage.mac.com/jonassalling/Shareware/Clicker/
検索すると
www.salling.com/clicker/Hack 9. Remote Control Linux with a Bluetooth Phone
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_9_remote_control_linux_with_a_bluetooth_phone.html
(V1:17.LinuxからBluetooth経由でGPRSを使う/ Hack 17 Bluetooth to GPRS in Linux) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-2-sect-6.htmlBluetooth stack and utilities
http://www.geocities.com/saravkrish/progs/bluemote
http://www.geocities.com/saravkrish/progs/bluemote/scripts.tar.gz
リンク切れbluemoteで検索
(Bluemote – remote control of a 8051 robot with bluetooth
https://redacacia.me/2010/09/21/bluemote-remote-control-of-a-8051-robot-with-bluetooth/ )Hack 10. Control XMMS with Bluetooth
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_10_control_xmms_with_bluetooth.html
(V1:19.BluetoothによるXMMSの制御/ Hack 19 Controlling XMMS with Bluetooth) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-2-sect-8.htmlHack 11. Liven Up Parties with a Participatory Slideshow
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_11_liven_up_parties_with_a_participatory_slideshow.html
Ubuntu
http://www.ubuntulinux.org/downloadHack 12. Send SMS from Linux
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_12_send_sms_from_linux.html
gsmsendsms utility from gsmlib
http://www.pxh.de/fs/gsmlib/index.htmlHack 13. Remote Control Windows with Bluetooth Phones and PDAs
PuppetMaster software
http://www.lim.com.au/PuppetMaste
リンク切れHack 14. Control Your Bluetooth Phone with FMA
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_14_control_your_bluetooth_phone_with_fma.html
flOat's Mobile Agent (FMA)
http://fma.sourceforge.netHack 15. Control Your Computer from Your Palm
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_15_control_your_computer_from_your_palm.html
VNC web
http://www.realvnc.comTightVNC
http://www.tightvnc.comUltraVNC
http://www.ultravnc.comOSXvnc
http://www.redstonesoftware.com/vnc.htmlPalmVNC
http://palmvnc2.free.frPebbles Project
http://www.pebbles.hcii.cmu.eduNo-IP.com
http://www.no-ip.comDynu
http://www.dynu.comDynDNS.org
http://www.dyndns.orgMergic VPN
http://www.mergic.com
リンク切れHack 16. Control Your Home Theater from Your Palm
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_16_control_your_home_theater_from_your_palm.html
OmniRemote
http://www.pacificneotek.com
リンク切れNoviiRemote
http://www.novii.tv
未確認RemoteCentral
http://www.remotecentral.comPacific Neo-Tek
http://www.pacificneotek.com
リンク切れHack 17. Choose a Cellular Data Plan
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_17_choose_a_cellular_data_plan.html
company URL AT&T(Cingular) https://www.att.com/wireless/ Orange France https://boutique.orange.fr EE (Orange UK) https://ee.co.uk Rogers https://www.rogers.com/consumer/home Sprint https://www.sprint.com T-Mobile https://www.t-mobile.com Telcel Mexico https://www.telcel.com Verizon Wireless https://www.verizonwireless.com/ Vodafone UK https://www.vodafone.co.uk Hack 18. Blog from Your Mobile Phone
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_18_blog_from_your_mobile_phone.html
Txtsolutions
http://blog.txtsolutions.comBlogger
http://www.blogger.comLiveJournal
http://www.livejournal.comTypePad
http://www.typepad.comRadio UserLand
http://radio.userland.comTextamerica
http://www.textamerica.comFotolog
http://www.fotolog.netFlickr
http://www.flickr.coma little open source J2ME (Java 2 Mobile Edition)
http://sourceforge.net/projects/moblogger2/http://manojtk.blogspot.com/2005/01/smtp-email-attachments-from-nokia-6600.html.
WordPress
http://www.wordpress.org/
http://wordpress.org/docs/installation/5-minute/http://blade.lansmash.com/index.php?cat=5
http://www.vienna360.net/files/wp-mail.phps.
http://your-domain-name/MyMoblog/wp-mail.php.
Cygwin toolkit
http://www.cygwin.com/Hack 19. Get Google Maps on Your Mobile Phone
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_19_get_google_maps_on_your_mobile_phone.html
Hack 20. Share Your GPS
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_20_share_your_gps.html
参考資料
Casey West's O'Reilly Network article on his cross-car road trip network: http://www.oreillynet.com/pub/a/wireless/2002/08/01/highway_lan.htmlHack 21. Broadcast Your GPS Position
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_21_broadcast_your_gps_position.html
NoCat community network
http://nocat.netBurning Man
http://www.burningman.com参考資料
802.11 beacons:
http://www.wi-fiplanet.com/tutorials/article.php/1492071Hack 22. Map Wi-Fi Networks with Kismet and GPSd
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_22_map_wi_fi_networks_with_kismet_and_gpsd.html
Ethereal
http://www.ethereal.com
はwireshark
に改名。
https://www.wireshark.orgNetwork Discovery and Monitoring
Hacks 23-39: Introduction
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hacks_2339_introduction.html
Hack 23. Find All Available Wireless Networks(20)
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_23_find_all_available_wireless_networks.html
(V1:20.すべての利用可能な無線ネットワークを発見する/ Hack 20 Find All Available Wireless Networks) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-2.html# # iwconfig eth0 eth0 no wireless extensions. # iwlist eth0 auth eth0 no authentication information. # iwspy eth0 eth0 Interface doesn't support wireless statistic collection # iwpriv eth0 eth0 no private ioctls.Hack 24. Discover Networks with NetStumbler
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_24_discover_networks_with_netstumbler.html
(V1:21. NetStumblerを用いたネットワークの発見/ Hack 21 Network Discovery Using NetStumbler) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-3.htmlNetStumbler
http://stumbler.netNetStumble Donation
http://www.stumbler.net/donateHack 25. Detect Networks with Handheld PCs
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_25_detect_networks_with_handheld_pcs.html
(V1:23.ハンドヘルドPCを使ってネットワークを検出/ Hack 23 Detecting Networks Using Handheld PCs) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-5.htmlMiniStumbler
http://stumbler.net
ministumblerのダウンロードURLあり。2011
http://stumbler.net/compatPocketPC
http://www.aspecto-software.com/WiFiFoFum
リンク切れHOWTO on installing Kismet
http://aurach.ewu.edu/ield/ield_course/lectures/ield_appC.
リンク切れ?iPAQ
http://grox.net/misc/ipaq/kismetHack 26. Find and Join Wireless Networks with AP Radar
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_26_find_and_join_wireless_networks_with_ap_radar.html
AP Radar source code
http://apradar.sourceforge.netHack 27. Detect Networks on Mac OS X
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_27_detect_networks_on_mac_os_x.html
(V1:22.Mac OS Xでのネットワーク検出/ Hack 22 Network Detection on Mac OS X) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-4.htmlMacStumbler
http://www.macstumbler.com
表紙だけ?iStumbler
http://istumbler.netHack 28. Scan Passively with KisMAC
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_28_scan_passively_with_kismac.html
(V1:24.KisMACによるパッシブスキャン/ Hack 24 Passive Scanning with KisMAC) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-6.htmlKisMAC http://www.binaervarianz.de/projekte/programmieren/KisMAC
リンク切れ
http://www.binaervarianz.de/projekte/
でkismacを選ぶと
http://kismac.de
に飛び、「German says: Good-bye KisMAC!」と出る。open source Viha AirPort driver http://www.dopesquad.net/security
リンク切れ?(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/KisMAC)
ATTENTION! KisMAC WiFi scanner is no longer being updated or maintained! The latest version 0.3.3 released Feb 07, 2011
(https://github.com/IGRSoft/KisMac2)
PLEASE NOTE, THIS PROJECT IS NO LONGER BEING MAINTAINED
Hack 29. Detect Networks with Kismet
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_29_detect_networks_with_kismet.html
(V1:31.Kismetでネットワークを検出/ Hack 31 Detecting Networks with Kismet) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-13.htmlKismet
http://www.kismetwireless.net参照(see also)
Tons of information on RF Monitoring drivers http://airsnort.shmoo.com
2015AirSnort on the iBook
http://www.macunix.net:443/ibook.html
リンク切れPassive RF Monitoring on the iBook http://www.swieskowski.net/code/wifi.php
リンク切れ?(kismetの使い方
https://qiita.com/yamori813/items/a34860f0bb7c5a344fe4 )(kismet raspberry PI
https://qiita.com/kaizen_nagoya/items/da2d741c9d35cda181ff )Hack 30. Monitor Wireless Links in Linux with Wavemon
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_30_monitor_wireless_links_in_linux_with_wavemon.html
(V1:33. Wavemonを用いたLinuxでのリンクモニタリング/ Hack 33 Link Monitoring in Linux with Wavemon) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-15.html
(初版のリンク切れの場所の記述はない。)http://freshmeat.net/projects/wavemon
は
https://github.com/uoaerg/wavemon
へ転送(redirect)RPM packages
http://rpm.pbone.netHack 31. Analyze Traffic with Ethereal
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_31_analyze_traffic_with_ethereal.html
(V1:38.Etherealによる視覚的なトラフィック解析/ Hack 38 Visual Traffic Analysis with Ethereal) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-20.htmlEthereal
http://www.ethereal.com/download.htm
http://www.ethereal.com/(Etherealはwiresharkに改名。)
(Wireshark 導入、記録、分析
https://qiita.com/kaizen_nagoya/items/d1d452d5f3eadd420d6e )(Raspberry PiでWiresharkを活用する12の関門
https://qiita.com/kaizen_nagoya/items/b3fa0a20855d44c3768d )(MacintoshにWiresharkを導入する7つの壁
https://qiita.com/kaizen_nagoya/items/69eb2d357a125f5368e1 )Hack 32. Track 802.11 Frames in Ethereal
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_32_track_80211_frames_in_ethereal.html
(V1:39.Etherealで802.11フレームを追跡する/ Hack 39 Tracking 802.11 Frames in Ethereal) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-21.htmlCombining Ethereal with Kismet or KisMAC makes one of the most flexible and powerful wireless analysis packages available.
Hack 33. Watch Network Traffic
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_33_watch_network_traffic.html
(V1:37.tcpdumpでトラフィックを観測/ Hack 37 Watching Traffic with tcpdump) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-19.htmltcpdump
Hack 34. grep Your Network
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_34_grep_your_network.html
(V1:41.ngrepによるネットワークモニタリング/ Hack 41 Network Monitoring with ngrep) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-23.htmlngrep
http://www.packetfactory.net/Projects/ngrep.Brazil query
http://www.imdb.com looking
the last one
http://www.dictionary.comHack 35. Check Wi-Fi Network Performance with Qcheck
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_35_check_wi_fi_network_performance_with_qcheck.html
Qcheck http://www.ixiacom.com/products/performance_applications/pa_display.php?skey=pa_q_check
リンク切れHack 36. Estimate Network Performance
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_36_estimate_network_performance.html
(V1:36.ネットワーク性能の推定/ Hack 36 Estimating Network Performance) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-18.htmlDSL Reports' Speed test
http://speedtest.dslreports.comiperf
http://dast.nlanr.net/Projects/Iperf.Hack 37. Get Real-Time Network Stats
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_37_get_real_time_network_stats.html
(V1:42.リアルタイムでネットワークの状態を取得するためにntopを起動する/ Hack 42 Running ntop for Real-Time Network Stats) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-24.htmlntop(network table of processes)
http://www.ntop.org(最新コマンドはntopng:ntop next generation, URLはそのまま)
Hack 38. Graph Your Wireless Performance
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_38_graph_your_wireless_performance.html
Netcat
http://www.securityfocus.com/tools/137Round Robin Database Tool (RRDtool)
http://people.ee.ethz.ch/~oetiker/Cacti
http://www.cacti.net
http://www.cacti.net/documentation.phpHack 39. Find Radio Manufacturers by MAC
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_39_find_radio_manufacturers_by_mac.html
(V1:27.MACアドレスでカードのメーカーを特定する/ Hack 27 Finding Radio Manufacturers by MAC Address) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-9.htmlIEEE organizationally unique identifiers (OUI)
http://standards.ieee.org/regauth/oui/index.shtmlhttp://standards.ieee.org/cgi-bin/ouisearch
cURL network utility
http://curl.sourceforge.net( arp一覧を作るmachine.plを手打ちしてエラー報告。未完。
https://qiita.com/kaizen_nagoya/items/26841520b9b9f9c61034)
(エラーは出なくなった。結果の出力がない。
perlとcurlの使い方がいまいちわかってないかも。)Wireless Security
Hacks 40-51: Introduction
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hacks_4051_introduction.html
Hack 40. Stop Moochers from Stealing Your Wi-Fi Bandwidth
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_40_stop_moochers_from_stealing_your_wi_fi_bandwidth.html
Winpcap
http://winpcap.polito.it/install/default.htmAirSnare
http://home.comcast.net/~jay.deboer/airsnare.Hack 41. Visualize a Network
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_41_visualize_a_network.html
(V1:35.EtherPEGとDriftNet/ Hack 35 EtherPEG and DriftNet) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-17.htmlEtherPEG
http://www.etherpeg.orgDriftNet
http://www.ex-parrot.com/~chris/driftnetweblog
http://www.oreillynet.com/pub/wlg/1414
リンク切れHack 42. Secure Your Linux Network with WPA
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_42_secure_your_linux_network_with_wpa.html
HostAP
Prism2/2.5/3 radio chipsets
http://hostap.epitest.fiMadwifi
Atheros 802.11a/b/g radio chipets http://madwifi.sourceforge.netAtmel
Atmel USB/PC Card chipsets http://atmelwlandriver.sourceforge.netDriverloader
Windows NDIS drivers
http://www.linuxant.com/driverloaderNdiswrapper
Windows NDIS drivers
http://ndiswrapper.sourceforge.netIPW2100
Intel ipw2100 chipsets
http://ipw2100.sourceforge.netIPW2200
Intel ipw2200 chipsets
http://ipw2200.sourceforge.netBroadcom
wl.o embedded driver
http://www.linksys.com/support/gpl.aspwpa_supplicant
http://hostap.epitest.fi/wpa_supplicantwpa_supplicant README
http://hostap.epitest.fi/cgi-bin/viewcvs.cgi/*checkout*/hostap/wpa_supplicant/README?rev=HEAD&content-type=text/plainopenSSL
http://www.openssl.org.Hack 43. Control Wireless Access by MAC
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_43_control_wireless_access_by_mac.html
FreeRADIUS
http://www.freeradius.orgHack 44. Authenticate Wireless Users
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_44_authenticate_wireless_users.html
Hack 45. Forward Ports over SSH
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_45_forward_ports_over_ssh.html
(V1:93.SSHによるポート転送/ Hack 93 Forwarding Ports over SSH) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-7-sect-9.html参照
man sshThe Secure Shell: The Definitive Guide http://www.oreilly.com/catalog/sshtdg
Hack 46. Proxy Web Traffic over SSH
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_46_proxy_web_traffic_over_ssh.html
(V1:91.SSH越しにsquidプロキシを使おう/ Hack 91 Squid Proxy over SSH) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-7-sect-7.htmlHack 47. Securely Connect Two Networks
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_47_securely_connect_two_networks.html
(V1:87.無線セキュリティの神話を崩す/ Hack 87 Dispel the Myth of Wireless Security) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-7-sect-3.htmlroute
Hack 48. Generate a Tunnel Configuration Automatically
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_48_generate_a_tunnel_configuration_automatically.html
(V1:99.vtund.confの自動生成/ Hack 99 Automatic vtund.conf Generator) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-7-sect-15.htmlvtundconf
Hack 49. Poll Wireless Clients
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_49_poll_wireless_clients.html
(V1:25.接続性を確立する/ Hack 25 Establishing Connectivity) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-7.htmlping
Hack 50. Interrogate the Network
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_50_interrogate_the_network.html
(V1:40.nmapを用いてネットワークを根堀り葉堀り詮索する/ Hack 40 Interrogating the Network with nmap) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-3-sect-22.htmlnmap
Hack 51. Track Wireless Users
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_51_track_wireless_users.html
(V1:100.arpwatchを用いた無線ユーザの追跡/ Hack 100 Tracking Wireless Users with arpwatch) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-7-sect-16.htmlLBNL's Network Research Group, arpwatch
http://www-nrg.ee.lbl.gov/nrg.htmlSnort
http://www.snort.orgHardware Hacks
Hacks 52-62: Introduction
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hacks_5262_introduction.html
Hack 52. Add an External Antenna
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_52_add_an_external_antenna.html
(V1:49.AirMacベースステーションにアンテナを追加/ Hack 49 Adding an Antenna to the AirPort) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-8.htmlPCMCIA cards
http://www.hyperlinktech.com/web/re09p.phpRange Extender http://www.proxim.com/products/all/orinoco/client/rea/index.html.
m HyperLink Technologies
http://www.hyperlinktech.com/web/re05t.phpLucent/Orinoco/Proxim Gold or Silver 802.11b
(Lucent -> Alcatel-Lucent, 2006
http://conversation.alcatel-lucent.com/en-stellar-mobility-wifi )Senao/Engenius NL2511-EXT2 802.11b
(Senao international -> Senao Networks, 2006
http://www.senao.com/English/Default.aspx?TYPE=test.htm&PT=search&sf1=Wifi&sf2=Null&tv_TCAT_POS=0&CATNO0=B&IDX=2&CNT=0 )Cisco Aironet 350 802.11b
(Cisco Aironet 4800, 802.11ac
https://www.cisco.com/c/ja_jp/products/wireless/aironet-4800-access-points/index.html?dtid=osscdc000334 )Proxim Orinoco 11b/g 802.11g
( Proxim wireless
https://www.proxim.com/en/products/wifi )Buffalo AirStation 802.11g
(Wi-Fi(無線LAN) : AirStation
https://www.buffalo.jp/product/category/wireless-lan.html )Wistron NeWeb CB9-GP 802.11a/b/g
(http://www.wnc.com.tw)Hack 53. Do-It-Yourself Access Point Hardware
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_53_do_it_yourself_access_point_hardware.html
(V1:51.DIYアクセスポイント/ Hack 51 Do-It-Yourself Access Point Hardware) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-10.htmlLinksys WRT54G
http://www.linksys.comSoekris
http://www.soekris.comMetrix Communication
http://metrix.netWRAP
http://www.pcengines.ch/wrap.htmMikrotik
http://www.mikrotik.com/Via-based computers
http://www.via.com.tw)Hack 54. Boot from a Compact Flash Hard Drive
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_54_boot_from_a_compact_flash_hard_drive.html
(V1:52.コンパクトフラッシュハードディスク/ Hack 52 Compact Flash Hard Drive) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-11.htmlCFADPT-CS from Mesa Electronics
http://www.mesanet.com/diskcardinfo.html.Hack 55. Increase the Range of a PowerBook
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_55_increase_the_range_of_a_powerbook.html
WirelessDriver project SourceForge http://wirelessdriver.sourceforge.net.
Hack 56. Send Power over Your Ethernet
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_56_send_power_over_your_ethernet.html
calculates the voltage drop for a given length of CAT5
http://www.gweep.net/~sfoskett/tech/poecalc.htmlHack 57. The NoCat Night Light
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_57_the_nocat_night_light.html
(V1:50.NoCat常夜燈/ Hack 50 The NoCat Night Light) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-9.htmlDSL Reports
http://www.dslreports.com/stest)Rob Flickenger (Design)
http://twitter.com/hackerfriendly
http://hackerfriendly.comAdam Flaherty (Construction)
Jim Rosenbaum (Funding)
Nate Boblitt
Roger Weeks (Idea Rats)
Hack 58. Upgrade the Linksys WET11
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_58_upgrade_the_linksys_wet11.html
(V1:45.WET11のアップグレード/ Hack 45 WET11 Upgrades) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-4.htmlLinksys WET11
http://www.linksys.com/products/product.asp?prid=432Details on upgrading Prism 2 firmware
http://linux.junsun.net/intersil-prismBelgian site
http://reseaucitoyen.be/?SourcePortableHack 59. Scan for Wireless Networks Automatically
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_59_scan_for_wireless_networks_automatically.html
drivers
http://aws.netzfund.deHack 60. Backlight Your Zipit
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_60_backlight_your_zipit.html
Zipit Wireless Communicator
http://www.zipitwireless.comMiller Engineering
http://www.microstru.comchip
http://www.jelu.se/shop/product_info.php?cPath=1_29&products_id=33
リンク切れHack 61. Unwire Your Pistol Mouse
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_61_unwire_your_pistol_mouse.html
PistolMouse FPS by MonsterGecko
http://www.monstergecko.com/products.htmlTargus AMB01US Bluetooth Mini Mouse http://www.targus.com/us/product_details.asp?sku=AMB01US
Flickr photoset
http://www.flickr.com/photos/_bt/sets/494023Hack 62. Mobilize Your WRT54G with the WiFiCar
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_62_mobilize_your_wrt54g_with_the_wificar.html
OpenWRT
http://wiki.openwrt.org/OpenWrtDocs/Customizingsample TCP socket server/client code written in C
http://pont.net/socketsource code
http://yasha.okshtein.net/wrt54gAcroname
http://www.acroname.com/robotics/parts/R6-754410.htmlfive-volt regulator model 7805
http://tinyurl.com/wqbvSoftware Hacks
Hacks 63-82: Introduction
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hacks_6382_introduction.html
Hack 63. Build Your Own Access Point with Linux
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_63_build_your_own_access_point_with_linux.html
West Sonoma County Internet Cooperative
http://www.wscicc.orgPrism54 Cards
http://www.prism54.org/supported_cards.phpHostAP
http://hostap.epitest.fi.Madwifi code releases
http://madwifi.org/wiki/UserDocs/GettingMadwifi.Hack 64. Bridge Your Linux AP
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_64_bridge_your_linux_ap.html
bridges
http://bridge.sourceforge.net参照(See Also)
Protect Your Bridge with a Firewall [Hack #65]
The Linux Bridge STP HOWTO
http://www.linux.org/docs/ldp/howto/BRIDGE-STP-HOWTO/The Linux Bridge and Firewall mini HOWTO http://www.tldp.org/HOWTO/mini/Bridge+Firewall.html
Hack 65. Protect Your Bridge with a Firewall
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_65_protect_your_bridge_with_a_firewall.html
(V1:59.ファイアウォール付きブリッジ/ Hack 59 Bridging with a Firewall) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-18.htmlebtables
http://ebtables.sourceforge.netHack 66. Filter MAC with HostAP and Madwifi
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_66_filter_mac_with_hostap_and_madwifi.html
(V1:61.Hermes AP/ Hack 61 Hermes AP) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-20.htmlimprov
Hack 67. Upgrade Your Wireless Router
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_67_upgrade_your_wireless_router.html
Broadcom radios
http://openwrt.org/TableOfHardwarehttp://openwrt.org/TableOfHardware
http://www.linksys.com/support/gpl.asp
http://linksysinfo.org
http://www.wrt54g.com.Hack 68. Set Up an OLSR Mesh Network
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_68_set_up_an_olsr_mesh_network.html
Freifunk Firmware,
http://ff-firmware.sourceforge.netstraight to Sven-Ola's (the maintainer) package directory: http://styx.commando.de/sven-ola/ipkg.
Hack 69. Extend Your Wireless Network with WDS
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_69_extend_your_wireless_network_with_wds.html
Madwifi Wiki
http://madwifi.org/UserDocs/WDSBridgeprism2_param
brctlHack 70. Pebble
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_70_pebble.html
(V1:53.Pebble/ Hack 53 Pebble) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-12.htmlPebble
http://www.nycwireless.net/pebbleBased on Debian GNU/Linux 3.0r1 (Woody)
Linux Kernel 2.4.26 with Crypto modules
HostAP 0.1.3 stable including utils and hostapd
Madwifi CVS version from 4/2004
bridge-tools
djbdns caching DNS server
NoCatAuth running as non-root user, post 0.81 nightly
openSSH server 3.4p1
openSSL 0.9.6c patched
pcmcia-cs
PPP and PPPoE
Zebra 0.92a-5Hack 71. Wall Off Your Wireless
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_71_wall_off_your_wireless.html
Wall
http://www.m0n0.chm0n0wall
http://www.m0n0.ch/wall/physdiskwrite.phpcomplete pinout reference
http://www.nullmodem.com/NullModem.htm.Hack 72. Run Your Mac as an Access Point
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_72_run_your_mac_as_an_access_point.html
Zipit
http://aibohack.com/zipit/serial.htmAiboHack(simple loader (ZRS.EXE))
http://aibohack.com/zipit/reflash.htmHTTP HEAD request
http://zipitwireless.com.autoupdate server
http://zipitwireless.net/~zippy/somerandomnumber.txt.DNS
http://www.zipitwireless.netGrab the AiboHack BURN3 image
http://www.aibohack.com/zipit/zipit_parts_burn3.zip.Zipit Wireless Yahoo Group
http://groups.yahoo.com/group/zipitwireless/JPRR CRYPT Password Generator
http://jpirr.nic.ad.jp/crypt_gen_web.html参照(See Also)
Zipit Wireless Yahoo Group
http://groups.yahoo.com/group/zipitwirelessRemote control your Aibo
http://aibohack.com/zipit/aibo.htmZipit-controlled iTunes
http://www.smassey.com/embedded.htmlWiFiDog
http://old.ilesansfil.org/wiki/WiFiDogHack 73. Run Linux on the Zipit Wireless Messenger
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_73_run_linux_on_the_zipit_wireless_messenger.html
Flashing the Zipit
http://aibohack.com/zipit/serial.htm.Hack 74. Capture Wireless Users with NoCatAuth
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_74_capture_wireless_users_with_nocatauth.html
source code
http://nocat.netHack 75. Capture Wireless Users on a Small Scale
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_75_capture_wireless_users_on_a_small_scale.html
NoCatSplash,
http://nocat.net/download/NoCatSplashHack 76. Build an Online Community in Your Offline Neighborhood
PlaceSite
http://www.placesite.comTomcat 5.0.28
http://jakarta.apache.org/site/downloads/downloads_tomcat-5.cgiMySQL 4.1
http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/4.1.htmlOpenWRT
http://www.ilesansfil.org/tiki-list_file_gallery.php?WiFiDog
http://old.ilesansfil.org/dist/WiFiDogPlaceSite
http://www.placesite.cominstall
http://old.ilesansfil.org/dist/WiFiDog/WiFiDog_1.1.1_mipsel.ipkOur modifications
http://placesite.comHack 77. Manage Multiple AirPort Base Stations
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_77_manage_multiple_airport_base_stations.html
AirPort Management Utility
http://www.apple.com/support/airport/.Hack 78. Advertise Bonjour Services in Linux
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_78_advertise_bonjour_services_in_linux.html
detailed documentation
http://www.zeroconf.orgHowl
http://www.porchdogsoft.com/products/howlInstallation instructions
http://www.porchdogsoft.com/products/howl/InstallUnix.htmlFink
http://fink.sourceforge.netwiki
http://example.local/wiki
not http://example.local/local daapd server
http://www.deleet.de/projekte/daap/daapdHack 79. Advertise Any Service with Bonjour in Mac OS X
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_79_advertise_any_service_with_bonjour_in_mac_os_x.html
http://www.chaoticsoftware.com/ProductPages/NetworkBeacon.html.
Hack 80. Redirect Brought to you by Bonjour Ads
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_80_redirect_brought_to_you_by_bonjour_ads.html
FreeNetworks
http://freenetworks.orgHack 81. Use a Windows-Only Wireless Card in Linux
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_81_use_a_windows_only_wireless_card_in_linux.html
WLAN DriverLoader
http://www.linuxant.com/driverloaderLinuxant
http://www.linuxant.com/driverloader/drivers.phplicense
https://www.linuxant.com/storeNdisWrapper.
http://ndiswrapper.sourceforge.net
http://ndiswrapper.sourceforge.net/phpwiki/index.php/List?WLAN DriverLoader
http://www.linuxant.com/driverloader
http://www.linuxant.com/driverloader/drivers.php.Hack 82. Use Your Orinoco Card with Hermes AP
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_82_use_your_orinoco_card_with_hermes_ap.html
(V1:62.マイクロ波ケーブルガイド: Hack 62 Microwave Cabling Guide) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-21.htmlHermes AP
http://hunz.org/hermesap.html,Do-It-Yourself Antennas
Hacks 83-93: Introduction
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hacks_8393_introduction.html
Hack 83. Make a Deep Dish Cylindrical Parabolic Reflector
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_83_make_a_deep_dish_cylindrical_parabolic_reflector.html
(V1:70.筒状深皿パラボラ反射板/ Hack 70 Deep Dish Cylindrical Parabolic Reflector) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-2.htmloriginal reflector template
http://www.freeantennas.com/projects/template/parabolic.pdfWET-11
http://www.freeantennas.com/projects/template/index.html.Hack 84. Spider Omni Antenna
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_84_spider_omni_antenna.html
(V1:71.スパイダーオムニ/ Hack 71 "Spider" Omni) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-3.htmlHack 85. Pringles Can Waveguide
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_85_pringles_can_waveguide.html
(V1:72.プリングルス缶の導波管/ Hack 72 Pringles Can Waveguide) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-4.htmlAndrew Clapp novel yagi antenna design
http://www.aeonic.com/~clapp/wirelessPirouette Can Waveguide
http://www.oreillynet.com/cs/weblog/view/wlg/448.Hack 86. Pirouette Can Waveguide
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_86_pirouette_can_waveguide.html
(V1:73.ピルエット缶の導波管/ Hack 73 Pirouette Can Waveguide) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-5.htmlWireless Cantenna Shoot-Out Battl
http://www.turnpoint.net/wireless/has.htmlwaveguide antenna
http://www.turnpoint.net/wireless/cantennahowto.htmlHack 87. Primestar Dish with Waveguide Feed
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_87_primestar_dish_with_waveguide_feed.html
(V1:74.導波管付きのPrimestar衛星パラボラ/ Hack 74 Primestar Dish with Waveguide Feed) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-6.htmloriginal
http://www.wwc.edu/~frohro/Airport/Primestar/Primestar.html.Hack 88. Primestar Dish with Biquad Feed
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_88_primestar_dish_with_biquad_feed.html
(V1:75.Primestar衛星パラボラ用のBiQuadフィード/ Hack 75 BiQuad Feed for Primestar Dish) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-7.htmloriginal
http://www.trevormarshall.com/biquad.htm.Hack 89. Cut a Cable Omni Antenna
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_89_cut_a_cable_omni_antenna.html
(V1:76.カットケーブル・オムニアンテナ/ Hack 76 Cut Cable Omni Antenna) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-8.htmlMaplin
http://www.maplin.co.ukoriginal
http://wireless.gumph.org/articles/homemadeomni.html.Hack 90. Build a Slotted Waveguide Antenna
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_90_build_a_slotted_waveguide_antenna.html
(V1:77.スロット型導波管/ Hack 77 Slotted Waveguides) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-9.htmloriginal
http://www.trevormarshall.com/waveguides.htm.Hack 91. The Passive Repeater
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_91_the_passive_repeater.html
(V1:78.パッシブリピータ(受動型中継器)/ Hack 78 The Passive Repeater) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-10.htmlHack 92. Determine Your Antenna Gain
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_92_determine_your_antenna_gain.html
(V1:79.アンテナの利得の測定/ Hack 79 Determining Antenna Gain) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-5-sect-11.htmlFresnel
http://www.ydi.com/deployinfo/ad-fresnel-zone.phpSWR meter
http://home.wanadoo.nl/erwin.gijzen/wifiswr/Hack 93. Build Cheap, Effective Roof Mounts
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_93_build_cheap_effective_roof_mounts.html
(V1:69.安くて効果的な屋上マウント/ Hack 69 Cheap but Effective Roof Mounts) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-28.htmlWireless Network Design
Hacks 94-100: Introduction
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hacks_94100_introduction.html
Hack 94. Analyze Elevation Profiles for Better Long-Range Wireless Networking
GRASS
http://grass.ibiblio.orgCPAN
http://www.cpan.orgNoCat Maps
http://maps.nocat.netGIS RPM
http://mappinghacks.com/rpmXMLRPC::Lite
http://geocoder.usElevation Data
http://seamless.usgs.govUniversal Transverse Mercator (UTM)
http://www.dmap.co.uk/utmworld.html.Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM)
http://www.landcover.orgSQLite 3
http://www.sqlite.org.Geocoder_URI http://rpc.geocoder.us/service/xmlrpc
Google Maps
http://www.google.com/apis/maps/signup.htmlHack 95. Build a Wireless Network for the Large House
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_95_build_a_wireless_network_for_the_large_house.html
http://www.groundcontrol.com/galileo/ch5-ethernet.htm
7.3.1. Two Antennas Are Better Than One
http://www.homepcnetwork.com/wireintrof.htm.
Hack 96. Establish Line of Sight
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_96_establish_line_of_sight.html
(V1:80.見通し線の確保/ Hack 80 Establishing Line of Sight) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-6-sect-2.htmlGPS Prospective LAT/LONG/ALT
http://maps.nationalgeographic.com/topoTopo USA and 3-D Topo-Quads
http://www.delorme.comHack 97. Calculate the Link Budget
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_97_calculate_the_link_budget.html
(V1:81.リンクバジェットの計算/ Hack 81 Calculating the Link Budget) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-6-sect-3.htmlGreen Bay Professional Packet Radio's Wireless Network Link Analysis
http://my.athenet.net/~multiplx/cgi-bin/wireless.main.cgi.Hack 98. Align Antennas at Long Distances
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_98_align_antennas_at_long_distances.html
(V1:82.長距離リンクのためのアンテナ調整法/ Hack 82 Aligning Antennas at Long Distances) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-6-sect-4.htmlHack 99. Slow Down to Speed Up
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_99_slow_down_to_speed_up.html
(V1:83.遅くすれば速くなる/ Hack 83 Slow Down to Speed Up) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-6-sect-5.htmlifconfig
Hack 100. Take Advantage of Antenna Polarization
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/hack_100_take_advantage_of_antenna_polarization.html
(V1:84.アンテナの偏向性を活用する/ Hack 84 Taking Advantage of Antenna Polarization) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-6-sect-6.htmlAppendix A. Wireless Standards
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/appendix_a_wireless_standards.html
Section A.1. 802.11: The Mother of All IEEE Wireless Ethernet
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a1_80211_the_mother_of_all_ieee_wireless_ethernet.html
(V1:1.802.11:すべてのIEEE無線イーサネットの生みの親/ Hack 1 802.11: The Mother of All IEEE Wireless Ethernet) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-2.htmlSection A.2. 802.11a: The Betamax of the 802.11 Family
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a2_80211a_the_betamax_of_the_80211_family.html
(V1:2.802.11a:802.11ファミリーのベータマックス/ Hack 2 802.11a: The Betamax of the 802.11 Family) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-3.htmlget IEEE 802
http://standards.ieee.org/getieee802/The Wi-Fi alliance
http://www.weca.netSection A.3. 802.11b: The De Facto Standard
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a3_80211b_the_de_facto_standard.html
(V1:3.802.11b:デファクトスタンダード/ Hack 3 802.11b: The De Facto Standard) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-4.htmlSection A.4. 802.11g: Like 802.11b, only Faster
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a4_80211g_like_80211b_only_faster.html
(V1:4.802.11g:より高速な802.11b/ Hack 4 802.11g: Like 802.11b, only Faster) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-5.htmlSection A.5. 802.16: WiMAX Long Distance Wireless Infrastructure
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a5_80216_wimax_long_distance_wireless_infrastructure.html
(V1:5. 802.16:長距離無線インフラ/ Hack 5 802.16: Long Distance Wireless Infrastructure) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-6.htmlSection A.6. Bluetooth: Cable Replacement for Devices
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a6_bluetooth_cable_replacement_for_devices.html
(V1:6.Bluetooth:デバイス間のケーブルの置き換え/ Hack 6 Bluetooth: Cable Replacement for Devices) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-7.htmlSection A.7. 900 MHz: Low Speed, Better Coverage
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a7_900_mhz_low_speed_better_coverage.html
(V1:7. 900MHz:低速度、高到達範囲(Hack 7 900 MHz: Low Speed, Better Coverage) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-8.html
Section A.8. CDPD, 1xRTT, and GPRS: Cellular Data Networks
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a8_cdpd_1xrtt_and_gprs_cellular_data_networks.html
(V1:8. CDPD、1xRTT、GPRS:携帯電話データネットワーク/ Hack 8 CDPD, 1xRTT, and GPRS: Cellular Data Networks) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-9.htmlHipTop by Danger
http://www.danger.com/HipTop by Danger
http://www.danger.com/Section A.9. FRS and GMRS: Super Walkie-Talkies
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a9_frs_and_gmrs_super_walkie_talkies.html
(V1:9.FRS、GMRS:スーパートランシーバー/ Hack 9 FRS and GMRS: Super Walkie-Talkies) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-10.htmlUniversal Licensing System
http://wireless.fcc.gov/uls/FCC rule-book
http://www.access.gpo.gov/nara/cfr/waisidx_00/47cfr95_00.htmlPersonal Radio Steering Group http://www.provide.net/~prsg/rules.htm
リンク切れSection A.10. 802.1x: Port Security for Network Communications
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a10_8021x_port_security_for_network_communications.html
(V1:10.802.1x:ネットワーク通信のためのポートセキュリティ/ Hack 10 802.1x: Port Security for Network Communications) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-11.htmlopen source 802.1x supplicant implementation project
http://www.open1x.org/
は
http://open1x.sourceforge.net
に転送(redirect)802.1x security methods and problems online
http://www.sans.org/rr/wireless/802.11.php
リンク切れメニューから選ぶ
https://www.sans.org/reading-room/
登録した。wireless見当たらず。Section A.11. WPA & 802.11i
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a11_wpa_80211i.html
WPA2 supports the more robust AES encryption algorithms to replace TKIP
Section A.12. BSS Versus IBSS
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_a12_bss_versus_ibss.html
(V1:12.BSS対IBSS/ Hack 12 BSS Versus IBSS) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-1-sect-13.htmlAppendix B. Wireless Hardware Guide
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/appendix_b_wireless_hardware_guide.html
Section B.1. Microwave Cabling
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_b1_microwave_cabling.html
(V1:62.マイクロ波ケーブルガイド/ Hack 62 Microwave Cabling Guide) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-21.htmlSection B.2. Microwave Connector Reference
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_b2_microwave_connector_reference.html
(V1:63.マイクロ波コネクタマニュアル/ Hack 63 Microwave Connector Reference) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-22.htmlBNC (Bayonet Neill Concelman)
TNC (threaded version of the BNC)
N (Neill) connector
SMA (Sub-Miniature, variation A)
SMC (very small version of the SMA)
SMB (quick-connect version of the SMC)APC-7 (Amphenol Precision connector 7mm sexless)
Section B.3. Antenna Guide
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_b3_antenna_guide.html
(V1:64.アンテナガイド/ Hack 64 Antenna Guide) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-23.htmlOmni:Omnidirectional antennas
Sector (or Sectoral)
Yagi
Waveguides and "Cantennas"
Parabolic DishesSection B.4. Pigtails
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_b4_pigtails.html
(V1:66.ピグテイルアダプタ/ Hack 66 Pigtails) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-25.htmlSection B.5. 802.11 Hardware Suppliers
https://flylib.com/books/en/2.434.1/section_b5_80211_hardware_suppliers.html
(V1:67.802.11ハードウェアベンダ/ Hack 67 802.11 Hardware Suppliers) https://vistech.net/~champ/online-docs/books/Wireless/0596005598_wirelesshks-chp-4-sect-26.htmlAeralix, Peabody, MA
http://www.aerialix.com
リンク切れAntenna Systems and Supplies, Schaumburg, IL http://www.antennasystems.com
未確認Down East Microwave, Frenchtown, NJ
http://www.downeastmicrowave.com
確認ElectroComm, Denver, CO
http://www.ecommwireless.com
リンク切れFAB Corp, Tampa Bay, FL
http://www.fab-corp.com
確認HD Communications, Ronkonkoma, NY
http://www.hdcom.com
2016Hyperlink Tech, Boca Raton, FL
http://www.hyperlinktech.com
確認Metrix, Seattle, WA
http://metrix.net
未確認NetGate, Spokane, WA
http://www.netgate.com
確認NetNimble, Sacramento, CA
http://www.netnimble.net
リンク切れPasadena Networks, Pasadena, CA
http://www.pasadena.net
未確認Superpass, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada
http://www.superpass.com
2014The RF Connection, Gaithersburg, MD
http://www.therfc.com
未確認参考資料(reference)
「Wireless Hack」by Rob Flickengerをハックしたい
https://qiita.com/kaizen_nagoya/items/df87e75fe9a931fff472著者(Rob Flickenger) weblog
wirelessで検索して出てきた radioタグの記事
TEN YEARS OF PRINGLES CANS
PUBLISHED ON JULY 16, 2011
http://hackerfriendly.com/ten-years-of-pringles-cans/THE VENEZIA EXPERIMENTS
PUBLISHED ON MARCH 17, 2010
http://hackerfriendly.com/the-venezia-experiments/10 KM LINK ACHIEVED!
PUBLISHED ON MARCH 4, 2010
http://hackerfriendly.com/10-km-link-achieved/PREPARING FOR TRIESTE
PUBLISHED ON FEBRUARY 18, 2010
http://hackerfriendly.com/preparing-for-trieste/文書履歴(document history)
ver. 0.01 初稿 20190305 午後5時
ver. 0.02 追記 20190305 午後6時
ver. 0.03 10章まで 20190305 午後7時
ver. 0.04 Appendix A 追記 20190305 午後8時
ver. 0.05 Appendix B 追記 20190305 午後9時
ver. 0.06 22章まで 20190305 午後10時
ver. 0.07 60章まで英文URL 20190305 午後11時
ver. 0.08 英文URL完了 20190306 午前7時
ver. 0.09 V1 URL追記 20190306 午前8時
ver. 0.10 V1/V2目次比較 20190306 午前9時
ver. 0.11 30章までURL記載 20190306 昼
ver. 0.12 60章までURL記載 20190306 夕
ver. 0.13 75章までURL記載 20190307 朝
ver. 0.14 100章までURL記載 20190307 午前
ver. 0.15 URL記載完了 20190307 昼
ver. 0.16 V1/V2対比表更新 20190307 午後対比表 初版、2版(英語)
Wireless Hacks, 2003 Wireless Hacks V2, 2005 Chapter 1. The Standards ORG Bluetooth, Mobile Phones, and GPS Section 1.1. Hacks #1-12 Hacks 1-22: Introduction Hack 1. 802.11: The Mother of All IEEE Wireless Ethernet A1 Hack 1. Set Up Bluetooth on Linux 16 Hack 2. 802.11a: The Betamax of the 802.11 Family A2 Hack 2. Set Up Bluetooth on Windows XP Hack 3. 802.11b: The De Facto Standard A3 Hack 3. Connect Mac OS X with a Bluetooth Phone Hack 4. 802.11g: Like 802.11b, only Faster A4 Hack 4. Connect Linux with a Bluetooth Phone Hack 5. 802.16: Long Distance Wireless Infrastructure A5 Hack 5. Connect Windows XP with a Bluetooth Phone Hack 6. Bluetooth: Cable Replacement for Devices A6 Hack 6. Use Your Treo as a Modem Hack 7. 900 MHz: Low Speed, Better Coverage A7 Hack 7. Send SMS from a PowerBook -14 Hack 8. CDPD, 1xRTT, and GPRS: Cellular Data Networks A8 Hack 8. Remote Control Mac OS X with Bluetooth Phones and PDAs 13 Hack 9. FRS and GMRS: Super Walkie-Talkies A9 Hack 9. Remote Control Linux with a Bluetooth Phone -17 Hack 10. 802.1x: Port Security for Network Communications A10 Hack 10. Control XMMS with Bluetooth 19 Hack 11. HPNA and Powerline Ethernet Hack 11. Liven Up Parties with a Participatory Slideshow Hack 12. BSS Versus IBSS A12 Hack 12. Send SMS from Linux Hack 13. Remote Control Windows with Bluetooth Phones and PDAs Chapter 2. Bluetooth and Mobile Data Hack 14. Control Your Bluetooth Phone with FMA Section 2.1. Hacks #13-19 Hack 15. Control Your Computer from Your Palm Hack 13. Remote Control OS X with a Sony Ericsson Phone 8 Hack 16. Control Your Home Theater from Your Palm Hack 14. SMS with a Real Keyboard -7 Hack 17. Choose a Cellular Data Plan Hack 15. Photo Blog Automatically with the Nokia 3650 Hack 18. Blog from Your Mobile Phone Hack 16. Using Bluetooth with Linux 1 Hack 19. Get Google Maps on Your Mobile Phone Hack 17. Bluetooth to GPRS in Linux -9 Hack 20. Share Your GPS Hack 18. Bluetooth File Transfers in Linux Hack 21. Broadcast Your GPS Position Hack 19. Controlling XMMS with Bluetooth 10 Hack 22. Map Wi-Fi Networks with Kismet and GPSd Chapter 3. Network Monitoring Network Discovery and Monitoring Section 3.1. Hacks #20-42 Hacks 23-39: Introduction Hack 20. Find All Available Wireless Networks 23 Hack 23. Find All Available Wireless Networks 20 Hack 21. Network Discovery Using NetStumbler 24 Hack 24. Discover Networks with NetStumbler 21 Hack 22. Network Detection on Mac OS X 27 Hack 25. Detect Networks with Handheld PCs 23 Hack 23. Detecting Networks Using Handheld PCs 25 Hack 26. Find and Join Wireless Networks with AP Radar Hack 24. Passive Scanning with KisMAC 28 Hack 27. Detect Networks on Mac OS X 22 Hack 25. Establishing Connectivity Hack 28. Scan Passively with KisMAC 24 Hack 26. Quickly Poll Wireless Clients with ping Hack 29. Detect Networks with Kismet 31 Hack 27. Finding Radio Manufacturers by MAC Address 39 Hack 30. Monitor Wireless Links in Linux with Wavemon 33 Hack 28. Rendezvous Service Advertisements in Linux Hack 31. Analyze Traffic with Ethereal 38 Hack 29. Advertising Arbitrary Rendezvous Services in OS X Hack 32. Track 802.11 Frames in Ethereal 39 Hack 30. "Brought to you by" Rendezvous Ad Redirector Hack 33. Watch Network Traffic 37 Hack 31. Detecting Networks with Kismet 29 Hack 34. grep Your Network 41 Hack 32. Running Kismet on Mac OS X Hack 35. Check Wi-Fi Network Performance with Qcheck Hack 33. Link Monitoring in Linux with Wavemon 30 Hack 36. Estimate Network Performance 36 Hack 34. Historical Link State Monitoring Hack 37. Get Real-Time Network Stats 42 Hack 35. EtherPEG and DriftNet Hack 38. Graph Your Wireless Performance Hack 36. Estimating Network Performance 36 Hack 39. Find Radio Manufacturers by MAC 27 Hack 37. Watching Traffic with tcpdump 33 Hack 38. Visual Traffic Analysis with Ethereal 31 Wireless Security Hack 39. Tracking 802.11 Frames in Ethereal 32 Hacks 40-51: Introduction Hack 40. Interrogating the Network with nmap Hack 40. Stop Moochers from Stealing Your Wi-Fi Bandwidth Hack 41. Network Monitoring with ngrep 34 Hack 41. Visualize a Network 35 Hack 42. Running ntop for Real-Time Network Stats 37 Hack 42. Secure Your Linux Network with WPA 86 Hack 43. Control Wireless Access by MAC Hack 44. Authenticate Wireless Users Hack 45. Forward Ports over SSH 93 Hack 46. Proxy Web Traffic over SSH 91 Hack 47. Securely Connect Two Networks 87 Hack 48. Generate a Tunnel Configuration Automatically 99 Hack 49. Poll Wireless Clients Hack 50. Interrogate the Network Hack 51. Track Wireless Users 100 Chapter 4. Hardware Hacks Section 4.1. Hacks #43-69 Hardware Hacks Hack 43. Add-on Laptop Antennas Hacks 52-62: Introduction Hack 44. Increasing the Range of a Titanium PowerBook Hack 52. Add an External Antenna -49 Hack 45. WET11 Upgrades 58 Hack 53. Do-It-Yourself Access Point Hardware 51 Hack 46. AirPort Linux Hack 54. Boot from a Compact Flash Hard Drive 52 Hack 47. Java Configurator for AirPort APs Hack 55. Increase the Range of a PowerBook Hack 48. Apple Software Base Station Hack 56. Send Power over Your Ethernet Hack 49. Adding an Antenna to the AirPort -52 Hack 57. The NoCat Night Light 50 Hack 50. The NoCat Night Light 57 Hack 58. Upgrade the Linksys WET11 45 Hack 51. Do-It-Yourself Access Point Hardware 53 Hack 59. Scan for Wireless Networks Automatically Hack 52. Compact Flash Hard Drive 54 Hack 60. Backlight Your Zipit Hack 53. Pebble 70 Hack 61. Unwire Your Pistol Mouse Hack 54. Tunneling: IPIP Encapsulation Hack 62. Mobilize Your WRT54G with the WiFiCar Hack 55. Tunneling: GRE Encapsulation Hack 56. Running Your Own Top-Level Domain Software Hacks Hack 57. Getting Started with Host AP Hacks 63-82: Introduction Hack 58. Make Host AP a Layer 2 Bridge Hack 63. Build Your Own Access Point with Linux Hack 59. Bridging with a Firewall 65 Hack 64. Bridge Your Linux AP Hack 60. MAC Filtering with Host AP 66 Hack 65. Protect Your Bridge with a Firewall 59 Hack 61. Hermes AP 82 Hack 66. Filter MAC with HostAP and Madwifi 60 Hack 62. Microwave Cabling Guide B1 Hack 67. Upgrade Your Wireless Router Hack 63. Microwave Connector Reference B2 Hack 68. Set Up an OLSR Mesh Network Hack 64. Antenna Guide B3 Hack 69. Extend Your Wireless Network with WDS Hack 65. Client Capability Reference Chart Hack 70. Pebble 53 Hack 66. Pigtails B4 Hack 71. Wall Off Your Wireless Hack 67. 802.11 Hardware Suppliers B5 Hack 72. Run Your Mac as an Access Point Hack 68. Home-Brew Power over Ethernet Hack 73. Run Linux on the Zipit Wireless Messenger Hack 69. Cheap but Effective Roof Mounts 93 Hack 74. Capture Wireless Users with NoCatAuth 89 Hack 75. Capture Wireless Users on a Small Scale Hack 76. Build an Online Community in Your Offline Neighborhood Hack 77. Manage Multiple AirPort Base Stations Hack 78. Advertise Bonjour Services in Linux Hack 79. Advertise Any Service with Bonjour in Mac OS X Hack 80. Redirect Brought to you by Bonjour Ads Hack 81. Use a Windows-Only Wireless Card in Linux Hack 82. Use Your Orinoco Card with Hermes AP 61 Chapter 5. Do-It-Yourself Antennas Do-It-Yourself Antennas Section 5.1. Hacks #70-79 Hacks 83-93: Introduction Hack 70. Deep Dish Cylindrical Parabolic Reflector 83 Hack 83. Make a Deep Dish Cylindrical Parabolic Reflector 70 Hack 71. "Spider" Omni 84 Hack 84. Spider Omni Antenna 71 Hack 72. Pringles Can Waveguide 85 Hack 85. Pringles Can Waveguide 72 Hack 73. Pirouette Can Waveguide 86 Hack 86. Pirouette Can Waveguide 73 Hack 74. Primestar Dish with Waveguide Feed 87 Hack 87. Primestar Dish with Waveguide Feed 74 Hack 75. BiQuad Feed for Primestar Dish 88 Hack 88. Primestar Dish with Biquad Feed 75 Hack 76. Cut Cable Omni Antenna 89 Hack 89. Cut a Cable Omni Antenna 76 Hack 77. Slotted Waveguides 90 Hack 90. Build a Slotted Waveguide Antenna 77 Hack 78. The Passive Repeater 91 Hack 91. The Passive Repeater 78 Hack 79. Determining Antenna Gain 92 Hack 92. Determine Your Antenna Gain 79 Hack 93. Build Cheap, Effective Roof Mounts 69 Wireless Network Design Hacks 94-100: Introduction Chapter 6. Long Distance Links Hack 94. Analyze Elevation Profiles for Better Long-Range Wireless Networking Section 6.1. Hacks #80-85 Hack 95. Build a Wireless Network for the Large House Hack 80. Establishing Line of Sight 96 Hack 96. Establish Line of Sight 80 Hack 81. Calculating the Link Budget 97 Hack 97. Calculate the Link Budget 81 Hack 82. Aligning Antennas at Long Distances 98 Hack 98. Align Antennas at Long Distances 82 Hack 83. Slow Down to Speed Up 99 Hack 99. Slow Down to Speed Up 83 Hack 84. Taking Advantage of Antenna Polarization 100 Hack 100. Take Advantage of Antenna Polarization 84 Hack 85. Map the Wireless Landscape with NoCat Maps Appendix A. Wireless Standards Appendix A. Wireless Standards Chapter 7. Wireless Security Section A.1. 802.11: The Mother of All IEEE Wireless Ethernet 1 Section 7.1. Hacks #86-100 Section A.2. 802.11a: The Betamax of the 802.11 Family 2 Hack 86. Making the Best of WEP 42 Section A.3. 802.11b: The De Facto Standard 3 Hack 87. Dispel the Myth of Wireless Security 47 Section A.4. 802.11g: Like 802.11b, only Faster 4 Hack 88. Cracking WEP with AirSnort: The Easy Way Section A.5. 802.16: WiMAX Long Distance Wireless Infrastructure 5 Hack 89. NoCatAuth Captive Portal 74 Section A.6. Bluetooth: Cable Replacement for Devices 6 Hack 90. NoCatSplash and Cheshire Section A.7. 900 MHz: Low Speed, Better Coverage 7 Hack 91. Squid Proxy over SSH 46 Section A.8. CDPD, 1xRTT, and GPRS: Cellular Data Networks 8 Hack 92. SSH SOCKS 4 Proxy Section A.9. FRS and GMRS: Super Walkie-Talkies 9 Hack 93. Forwarding Ports over SSH 45 Section A.10. 802.1x: Port Security for Network Communications 10 Hack 94. Quick Logins with SSH Client Keys Section A.11. WPA & 802.11i Hack 95. "Turbo-Mode" SSH Logins Section A.12. BSS Versus IBSS 12 Hack 96. OpenSSH on Windows Using Cygwin Hack 97. Location Support for Tunnels in OS X Appendix B. Wireless Hardware Guide Hack 98. Using vtun over SSH Appendix B. Wireless Hardware Guide Hack 99. Automatic vtund.conf Generator 48 Section B.1. Microwave Cabling 62 Hack 100. Tracking Wireless Users with arpwatch 51 Section B.2. Microwave Connector Reference 63 Section B.3. Antenna Guide 64 Appendix A. Deep Dish Parabolic Reflector Template Section B.4. Pigtails 66 Section B.5. 802.11 Hardware Suppliers 67
- 投稿日:2019-03-05T16:33:19+09:00
Debian noroot 環境に plank を導入する
はじめに
Debian noroot とは、 Android OS 上において root 権限を取ることなく Debian 環境を構築するためのアプリケーションです。
CPU の性能とメモリ容量が潤沢にある Android OS 端末であれば、 Debian noroot の導入によって Android OS 端末上で非常に軽快な Debian 環境を実現することが出来ます。
Debianのデスクトップ環境において、 Dock ランチャーソフトウェアを導入する事は、通常頻繁に使用するソフトウェアの起動を容易にする等、デスクトップ環境の利便性の向上に関して非常に有用となります。
ここで、Debianのデスクトップ環境において、軽量な Dock ランチャーソフトウェアの1つとして plank が挙げられます。
しかし、 Debian Jessie をベースにした Debian noroot 環境においては、 plank を導入するための適切な deb パッケージが存在しません。
そこで、 plank をソースコードからビルドし、MATE 環境の起動時において自動起動を行うように設定した所、Debian noroot 環境上における各種デスクトップ環境において plank を使用する事が出来るようになりました。
本稿では、 Debian noroot 環境における plank の導入手法について述べます。
本稿では最初に、 "plank の導入" の章において、軽量な Dock ランチャーソフトウェアである plank の Debian noroot 環境への導入手法について述べます。
次に、 "デスクトップ環境への導入" の章において、前章で導入した plank を Debian noroot 環境上の各種デスクトップ環境へ導入する手法について述べます。
そして、 "plank の問題点" の章において、現時点での Debian noroot 環境に導入した plank の問題点について述べます。
最後に、 "結論" の章において、本稿の結論について述べます。
plank の導入
本章においては、最初に、 "plank に依存するパッケージの導入" の節において、 Debian noroot 環境に plank を導入する際に、予め導入するべき plank の依存パッケージの導入について述べます。
次に、 "plank の実行ファイル等のビルド" の節において、 plank 本体のソースコードの取得と、 Debian noroot 環境上で plank 本体のソースコードから plank の実行ファイル等のビルドを行う手法について述べます。
最後に、 "plank のインストール" の節において、前節においてソースコードからビルドした plank の実行ファイル等を Debian noroot 環境上にインストールする手法について述べます。
plank に依存するパッケージの導入
まず最初に、 Debian noroot 環境において plank をビルドする上で、 plank に依存する Debian パッケージの導入を以下の通りに行います。
$ sudo apt-get install automake gnome-common intltool pkg-config valac libbamf3-dev libdbusmenu-gtk3-dev libgdk-pixbuf2.0-dev libgee-dev libglib2.0-dev libgtk-3-dev libwnck-3-dev libx11-dev libgee-0.8-devまた、上記に加えて、パッケージ
xstowの導入も以下の通りに併せて行います。これは、ソースコードからビルドした plank の実行ファイル等をディレクトリ/usr/local以下に導入する際に plank の実行ファイル等の管理を容易にする為です。$ sudo apt-get install xstowplank の実行ファイル等のビルド
次に、 plank 本体のソースコードをplank の公式ページより取得します。なお本稿では、 plank のバージョン 0.11.4 のソースコードである
plank-0.11.4.tar.xzを以下の通りに取得します。plank のソースコードの取得が完了した後は、 plank のソースコードである
plank-0.11.4.tar.xzを適切なディレクトリに展開します。$ cd /path/to/build # (ここに、 /path/to/build は、 plank の実行ファイル等をビルドするための作業ディレクトリ。) $ wget https://launchpad.net/plank/1.0/0.11.4/+download/plank-0.11.4.tar.xz $ tar -Jxvf plank-0.11.4.tar.xzそして、カレントディレクトリを
./plank-0.11.4に移動して、以下の通りにソースコードから実行ファイル等をビルドします。ここで、plank のインストール先となるディレクトリは、前節で述べた
xstowによって plank の管理を容易にする為に/usr/local/opt/plank-0.11.4とします。$ cd ./plank-0.11.4 $ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/opt/plank-0.11.4 --disable-silent-rules $ makeplank のインストール
前節によって、正常に plank の実行ファイル等のビルドが完了した後は、コマンド
make installを実行して、 plank の実行ファイル等を/usr/local/opt/plank-0.11.4にインストールします。$ make installそして、カレントディレクトリを
/usr/local/optに移動して以下のコマンドを実行します。コマンドxstow -v ./plank-0.11.4の実行により、 plank の実行ファイル等のシンボリックリンクがディレクトリ/usr/local以下に張られます。$ cd /usr/local/opt $ xstow -v ./plank-0.11.4 ...(略)... $最後に、以下の通りに
plankコマンドを実行して、正常に plank が起動する事を確認します。$ plankなお、もし plank のソースコードをコンパイルする事が煩わしい場合や何らかの問題で困難である場合は、次に示す URL に置かれているシェルスクリプトを用いて、以下のように plank のソースコードのダウンロード及びビルドとインストールを自動的に行っても構いません。
- build-plank.sh (最新版)
$ bash -c "$(wget -q -O - https://git.io/debian-noroot-build-plank.sh)" ...(略)... $ plank # (plank の動作確認を行う。)デスクトップ環境への導入
本章では、前章で述べた手法でインストールした plank を Debian noroot 環境上の各種デスクトップ環境の起動時において自動的に起動するように設定する手法について述べます。
まず、 "MATE への導入" の節において、 Linux MINT において採用されているデスクトップ環境である MATE に plank を導入する手法について述べます。
次に、 "LXDE への導入" の節において、軽量なデスクトップ環境の1つである LXDE に plank を導入する手法について述べます。
最後に、 "xfce4 への導入" の節において、 Debian noroot 環境におけるデフォルトのデスクトップ環境である xfce4 に plank を導入する手法について述べます。
なお、以降で述べる設定手法で示す各画像において表示されている plank については、 plank の動作確認時において plank の各種設定を修正したものであり、デフォルトの plank の表示とは若干異なることに留意して下さい。
MATE への導入
まず、 plank をデスクトップ環境 MATE において自動的に起動するように設定する手法について述べます。
- まず最初に、以下の画像のようにして [設定] のメニューを開き、 [コントロールセンター] の項目を選択します。
- 次に、以下の画像のように [コントロールセンター] のパネルにおいて、 [自動起動するアプリ] のボタンをクリックします。
- そして、以下の画像のように [自動起動するアプリの設定] のウィンドウにおいて、 [追加]のボタンをクリックします。
- その後、以下の画像のように [自動起動するプログラムの編集] のウィンドウにおいて、 plank の自動起動についての各項目を指定します。ここで、plank の実行ファイルの絶対パスは、必ず
/usr/local/bin/plankとする必要があります。
以上の設定が完了した後、 Debian noroot 環境を再起動して、以下の画像の通りに plank が自動的に起動する事を確認します。
LXDE への導入
次に、 plank を軽量なデスクトップ環境 LXDE において自動的に起動するように設定する手法について述べます。
- まず最初に、以下の画像のようにして [設定] のメニューを開き、 [LXSession のデフォルトのアプリケーション] の項目を選択します。
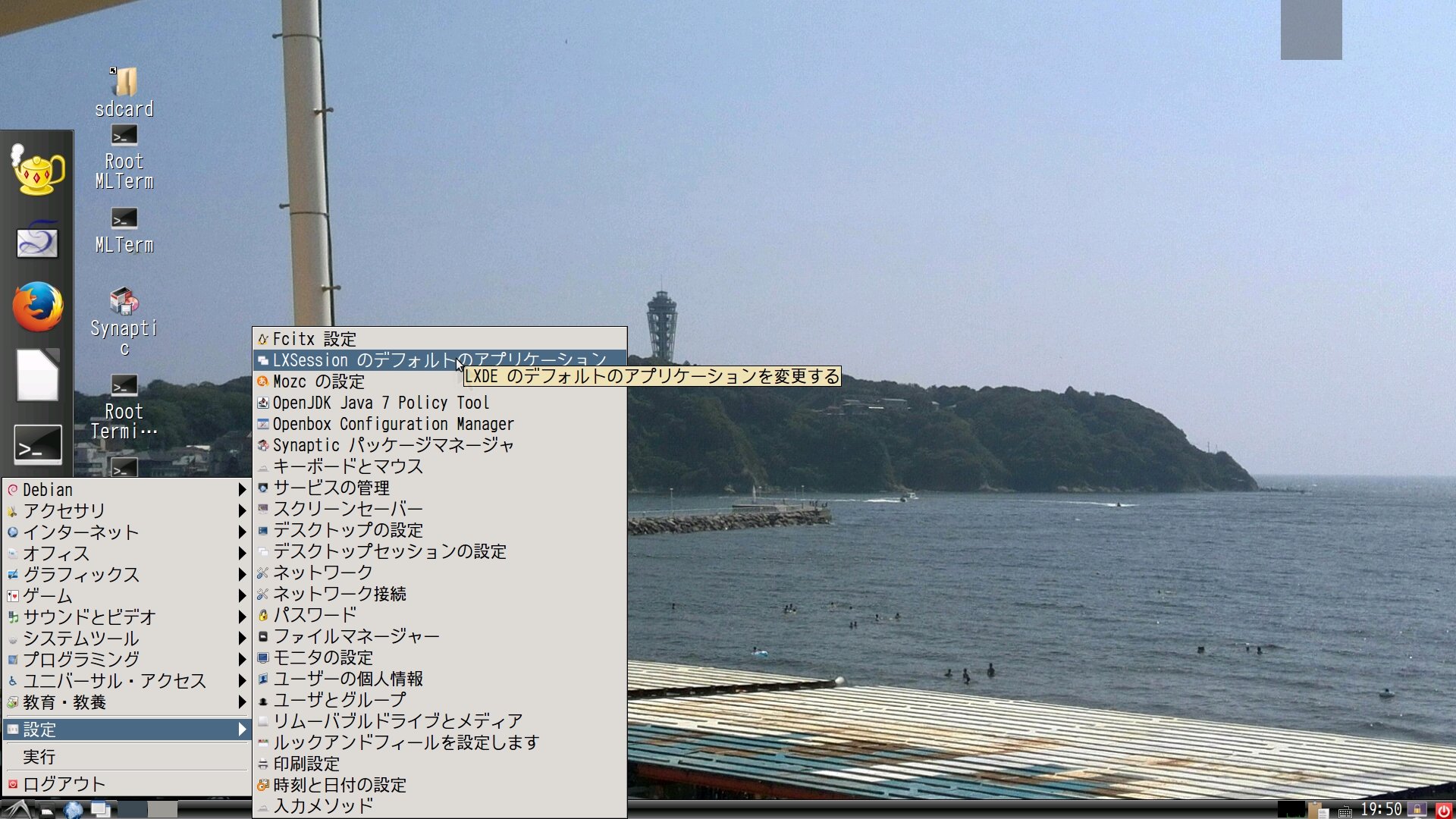
- ここで、 [LXSession Configuration] のウィンドウが開くので [Autostart] の項目を選択します。
- すると、以下の画像のように Manual Autostart Application のリストの末尾に [追加] のボタンと、その右隣にてテキストエリアが表示されているので、ここでテキストエリア内に
@plankと入力して [追加] ボタンを押します。
- [追加] ボタンを押した後、以下の画像のように Manual Autostart Application のリストの末尾に
@plankが登録されていることを確認します。
以上の設定が完了した後、 Debian noroot 環境を再起動して、 plank が自動的に起動する事を確認します。
fxce4 への導入
そして、plank を Debian noroot 環境のデフォルトのデスクトップ環境である [fxce4 環境][FXCE]において自動的に起動するように設定する手法について述べます。
- まず最初に、以下の画像のようにして [設定] のメニューを開き、 [セッションと起動] の項目を選択します。
- そして、以下の画像のように [セッションと起動] のウィンドウにおいて、[自動開始アプリケーション] の項目を選択します。
- すると、以下の画像のように自動起動するアプリケーションの一覧が表示されます。ここで、未だ plank が一覧に登録されていない場合は [追加] ボタンを押し、登録されている場合は plank が登録されている行をクリックして [編集] ボタンを押します。
- その後、以下の画像のように [アプリケーションの編集] のウィンドウにおいて、 plank の自動起動についての各項目を指定します。ここで、plank の実行ファイルの絶対パスは、必ず
/usr/local/bin/plankとする必要があります。
以上の設定が完了した後、 Debian noroot 環境を再起動して、 plank が自動的に起動する事を確認します。
plank に関する問題点
本章において、 plank について、現時点で判明してい問題点について述べます。
まず、何らかの理由で plank のプロセスに SIGKILL 等の SIGTERM でないシグナルが送られる事により異常終了した場合等において、再度 plank を起動した場合に以下のエラーメッセージを出力して plank が起動しない場合があります。
$ plank ...(略)... [ERROR 01:22:33.123456] [Utils:42] GSettingsSchema 'net.launchpad.plank' not found Trace/breakpoint trap $この場合は以下のコマンドの実行により、 plank が起動しない問題を回避します。
$ sudo glib-compile-schemas /usr/local/share/glib-2.0/schemas上記のコマンドの実行によっても、問題が回避できない場合は、 plank のビルド及びインストールを再度行って下さい。
結論
本稿では、 "plank の導入" の章において、 Debian noroot 環境上で、 plank のソースコードから、実行ファイル等をビルドし、ディレクトリ
/usr/local以下にインストールする手法について示しました。そして、 "デスクトップ環境への導入" の章において、 "plank の導入" の章でインストールした plank を、 Debian noroot 環境上で動作する各種デスクトップ環境の起動時に自動的に起動させるように設定を行う手法について示しました。
以上で示した手法によって Debian noroot 環境へ plank を導入することにより、 Debian noroot 環境の起動時に軽量な Dock ランチャーソフトウェアである plank が自動的に起動して、高頻度で使用するソフトウェアの起動が容易になることが示されました。
また、デスクトップ環境 MATE が導入された Debian noroot 環境において、 plank を左端の中央に配置する設定を行うことにより、 Unity ライクなデスクトップ環境の外観が実現でき、多くの PC 端末と同様の快適性を持つデスクトップ環境が実現できることが判りました。
謝辞
本稿の記述に当たって、 Android OS 端末上で非常に軽快な Debian 環境を実現することを可能にした Debian noroot 環境の開発者である pelya 氏に心より感謝致します。
なお、 plank 本体をソースコードから実行ファイル等へビルドし、インストールを行う手法に関しては、techbar 氏による "Installing Plank Dock on Debian Jessie | Techbear" を参考にしました。 techbar 氏に心より感謝致します。
そして最後に、 Debian noroot 環境と Android OS 及び Debian 環境の全ての事に関わる全ての皆様に心より感謝致します。
- 投稿日:2019-03-05T15:39:27+09:00
SSH じゃないポートフォワーディング
localhost のあるポートを別のホストのポートにリダイレクトしたい場合、よくやるのは以下のように SSH ポートフォワーディングする方法。
$ ssh example.com -N -L 8080:localhost:80この例だと、localhost のポート 8080 にアクセスすると example.com のポート 80 に繋がる。
しかしこの方法では、ホスト (この例でいうと
example.com) に SSH 接続できないとポートフォワーディングできない。
もし対象ホストの対象ポートが外向けに公開されているのであれば、socatを使って以下のようにしても同じことができる。$ socat TCP4-LISTEN:8080,fork TCP4:example.com:80ポートフォワーディングと言うより、TCP リレーとか TCP リダイレクトと言う方が正確かもしれない。
- 投稿日:2019-03-05T14:20:23+09:00
Linuxファイルシステム基礎
おはようございます、こんちには、こんばんは!
ファイルシステムとはファイルとしてデータを扱う仕組みです。
1、ext2 ext3
限界ファイルサイズ2TiB、最大容量(ボリュームサイズ)16TiB、ジャーナルには非対応となっているので、使うのは避けたほうがよいです。
ジャーナルに非対応なため、一度クラッシュすると復旧に時間がかかる、このファイルシステムは旧式なので「ext4」の使用をおすすめします。2、ext4
の拡張であり、現在のlinuxファイルシステムのデファクトスタンダードです。
最大ファイルサイズは16TiBと拡張され、最大ボリューム サイズも1EiBとなっています。
また日付範囲も1901年12月14日から2514年4月25日までと拡張されており、下位互換もたもたれています。
ext3としてマウントすることも可能です。3JFS
- 投稿日:2019-03-05T13:59:34+09:00
Linuxを触りたての頃に知っておきたかったよ〜ってことのまとめ
B4になって研究室配属され、一年たって
なんで早く教えてくれなかったのってことが多数あるから
後輩のためにも記録を残そうと思う。ターミナル系
そもそもログインシェルは
bashなんて使わなくてよく、
おすすめはzshである。
bashからzshに移行する方法は お前らのターミナルはダサいが非常によく参考になる。(さらbash)シェルの機能系
>,>>,|,&&について
>: 標準出力に表示されるものを指定ファイルに上書きする。ちょっとしたファイルを作成するときに使える。example$ echo mou_kenkyu_sitakunai > test.dat $ cat test.dat mou_kenkyu_sitakunai仮に、指定ファイルと同名のものがあると上書きされるため注意が必要。
>>: 標準出力に表示されるものを指定ファイルの下に書き足す。こちらは2つに分かれているプロットしたいデータを連結したり、
トポロジーファイルの合体に使えたりと、よく使う。example$ cat test.dat ohayo $ echo konnichiha >> test.dat $ cat test.dat ohayo konnichiha
|: パイプといい、左側の出力結果を右のコマンドに標準入力として渡せる。例で説明すると、
example$ ls #ディレクトリの中身の表示 aaa.mp3 aaa.png aaa.dat aaa.txt bbb.png ccc.png ddd.dat $ ls | grep png #ディレクトリの中身から[png]がついてるものだけを表示 aaa.png bbb.png ccc.pngこのように、ディレクトリの中のファイル数が多くなって見づらい時とかに使える。
また長いファイルから特定の文字が含まれる行だけを抜き出すこともできるため、example$ cat test.dat #ファイルの中身の表示 hogehoge 0 hogehoge 8 aaaaaaa 1 bbbbbbb 7 ccccccc 6 tip3p 10 hogehoge 20 hogehoge 38 aaaaaaa 16 bbbbbbb 76 ccccccc 67 tip3p 18 : $ cat test.dat | grep tip3p #ファイルの中身から[tip3p]がついてる行だけを表示 tip3p 10 tip3p 18などの用途がある。
&&左のコマンドが終わったら右のコマンドを実行簡単な例としては。新規ディレクトリを作りそこに移動とか?
example#従来法 $ mkdir testdir $ cd testdir ##こっちが楽 $ mkdir testdir && cd testdir他にも、グラフをgnuplotでプロットしたあと画像ファイルに変換とかできる。
conv.sh#!/bin/bash pict_name=`ls -t | head -n1 | head -c-4` #pict_name is "test." echo " #################################################################" echo "" echo " " `ls -t | head -n1` " -->> ${pict_name}png" echo "" echo " #################################################################" convert -density 1000 `ls -t | head -n1` ${pict_name}png display -resize 1680x1050 ${pict_name}pngこのシェルスクリプトは、今いるデイレクトリで一番新しく生成された画像を
pngに変換するものである。
これをホームディレクトリに保存し、
gnuplot aaa.plt && ~/conv.sh
で画像の生成まで一発である。ワイルドカード指定
*:任意の複数文字?:任意の複数文字example##現ディレクトリから`.jpg`のファイルだけを移動する。 $ mv *.jpg ~/picture/ブレース展開
連番でループしたいときに便利。
いちいちシェルスクリプトを書く必要もない。example$ echo {1..10} 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 $ echo {A..Z} A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z $ echo test{1..30..2} test1 test3 test5 test7 test9 test11 test13 test15 test17 test19 test21 test23 test25 test27 test29 $ echo {A..C}{1..3} A1 A2 A3 B1 B2 B3 C1 C2 C3このように、文字でもループできるし、インクリメント数も変更できる。
例ではechoを上げたが、当然すべてのコマンドで使える。
面白いのは、4番目の例のように二個の展開を試みると数学の分配法則のようになる点である。
なお、文字でのループはBashのバージョンによってはできないこともあるので注意。コマンド系
cd誰もが知っているディテクトリ移動のコマンドだが、一つ前にいたディレクトリに戻りたいとき、
$ cd -とすると戻れる。
example$ pwd test1/ $ cd test2 $ pwd test1/test2/ $ cd - $ pwd test1/
tailファイルの中身を表示するコマンドだが、ファイルの最後10行を表示できる。
長いファイルの最後だけを確認するときに使えるし、また
-fオプションをつける(tail -f)で見ているファイルが更新されたら順次表示も更新されていく。
MDのアウトプットファイルがちゃんと更新されていくかどうかの確認で使える。
ただし、ctrl + cを入力するまで終わらないことに注意。example$ tail -f mdrun.out 0 aaa 1 bbb 2 ccc :(どんどん更新されていく) ctrl + c を押すまで表示されるエディター系(Vi,Vim)
Vi(Vim)ははじめは使いにくいと思うかもしれないが、慣れたりカスタマイズするとすごく便利
カスタマイズする
~/.vimrcに設定を書いておくと様々な設定を起動時に読み込んでくれる。
自分の使ってるものは、予測変換がついたり何かと高機能だがデフォルトのVimでは
一部機能が有効にならないので以下を参考に新しいVimをインストールすべし。
(centos vim lua 有効)とかでググる。インストールの後、以下の内容を
~/.vimrcに記述~/.vimrcset encoding=utf-8 scriptencoding utf-8 " ↑1行目は読み込み時の文字コードの設定 " ↑2行目はVim Script内でマルチバイトを使う場合の設定 " Vim scriptにvimrcも含まれるので、日本語でコメントを書く場合は先頭にこの設定が必要になる "---------------------------------------------------------- " NeoBundle "---------------------------------------------------------- if has('vim_starting') " 初回起動時のみruntimepathにNeoBundleのパスを指定する set runtimepath+=~/.vim/bundle/neobundle.vim/ " NeoBundleが未インストールであればgit cloneする if !isdirectory(expand("~/.vim/bundle/neobundle.vim/")) echo "install NeoBundle..." :call system("git clone git://github.com/Shougo/neobundle.vim ~/.vim/bundle/neobundle.vim") endif endif call neobundle#begin(expand('~/.vim/bundle/')) " インストールするVimプラグインを以下に記述 " NeoBundle自身を管理 NeoBundleFetch 'Shougo/neobundle.vim' " カラースキームmolokai NeoBundle 'tomasr/molokai' "カラースキームiceberg NeoBundle 'cocopon/iceberg.vim' "カラースキームjellybeans NeoBundle 'nanotech/jellybeans.vim' "カラースキームhybrid NeoBundle 'w0ng/vim-hybrid' " ステータスラインの表示内容強化 NeoBundle 'itchyny/lightline.vim' " インデントの可視化 NeoBundle 'Yggdroot/indentLine' " 末尾の全角半角空白文字を赤くハイライト NeoBundle 'bronson/vim-trailing-whitespace' " 構文エラーチェック NeoBundle 'scrooloose/syntastic' " 多機能セレクタ NeoBundle 'ctrlpvim/ctrlp.vim' " CtrlPの拡張プラグイン. 関数検索 NeoBundle 'tacahiroy/ctrlp-funky' " CtrlPの拡張プラグイン. コマンド履歴検索 NeoBundle 'suy/vim-ctrlp-commandline' " CtrlPの検索にagを使う NeoBundle 'rking/ag.vim' " プロジェクトに入ってるESLintを読み込む NeoBundle 'pmsorhaindo/syntastic-local-eslint.vim' "カッコの補完 NeoBundle 'cohama/lexima.vim' "ブロックのendを自動で挿入 NeoBundle 'tpope/vim-endwise' "ツリー型のファイル表示 NeoBundle 'scrooloose/nerdtree' "autocmd vimenter * NERDTree let g:NERDTreeDirArrows = 1 let g:NERDTreeDirArrowExpandable = '▶' let g:NERDTreeDirArrowCollapsible = '▼' "NeoBundle 'Shougo/neocomplete.vim' "NeoBundle 'Shougo/vimproc.vim', { " \ 'build' : { " \ 'windows' : 'make -f make_mingw32.mak', " \ 'cygwin' : 'make -f make_cygwin.mak', " \ 'mac' : 'make -f make_mac.mak', " \ 'unix' : 'make -f make_unix.mak', " \ }, " \ } "NeoBundle 'justmao945/vim-clang' "NeoBundle 'Shougo/neoinclude.vim' " "" 'Shougo/neocomplete.vim' {{{ "let g:neocomplete#enable_at_startup = 1 "if !exists('g:neocomplete#force_omni_input_patterns') " let g:neocomplete#force_omni_input_patterns = {} "endif "let g:neocomplete#force_overwrite_completefunc = 1 "let g:neocomplete#force_omni_input_patterns.c = '[^.[:digit:] *\t]\%(\.\|->\)' "let g:neocomplete#force_omni_input_patterns.cpp = '[^.[:digit:] *\t]\%(\.\|->\)\|\h\w*::' """"}}} " "" 'justmao945/vim-clang' {{{ " "" disable auto completion for vim-clanG "let g:clang_auto = 0 "let g:clang_complete_auto = 0 "let g:clang_auto_select = 0 "let g:clang_use_library = 1 " "" default 'longest' can not work with neocomplete "let g:clang_c_completeopt = 'menuone' "let g:clang_cpp_completeopt = 'menuone' " "if executable('clang-3.6') " let g:clang_exec = 'clang-3.6' "elseif executable('clang-3.5') " let g:clang_exec = 'clang-3.5' "elseif executable('clang-3.4') " let g:clang_exec = 'clang-3.4' "else " let g:clang_exec = 'clang' "endif " "if executable('clang-format-3.6') " let g:clang_format_exec = 'clang-format-3.6' "elseif executable('clang-format-3.5') " let g:clang_format_exec = 'clang-format-3.5' "elseif executable('clang-format-3.4') " let g:clang_format_exec = 'clang-format-3.4' "else " let g:clang_exec = 'clang-format' "endif " "let g:clang_c_options = '-std=c11' "let g:clang_cpp_options = '-std=c++11 -stdlib=libc++' " "" }}} " "コメントアウト NeoBundle 'tomtom/tcomment_vim' " vimのlua機能が使える時だけ以下のVimプラグインをインストールする if has('lua') " コードの自動補完 NeoBundle 'Shougo/neocomplete.vim' " スニペットの補完機能 NeoBundle "Shougo/neosnippet" " スニペット集 NeoBundle 'Shougo/neosnippet-snippets' endif call neobundle#end() " ファイルタイプ別のVimプラグイン/インデントを有効にする filetype plugin indent on " 未インストールのVimプラグインがある場合、インストールするかどうかを尋ねてくれるようにする設定 NeoBundleCheck "---------------------------------------------------------- " カラースキーム "---------------------------------------------------------- "if neobundle#is_installed('molokai') " colorscheme molokai " カラースキームにmolokaiを設定する " endif colorscheme iceberg " カラースキームにicebergを設定する " colorscheme jellybeans " カラースキームにjellybeansを設定する " colorscheme hybrid" カラースキームにhybrid(in white background)を設定する set t_Co=256 " iTerm2など既に256色環境なら無くても良い syntax enable " 構文に色を付ける "---------------------------------------------------------- " 文字 "---------------------------------------------------------- set fileencoding=utf-8 " 保存時の文字コード set fileencodings=ucs-boms,utf-8,euc-jp,cp932 " 読み込み時の文字コードの自動判別. 左側が優先される set fileformats=unix,dos,mac " 改行コードの自動判別. 左側が優先される set ambiwidth=double " □や○文字が崩れる問題を解決 "---------------------------------------------------------- " ステータスライン "---------------------------------------------------------- set laststatus=2 " ステータスラインを常に表示 set showmode " 現在のモードを表示 set showcmd " 打ったコマンドをステータスラインの下に表示 set ruler " ステータスラインの右側にカーソルの位置を表示する "---------------------------------------------------------- " コマンドモード "---------------------------------------------------------- set wildmenu " コマンドモードの補完 set history=5000 " 保存するコマンド履歴の数 "---------------------------------------------------------- " タブ・インデント "---------------------------------------------------------- set expandtab " タブ入力を複数の空白入力に置き換える set tabstop=4 " 画面上でタブ文字が占める幅 set softtabstop=4 " 連続した空白に対してタブキーやバックスペースキーでカーソルが動く幅 set autoindent " 改行時に前の行のインデントを継続する set smartindent " 改行時に前の行の構文をチェックし次の行のインデントを増減する set shiftwidth=4 " smartindentで増減する幅 "---------------------------------------------------------- " 文字列検索 "---------------------------------------------------------- set incsearch " インクリメンタルサーチ. 1文字入力毎に検索を行う set ignorecase " 検索パターンに大文字小文字を区別しない set smartcase " 検索パターンに大文字を含んでいたら大文字小文字を区別する set hlsearch " 検索結果をハイライト " ESCキー2度押しでハイライトの切り替え nnoremap <silent><Esc><Esc> :<C-u>set nohlsearch!<CR> "---------------------------------------------------------- " カーソル "---------------------------------------------------------- set whichwrap=b,s,h,l,<,>,[,],~ " カーソルの左右移動で行末から次の行の行頭への移動が可能になる set number " 行番号を表示 set cursorline " カーソルラインをハイライト " 行が折り返し表示されていた場合、行単位ではなく表示行単位でカーソルを移動する nnoremap j gj nnoremap k gk nnoremap <down> gj nnoremap <up> gk " バックスペースキーの有効化 set backspace=indent,eol,start "カーソルの最終編集位置へ augroup vimrcEx au BufRead * if line("'\"") > 0 && line("'\"") <= line("$") | \ exe "normal g`\"" | endif augroup END "---------------------------------------------------------- " カッコ・タグの対応 "---------------------------------------------------------- set showmatch " 括弧の対応関係を一瞬表示する set matchtime=1 " 0.1秒だけ "let loaded_matchparen=1 止めるとき source $VIMRUNTIME/macros/matchit.vim " Vimの「%」を拡張する "hi MatchParen ctermbg=1" "hi MatchParen term=standout ctermbg=Black ctermfg=LightGrey guibg=Black guifg=LightGrey "---------------------------------------------------------- " マウスでカーソル移動とスクロール "---------------------------------------------------------- if has('mouse') set mouse=a if has('mouse_sgr') set ttymouse=sgr elseif v:version > 703 || v:version is 703 && has('patch632') set ttymouse=sgr else set ttymouse=xterm2 endif endif "---------------------------------------------------------- " クリップボードからのペースト "---------------------------------------------------------- " 挿入モードでクリップボードからペーストする時に自動でインデントさせないようにする if &term =~ "xterm" let &t_SI .= "\e[?2004h" let &t_EI .= "\e[?2004l" let &pastetoggle = "\e[201~" function XTermPasteBegin(ret) set paste return a:ret endfunction inoremap <special> <expr> <Esc>[200~ XTermPasteBegin("") endif "---------------------------------------------------------- " height of menu "---------------------------------------------------------- set pumheight=10 "if value is 0 , show menu all "---------------------------------------------------------- " スペルチェック(試験) "---------------------------------------------------------- set spelllang=en,cjk fun! s:SpellConf() redir! => syntax silent syntax redir END set spell hi clear SpellBad hi SpellBad cterm=underline hi clear SpellCap hi SpellCap cterm=underline,bold if syntax =~? '/<comment\>' syntax spell default syntax match SpellMaybeCode /\<\h\l*[_A-Z]\h\{-}\>/ contains=@NoSpell transparent containedin=Comment contained else syntax spell toplevel syntax match SpellMaybeCode /\<\h\l*[_A-Z]\h\{-}\>/ contains=@NoSpell transparent endif syntax cluster Spell add=SpellNotAscii,SpellMaybeCode endfunc augroup spell_check autocmd! autocmd BufReadPost,BufNewFile,Syntax * call s:SpellConf() augroup END "---------------------------------------------------------- " neocomplete・neosnippetの設定 "---------------------------------------------------------- if neobundle#is_installed('neocomplete.vim') " Vim起動時にneocompleteを有効にする let g:neocomplete#enable_at_startup = 1 " smartcase有効化. 大文字が入力されるまで大文字小文字の区別を無視する let g:neocomplete#enable_smart_case = 1 " 3文字以上の単語に対して補完を有効にする let g:neocomplete#min_keyword_length = 3 " 区切り文字まで補完する let g:neocomplete#enable_auto_delimiter = 1 " 1文字目の入力から補完のポッ"プアップを表示 let g:neocomplete#auto_completion_start_length = 1 " バックスペースで補完のポップアップを閉じる inoremap <expr><BS> neocomplete#smart_close_popup()."<C-h>" " エンターキーで補完候補の確定. スニペットの展開もエンターキーで確定 imap <expr><CR> neosnippet#expandable() ? "<Plug>(neosnippet_expand_or_jump)" : pumvisible() ? "<C-y>" : "<CR>" " タブキーで補完候補の選択. スニペット内のジャンプもタブキーでジャンプ imap <expr><TAB> pumvisible() ? "<C-n>" : neosnippet#jumpable() ? "<Plug>(neosnippet_expand_or_jump)" : "<TAB>" endif "---------------------------------------------------------- " Syntastic "---------------------------------------------------------- " 構文エラー行に「>>」を表示 let g:syntastic_enable_signs = 1 " 他のVimプラグインと競合するのを防ぐ let g:syntastic_always_populate_loc_list = 1 " 構文エラーリストを非表示 let g:syntastic_auto_loc_list = 0 " ファイルを開いた時に構文エラーチェックを実行する let g:syntastic_check_on_open = 1 " 「:wq」で終了する時も構文エラーチェックする let g:syntastic_check_on_wq = 1 " python setting let g:syntastic_python_checkers = ['flake8'] "" Javascript用. 構文エラーチェックにESLintを使用 "let g:syntastic_javascript_checkers=['eslint'] "" Javascript以外は構文エラーチェックをしない "let g:syntastic_mode_map = { 'mode': 'passive', " \ 'active_filetypes': ['javascript'], " \ 'passive_filetypes': [] } " "---------------------------------------------------------- " CtrlP "---------------------------------------------------------- let g:ctrlp_match_window = 'order:ttb,min:20,max:20,results:100' " マッチウインドウの設定. 「下部に表示, 大きさ20行で固定, 検索結果100件」 let g:ctrlp_show_hidden = 1 " .(ドット)から始まるファイルも検索対象にする let g:ctrlp_types = ['fil'] "ファイル検索のみ使用 let g:ctrlp_extensions = ['funky', 'commandline'] " CtrlPの拡張として「funky」と「commandline」を使用 " CtrlPCommandLineの有効化 command! CtrlPCommandLine call ctrlp#init(ctrlp#commandline#id()) " CtrlPFunkyの絞り込み検索設定 let g:ctrlp_funky_matchtype = 'path' if executable('ag') let g:ctrlp_use_caching=0 " CtrlPのキャッシュを使わない let g:ctrlp_user_command='ag %s -i --hidden -g ""' " 「ag」の検索設定 endif "--------------------------------------------------------- " CtrlP "---------------------------------------------------------- let g:lightline = { \ 'colorscheme': 'wombat', \ 'mode_map': {'c': 'NORMAL'}, \ 'active': { \ 'left': [ [ 'mode', 'paste' ], [ 'fugitive', 'filename' ] ] \ }, \ 'component_function': { \ 'modified': 'LightlineModified', \ 'readonly': 'LightlineReadonly', \ 'fugitive': 'LightlineFugitive', \ 'filename': 'LightlineFilename', \ 'fileformat': 'LightlineFileformat', \ 'filetype': 'LightlineFiletype', \ 'fileencoding': 'LightlineFileencoding', \ 'mode': 'LightlineMode' \ } \ } function! LightlineModified() return &ft =~ 'help\|vimfiler\|gundo' ? '' : &modified ? '+' : &modifiable ? '' : '-' endfunction function! LightlineReadonly() return &ft !~? 'help\|vimfiler\|gundo' && &readonly ? 'x' : '' endfunction function! LightlineFilename() return ('' != LightlineReadonly() ? LightlineReadonly() . ' ' : '') . \ (&ft == 'vimfiler' ? vimfiler#get_status_string() : \ &ft == 'unite' ? unite#get_status_string() : \ &ft == 'vimshell' ? vimshell#get_status_string() : \ '' != expand('%:t') ? expand('%:t') : '[No Name]') . \ ('' != LightlineModified() ? ' ' . LightlineModified() : '') endfunction function! LightlineFugitive() if &ft !~? 'vimfiler\|gundo' && exists('*fugitive#head') return fugitive#head() else return '' endif endfunction function! LightlineFileformat() return winwidth(0) > 70 ? &fileformat : '' endfunction function! LightlineFiletype() return winwidth(0) > 70 ? (&filetype !=# '' ? &filetype : 'no ft') : '' endfunction function! LightlineFileencoding() return winwidth(0) > 70 ? (&fenc !=# '' ? &fenc : &enc) : '' endfunction function! LightlineMode() return winwidth(0) > 60 ? lightline#mode() : '' endfunction我ながら凄まじい量だと思うが、すべてを使う必要もないと思う。
幸いコメントが書いてあるので、使わない部分は消してもらって構わない。
ここからはVimの挿入・ヴィジュアルモードくらいは理解しているものとして説明する。Vimの便利な機能
一括置換
:%s/置換したい文字/置換後の文字/g文章中のすべての置換したい文字を置き換えてくれる。
また%sを92sとかにすると92行目だけ置換が行われる。文字列検索
/検索したい文字一致する文字を検索し、表示してくれる。また
nキーを押すことで次に一致する部分までジャンプ。
検索を辞めたければ、escキーを連打すればいい。
また先ほどの.vimrcを記述していれば
小文字で検索をかければ大文字も検索でき、
大文字で検索をすると大文字しかヒットしません。一括挿入
①ctrl + vでヴィジュアルブロックモードに入る
②挿入したい範囲を選ぶ
③shift + iで挿入モードへ
④挿入する語句を打ち込む
⑤エスケープキーを押すと挿入される。一括切り取り
上とおんなじ理屈で文字を切り取ることもできる。
コメントアウトした部分を一気に戻すのに便利。①ctrl + vでヴィジュアルブロックモードに入る
②切り取りたい範囲を選ぶ
③xで切り取るVimdiff:差分表示
vimdiff ファイル1 ファイル2で2つのファイルの
異なる部分だけを表示できる。
MDの設定ファイルの間違い探しなどで便利example$ vimdiff test1.dat test2.dat日本語入力系
かな漢字を選べば、日本語入力は一応できるが、超絶使いにくいのでMozcのインストールを推奨。
Centos7でMozc(Google日本語入力)を使う方法
を、参考にしてほしい(宣伝)。MD系
VMDでのスナップショットの保存の仕方
VMD(Visual Molecular Dynamics)でMDシミュレーションの綺麗なスナップショットを作る
を、参考にしてほしい(宣伝)。Pythonによる解析ツール
輪講で習うFortranなんて捨てたほうがいい。
今流行りのPythonを勉強して、便利な解析ツールを使おう!
MDの計算結果を解析できるPythonライブラリ:MDAnalysisのチュートリアルを日本語化する#1
を、参考にしてほしい(宣伝)。
- 投稿日:2019-03-05T11:29:01+09:00
Ubuntuに切り替えて便利だったこと・不便だったこと
今回は、Windows10からUbuntu18.04に切り替えて便利だったこと・不便だったことを書きます。
切り替えたと言っても、デュアルブートなんでWindows残ってるんですが、、、(業務で使うもんでして)
*まだ切り替えたばっかなので、あまり分かっていません。アドバイスいただけると嬉しいです。PCはPanasonicのLet's noteです。
機種によって設定方法が違うらしいので、参考までに、、、不便だったこと
明るさ変更
明るさ変更できねえじゃん!ってなったんで、こちらの記事を参考に明るさ変更できるようになった。
http://tkyma.hatenablog.jp/entry/2015/10/24/012902
(2016/07/25追記2)の部分後、充電器を挿したら勝手に明るさが1番暗くなるという、、、
この問題解消はまだアクション起こしてません。(後で追加予定)かな変更とキーボードレイアウトの設定
かな変換も不便だったんで自分で設定変更
Mozcをインストールし、「変換」キーで日本語かな(Mozc)、「無変換」キーで日本語英数字(Mozc)に変更できるようにしました。
後は、「設定⇒地域と言語」で英語を追加しました。「Start+Space」で切り替えられます。キーボードのレイアウト変更も必要です。
恐らく、アメリカ?のレイアウトになっているのか、「@」などが変な位置にいっている。
「Shift+...」で打つ文字が1個ずつ右にずれていました。こちらで解消されましたが、一度シャットダウンすると元に戻ってしまう、、、
こちらで解決できました!
ありがとうございますホイールパッド
Windowsでは、上下にスクロールするために、ホイールパッドを回転させていました。
しかし、Ubuntuでは反応しない、、、
2本指スライドでスクロールできました!音量
alsamixerで変更できた!
って思ったら、イヤホンからは音出るけど、スピーカーからは音出ない。
色々調べたが解決できず、、、
どなたか解決方法教えてください。日付と時刻の設定
Windowsを起動した時、たまに時間が9時間ずれる(ロンドンの時間になる)
そんな困ってないので、設定やってません。(後で追加予定)Microsoft Office などの便利なアプリが使えない
WordみたいなのとかペイントとかがUbuntuに用意されているけど、、、
WindowsのOfficeのほうが使いやすい。
代用で、スクショは「Shutter」というアプリを、ペイントは「Pinta」を使っています。便利だったこと
作業スペースが複数ある
Ctrl+shift+Alt:新しい作業スペースに今のページを移動させる
Ctrl+shift:作業スペースを移動できるWindowsのファイルにもアクセスできる
フォルダの1番最初に戻ったらWindows欄があるぞ!
いろんなアプリを使える
Windowsでは使えなかったDockerなどを使える。
プログラマーには必須な機能が楽に実装できて素晴らしい。
- 投稿日:2019-03-05T11:29:01+09:00
WindowsからUbuntuに切り替えて便利だったこと・不便だったこと
今回は、Windows10からUbuntu18.04に切り替えて便利だったこと・不便だったことを書きます。
切り替えたと言っても、デュアルブートなんでWindows残ってるんですが、、、(業務で使うもんでして)
*まだ切り替えたばっかなので、あまり分かっていません。アドバイスいただけると嬉しいです。PCはPanasonicのLet's noteです。
機種によって設定方法が違うらしいので、参考までに、、、不便だったこと
明るさ変更
明るさ変更できねえじゃん!ってなったんで、こちらの記事を参考に明るさ変更できるようになった。
http://tkyma.hatenablog.jp/entry/2015/10/24/012902
(2016/07/25追記2)の部分後、充電器を挿したら勝手に明るさが1番暗くなるという、、、
この問題解消はまだアクション起こしてません。(後で追加予定)かな変更とキーボードレイアウトの設定
かな変換も不便だったんで自分で設定変更
Mozcをインストールし、「変換」キーで日本語かな(Mozc)、「無変換」キーで日本語英数字(Mozc)に変更できるようにしました。
後は、「設定⇒地域と言語」で英語を追加しました。「Start+Space」で切り替えられます。キーボードのレイアウト変更も必要です。
恐らく、アメリカ?のレイアウトになっているのか、「@」などが変な位置にいっている。
「Shift+...」で打つ文字が1個ずつ右にずれていました。こちらで解消されましたが、一度シャットダウンすると元に戻ってしまう、、、
こちらで解決できました!
ありがとうございますホイールパッド
Windowsでは、上下にスクロールするために、ホイールパッドを回転させていました。
しかし、Ubuntuでは反応しない、、、
2本指スライドでスクロールできました!音量
alsamixerで変更できた!
って思ったら、イヤホンからは音出るけど、スピーカーからは音出ない。
色々調べたが解決できず、、、
どなたか解決方法教えてください。日付と時刻の設定
Windowsを起動した時、たまに時間が9時間ずれる(ロンドンの時間になる)
そんな困ってないので、設定やってません。(後で追加予定)Microsoft Office などの便利なアプリが使えない
WordみたいなのとかペイントとかがUbuntuに用意されているけど、、、
WindowsのOfficeのほうが使いやすい。
代用で、スクショは「Shutter」というアプリを、ペイントは「Pinta」を使っています。便利だったこと
作業スペースが複数ある
Ctrl+shift+Alt:新しい作業スペースに今のページを移動させる
Ctrl+shift:作業スペースを移動できるWindowsのファイルにもアクセスできる
フォルダの1番最初に戻ったらWindows欄があるぞ!
いろんなアプリを使える
Windowsでは使えなかったDockerなどを使える。
プログラマーには必須な機能が楽に実装できて素晴らしい。
- 投稿日:2019-03-05T09:15:18+09:00
1日目 LinuxとShellscriptとルート権限
Qiita投稿は初で、殆ど自分用なので長文駄文は無視して戴きたい。
Linux
メイン課題
- ディレクトリ1を作成
- ディレクトリ1の中にファイル1を作成
- ディレクトリ2を作成
- ディレクトリ2の中にディレクトリ3を作成
- ディレクトリ1をディレクトリ3の中に移動
なお、ディレクトリ1/2/3:dir1/2/3、ファイル1:file1とした
最終的に簡潔になったコードmkdir dir1 touch dir1/file1 mkdir -p dir2/dir3 mv dir1 dir2/dir3コマンドのオプションが分からなくなった時
man コマンド名今回使用したオプション付きコマンド
mkdir -p`` # -p, --parents no error if existing, make parent directories as needed mv-O1-O2 # O2が同ディレクトリ内に存在しないとき:リネームされる # O2が同ディレクトリ内に存在するとき:移動 rm -r # -r, -R, --recursive remove directories and their contents recursively # recursive:再帰的:ディレクトリ内のものに一つ一つに対し処理 ls -la # manコマンドで調べると-la自体は無いが、-lと-aオプションが存在する # -a, --all do not ignore entries starting with # すべてのファイルやディレクトリを表示する #この時、隠しフォルダや。から始まるディレクトリも表示される。 # -l use a long listing format # ファイルの詳細を表示するシェルスクリプト
OSのシェルまたはコマンドラインインタプリタ向けに書かれたスクリプト言語。拡張子は『.sh』。
#シェルスクリプト作成(例 touch test.sh #シェルスクリプト内編集(先の課題のコードを記述してみる #!/bin/sh mkdir dir1 touch dir1/file1 mkdir -p dir2/dir3 mv dir1 dir2/dir31行目は『シバン』と呼ばれ、UNIXのスクリプトの #! から始まる1行目を指す。起動してスクリプトを読み込むインタプリタを指定する。
インタプリタ(interpreter)とは、プログラミング言語で書かれたソースコードないし中間表現を逐次解釈しながら実行(英語版)するプログラムのこと。(※よくわからなかったので、あとで調べる)このtest.shを活用することで、先の課題を自動的に行うことができる
#起動方法 ./test.shルート権限
まず、先のtest.shに対する権限を確認
#コマンド ls -la test.sh #表示結果 -rw-rw-r-- 1 vagrant vagrant 0 Mar 4 23:48 test.sh #左のチャンクから、user:所有者、usergroup:vagrant、others:誰でも、を意味する。 #また、r=read権限、w=write権限、ここでは見えないがx=execute権限(実行許可)を指す。権限編集方法
chmod=change mode
# すべてのユーザーに実行権限を与える/禁止する chmod +x test.sh / chmod -x test.sh #グループに書き込み権限をその他のユーザーには実行許可を禁止する chmod g+w,o-x test.sh別の表示方法(数字)
# r、w、xにそれぞれ4,2,1を割り当て、表すことができる rw-r--r-- => 644 r-xr--r-- => 544 #数字表示での権限編集 #すべてのユーザーに書き込み権限と読込権限を与える chmod 666 test.sh
- 投稿日:2019-03-05T09:15:18+09:00
1日目 LinuxとShellscriptとPermission
Qiita投稿は初で、殆ど自分用なので長文駄文は無視して戴きたい。
Linux
メイン課題
- ディレクトリ1を作成
- ディレクトリ1の中にファイル1を作成
- ディレクトリ2を作成
- ディレクトリ2の中にディレクトリ3を作成
- ディレクトリ1をディレクトリ3の中に移動
なお、ディレクトリ1/2/3をdir1/2/3、ファイル1をfile1とした。
最終的に簡潔になったコード。mkdir dir1 touch dir1/file1 mkdir -p dir2/dir3 mv dir1 dir2/dir3コマンドのオプションが分からなくなった時
man コマンド名今回使用したオプション付きコマンド
mkdir -p`` # -p, --parents no error if existing, make parent directories as needed mv-O1-O2 # O2が同ディレクトリ内に存在しないとき:リネーム # O2が同ディレクトリ内に存在するとき:移動 rm -r # -r, -R, --recursive remove directories and their contents recursively # recursive:再帰的:ディレクトリ内のものに一つ一つに対し処理 ls -la # manコマンドで調べると-la自体は無いが、-lと-aオプションが存在する。 # -a, --all do not ignore entries starting with # すべてのファイルやディレクトリを表示する。 #この時、隠しフォルダや。から始まるディレクトリも表示される。 # -l use a long listing format # ファイルの詳細を表示する。シェルスクリプト
OSのシェルまたはコマンドラインインタプリタ向けに書かれたスクリプト言語。拡張子は『.sh』。
#シェルスクリプト作成(例 touch test.sh #シェルスクリプト内編集(先の課題のコードを記述してみる。 #!/bin/sh mkdir dir1 touch dir1/file1 mkdir -p dir2/dir3 mv dir1 dir2/dir31行目は『シバン』と呼ばれ、UNIXのスクリプトの #! から始まる1行目を指す。起動してスクリプトを読み込むインタプリタを指定する。
インタプリタ(interpreter)とは、プログラミング言語で書かれたソースコードないし中間表現を逐次解釈しながら実行(英語版)するプログラムのこと。(※よくわからなかったので、あとで調べる)このtest.shを活用することで、先の課題を自動的に行うことができる。
#起動方法 ./test.shPermission
まず、先のtest.shに対する権限を確認。
#コマンド ls -la test.sh #表示結果 -rw-rw-r-- 1 vagrant vagrant 0 Mar 4 23:48 test.sh #左のチャンクから、user:所有者、usergroup:vagrant、others:誰でも、を意味する。 #また、r=read権限、w=write権限、ここでは見えないがx=execute権限(実行許可)を指す。権限編集方法
chmod=change mode
# すべてのユーザーに実行権限を与える/禁止する。 chmod +x test.sh / chmod -x test.sh #グループに書き込み権限をその他のユーザーには実行権限を禁止する。 chmod g+w,o-x test.sh別の表示方法(数字)
# r、w、xにそれぞれ4,2,1を割り当て、表すことができる。 rw-r--r-- => 644 r-xr--r-- => 544 #数字表示での権限編集 #すべてのユーザーに書き込み権限と読込権限を与える。 chmod 666 test.shP.S. PermissionとPermitの違い(※プログラムはPermission
どちらも名詞で『許可』を意味するが、ニュアンスが違う。
日本語で説明するとズレるので、英英辞典で確認したい。
あと、Permissionのスペル注意。
- 投稿日:2019-03-05T08:33:57+09:00
LinuxのパーミッションとWebサーバの挙動を確認してみた
パーミッションとは
Linuxのディレクトリとファイルに設定する。
「誰に」「どのような操作」を許可するかを設定。誰に
誰に 意味 Owner(所有者) ファイル・ディレクトリの所有者 Group(グループ) ユーザーが属するグループ Other(その他) その他のユーザー どのような操作
パーミッションの種類
パーミッションの種類には、「読み取り」「書き込み」「実行」の3種類の権限がある。
パーミッションの表記には、アルファベットと数値の表記がある。
種類 読み取り r 4 書き込み w 2 実行 x 1
ディレクトリとファイルのそれぞれのパーミッションの内容は以下。ディレクトリの場合
種類 どのような操作 使用可能なコマンド例 r ディレクトリ内のリスト表示が可能。 ls w ディレクトリ内のディレクトリまたはファイルの新規作成・削除が可能。 mkdir, touch, rm x カレントディレクトリとして移動可能。 cd ファイルの場合
種類 どのような操作 使用可能なコマンド例 r ファイルの読み取りが可能。 less, more, cp w ファイルの編集が可能。 vi x ファイルの実行が可能。 パーミッションの確認方法
パーミッション早見表
r x w 0-7 パーミッション rwx 7 読み取り 書き込み 実行 rx- 6 読み取り 書き込み r-x 5 読み取り 実行 r-- 4 読み取り -wx 3 書き込み 実行 -w- 2 書き込み --x 1 実行 --- 0
「ls」コマンドに「-l」オプションをつけて確認する。
$ ls -l /home/develop/public_html/ drwxrwxr-x 5 develop develop 71 3月 4 03:26 app -rw-rw--r-- 1 develop develop 13 3月 4 03:24 index.html lrwxrwxrwx 1 develop develop 41 3月 4 22:04 link.html -> /home/develop/public_html/app/sample.html
左の謎の暗号らしきものがパーミッションで、以下の並びで意味をもっている。
[ファイルの種類][Ownerの権限][Groupの権限][Otherの権限]drwxrwxr-x
意味 1文字目 d ファイルの種類 ディレクトリ 2~4文字目 rwx Ownerの権限 読み取り 書き込み 実行 5~7文字目 rwx Groupの権限 読み取り 書き込み 実行 8~10文字目 r-x Otherの権限 読み取り 実行 -rw-rw-r--
意味 1文字目 - ファイルの種類 ファイル 2~4文字目 rw- Ownerの権限 読み取り 書き込み 5~7文字目 rw- Groupの権限 読み取り 書き込み 8~10文字目 r-- Otherの権限 読み取り lrwxrwxrwx
意味 1文字目 l ファイルの種類 シンボリックリンク 2~4文字目 rwx Ownerの権限 読み取り 書き込み 実行 5~7文字目 rwx Groupの権限 読み取り 書き込み 実行 8~10文字目 rwx Otherの権限 読み取り 書き込み 実行 パーミッションの設定方法
「chmod」コマンドで設定をする。
アルファベットで設定するシンボリックモードと、
数値で設定するオクタルモードの2種類の設定方法がある。シンボリックモード
chmod [ユーザー][操作][権限] file以下の項目の組み合わせで設定
ユーザー 意味 u Ownerの権限 g Groupの権限 o Otherの権限 a すべてのユーザーの権限
操作 意味 + 権限を付与 - 権限を削除 = 指定した権限にする
権限 意味 r 読み取り w 書き込み x 実行 パーミッションが「rw-rw--r--」のindex.htmlのOtherの権限に「書き込み(w)」権限を付与する場合
$ ls -l /home/develop/public_html/ -rw-rw--r-- 1 develop develop 13 3月 4 03:24 index.html chmod o+w /home/develop/public_html/index.html $ ls -l /home/develop/public_html/ -rw-rw-rw- 1 develop develop 13 3月 4 03:24 index.html
カンマで区切りで複数の権限をまとめて設定することも可能
chmod u-x,go+w /home/develop/public_html/index.htmlオクタルモード
Owner・Group・Otherそれぞれの権限を数値で指定する。
chmod [Owner][Group][Other] file
早見表の数値で設定
r x w 0-7 パーミッション rwx 7 読み取り 書き込み 実行 rx- 6 読み取り 書き込み r-x 5 読み取り 実行 r-- 4 読み取り -wx 3 書き込み 実行 -w- 2 書き込み --x 1 実行 --- 0 /home/develop/public_html/index.htmlに以下のパーミッションを設定する場合
Owner ・・・読み取り・書き込み
Group ・・・読み取り・書き込み
Other ・・・読み取りchmod 664 /home/develop/public_html/index.html $ ls -l /home/develop/public_html/ -rw-rw-r-- 1 develop develop 13 3月 4 03:24 index.htmlデフォルトのパーミッション
ファイルやディレクトリを作成すると、デフォルトでパーミッションが設定される。
デフォルトのパーミッションは「umask値」によって決まる。
「umask」コマンドで確認が可能。# umask 0022 $ unmask 0002rootと一般ユーザーでumask値が異なるので、
rootと一般ユーザーのデフォルトのパーミッションも異なる。rootの場合
umask値のパーミッション「022」を作成時のパーミッションから削除
ディレクトリ ファイル 作成時 rwx rwx rwx(777) rw- rw- rw-(666) umask値 --- -w- -w- (022) --- -w- -w-(022) デフォルト rwx r-x r-x (755) rw- r-- r--(644) 一般ユ-ザーの場合
umask値のパーミッション「002」を作成時のパーミッションから削除
ディレクトリ ファイル 作成時 rwx rwx rwx(777) rw- rw- rw-(666) umask値 --- --- -w- (002) --- --- -w-(002) デフォルト rwx rwx r-x (775) rw- rw- r--(664)
まとめると、rootと一般ユーザーのデフォルトのパーミッションは以下になる。
ユーザー ディレクトリ ファイル root rwx r-x r-x (755) rw- r-- r--(644) 一般ユーザー rwx rwx r-x(775) rw- rw- r--(664) ブラウザでファイルを表示するときのユーザーは?
所有者が「develop」のindex.htmlがWebサーバ上にあるとする。
ブラウザで
https://ドメイン/index.htmlとURLを叩いて、index.htmlを読み込む時のユーザーは誰だ...?root?ファイルの所有者のdevelop?
いろんな見知らぬ人がアクセスするからその他のユーザー?答えはその他のユーザー。
しかし、ブラウザからアクセスする人がユーザーではない。Webサーバがレスポンスを返す際に、
リクエストされたファイルへアクセスするのはWebサーバである。WebサーバにApacheを利用している場合、
Apahceのユーザーとグループはhttpd.confに設定されている。/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confUser apache Group apache
つまりこの場合、ファイルへアクセスするユーザーは「apache」となる。
パーミッションのユーザー分類としては、「Other」に分類される。そのため、Webサーバにディレクトリやファイルを配置する際には、
Otherのパーミッションを適切に設定する必要がある。※所有者やグループをapacheに設定している場合は、Otherではないので注意。
パーミッションを変更してWebサーバの挙動を確認
パーミッションを変更するとWebサーバの挙動はどうなるのか、
public_htmlとindex.htmlのディレクトリ・ファイル構造で確認してみる。今回は、Webサーバが分類されるOtherのパーミッションを変更した場合の挙動を確認するので、
OwnerとGroupに設定しているパーミッションは今回は特に気にせずに!■ディレクトリ
/home/develop/public_html
所有者:develop■ファイル
/home/develop/public_html/index.html
所有者:develop■ドキュメントルート
/home/develop/public_htmlよくあるデフォルトの設定
dir / file パーミッション public_html rwx r-x r-x (755) index.html rw- r-- r-- (644) ディレクトリから実行権限( x )を削除 / ファイルはデフォルト
ディレクトリはデフォルトの設定から実行権限をなくし、ファイルはデフォルトの設定。
dir / file パーミッション public_html rwx r-x r-- (754) index.html rw- r-- r-- (644)
ブラウザでアクセスしてみると、403 Forbiddenでアクセスできなくなる。
一見いけそうな気もするが、
これはカレントディレクトリとして移動する権限がないため、public_htmlにアクセスができないから。
種類 何ができるか 使用可能なコマンド例 x カレントディレクトリとして移動可能。 cd
Otherに分類されるユーザーで、コマンドでも試してみる。
[other@localhost ~]$ cd /home/develop/public_html/ -bash: cd: /home/develop/public_html/: 許可がありません許可がないためpublic_htmlにアクセスできない。
index.htmlにもアクセスしてみる。
[other@localhost ~]$ less /home/develop/public_html/index.html /home/develop/public_html/index.html: 許可がありませんindex.htmlが配置されているpublic_htmlをカレントディレクトリにできないため、
index.htmlに読み取り権限があってもこちらもアクセスできない。ディレクトリはデフォルト / ファイルから読み取り権限( r )を削除
ディレクトリはデフォルトの設定で、ファイルはデフォルトの設定から読み取り権限をなくす。
dir / file パーミッション public_html rwx r-x r-x (755) index.html rw- r-- --- (640) ブラウザでアクセスしてみると、403 Forbiddenでアクセスできなくなる。
Otherに分類されるユーザーで、コマンドでも試してみる。
[others@localhost ~]$ less /home/develop/public_html/index.html /home/develop/public_html/index.html: 許可がありません読み込み権限がないため、もちろん開けない。
ブラウザでファイルへアクセスするためには
アクセスするファイルに到達するまでのディレクトリとファイルの
Otherのパーミッションの設定に、以下の権限が最低限必要になる。・ディレクトリ → 「実行 ( x ) 」
・ファイル → 「読み取り ( r ) 」ディレクトリに関しては、
目的のファイルに到達するまでのディレクトリ全てに、実行権限が必要なので要注意!ブラウザからアクセスして403エラーになってしまう場合は、まずはこのへんを確認してみよう。
※所有者やグループをapacheに設定している場合は、Otherではないので注意。ディレクトリの中身が丸見えになってしまうケース

Webサーバとパーミッションの設定しだいでは、
ブラウザからリクエストした際に、Webサーバのディレクトリの中身が丸見えになってしまうケースがある...!ブラウザでファイル名まで指定せずに、
https:// ドメイン / ディレクトリ /と入力してURLを叩くと、
Webサーバの設定しだいでは、ディレクトリの中身がブラウザに表示されてしまう。丸見え条件
・アクセスするディレクトリに「読み取り ( r ) 」権限がある
・アクセスするディレクトリ直下にhttpd.confのDirectoryIndexで指定したファイルが存在しない
・httpd.confのディレクティブの設定で「Options」の項目に「Indexes」を設定
・「https:// ドメイン / ディレクトリ / 」でリクエストディレクトリの「読み取り ( r ) 」権限
ディレクトリ内のリスト表示が可能。
DirectoryIndex
ファイルを指定せずに、ディレクトリだけを指定してクライアントからリクエストを受けた場合に、
ディレクトリ直下のどのファイルをレスポンスとして返すかの設定/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf<IfModule dir_module> DirectoryIndex index.html </IfModule>この場合、ファイルを指定せずにディレクトリだけを指定してリクエストを受けた場合、
そのディレクトリ直下のindex.htmlをレスポンスで返す。Options Indexes
DirectoryIndexで指定したファイルが存在しない場合に、ディレクトリ内ファイルの一覧を表示する
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf<VirtualHost *:80> DocumentRoot /home/develop/public_html ServerName develop.localdomain <Directory "/home/develop/public_html/"> AllowOverride All Require all granted Options Indexes </Directory> </VirtualHost>
上記の設定で
http:// ドメイン / ディレクトリ /でURLを叩いてみる。
丸見えや
!!
もしconfigやlogファイル等がアクセスできる状態だったら、
ブラウザからファイルの中身が普通に表示できてしまう。これはセキュリティ的によろしくない。
ちなみに「Options」の項目自体を設定していない場合も、
同様にディレクトリ内ファイルの一覧を表示する設定になるので要注意!一覧表示をしないためには、「-」をつけてIndexesを無効にする必要がある。
Options -Indexes
もう一度アクセスしてみる。
ディレクトリの中身が一覧表示されなくなった...!
さいごに
ここまで読んでくださりありがとうございます。
パーミッションについて改めて学習する機会がありましたが、
具体的に使えるコマンドやWebサーバの挙動って意外とすぐ忘れてしまうので、学んだことをつらつら書いてみました。誤りなどあればご指摘いただけるとありがたいです。
何か参考になれば幸いです〜!
- 投稿日:2019-03-05T08:22:47+09:00
Linuxのddコマンドで特定サイズのファイルを作る方法
実行方法
bsで指定した値とcountで指定した値を掛け合わせたサイズのファイルを作成する。
# dd if=<file> of=<file> bs=<block_size> count=<block_count>オプション説明
- if:inputのファイルを指定する。
/dev/zero(よく使われる)を指定した場合はNULL文字を出力しつづける特殊なファイルを指定することになる。- of:outputのファイル名を指定する。カレントディレクトリにファイルを生成する。
- bs:ブロックサイズを指定する。単位はk(キロ)、M(メガ)、G(ギガ)でも指定可。
- count:ブロック数を指定する。
(ちなみに)ddコマンドで作ったファイルの中身の実体
lessコマンドで覗いてみたらバイナリ?データでした。
- 投稿日:2019-03-05T01:30:46+09:00
C言語でリンクリスト(list_head/queue)
C言語でリストを実装する例です。
下記2つのマクロを使って双方向リストを実装してみます。
- linux kernelでよく使われるリスト操作用マクロであるlist_head
- BSD系のリスト操作マクロであるqueue
実行環境はCentOS7 64bit, gcc 4.8.5です。
list_headを使ったリスト
linux kernelには以下のような構造体と、この構造体を使ってリスト操作を行うマクロがいくつか用意されています。
struct list_head { struct list_head *next, *prev; };仕組みを理解するのが難しいですが、使い方を覚えると中々便利なマクロです。
kernelのソースコードを取得
まずは、kernelのソースコードを取ってきます。
# yum install kernel-devel ... インストール: kernel-devel.x86_64 0:3.10.0-957.5.1.el7 完了しました!listのマクロはlinux/list.hなので下記ファイルとなります。
/usr/src/kernels/3.10.0-957.5.1.el7.x86_64/include/linux/list.hlist.hの加工
linux/list.hはkernel用のヘッダファイルなので、そのままユーザランドのアプリケーションで使おうとするとコンパイルエラーが多発して都合が悪いです。(
エラー解消するのが面倒くさい)なので、少々改造します。
$ cp /usr/src/kernels/3.10.0-957.5.1.el7.x86_64/include/linux/list.h . $ vim list.h改造点
- hlistを削除(今回使わないため)
- LIST_POISON1, LIST_POISON2を0xdeadbeefに置換
- typeof()を __typeof()に置換
- container_of()マクロをlinux/kernel.hからコピペ
改造後のlist.h
#ifndef _LINUX_LIST_H #define _LINUX_LIST_H struct list_head { struct list_head *next, *prev; }; /** * container_of - cast a member of a structure out to the containing structure * @ptr: the pointer to the member. * @type: the type of the container struct this is embedded in. * @member: the name of the member within the struct. * */ #define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \ const __typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \ (type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );}) /* * Simple doubly linked list implementation. * * Some of the internal functions ("__xxx") are useful when * manipulating whole lists rather than single entries, as * sometimes we already know the next/prev entries and we can * generate better code by using them directly rather than * using the generic single-entry routines. */ #define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) } #define LIST_HEAD(name) \ struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list) { list->next = list; list->prev = list; } /* * Insert a new entry between two known consecutive entries. * * This is only for internal list manipulation where we know * the prev/next entries already! */ #ifndef CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next) { next->prev = new; new->next = next; new->prev = prev; prev->next = new; } #else extern void __list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next); #endif /** * list_add - add a new entry * @new: new entry to be added * @head: list head to add it after * * Insert a new entry after the specified head. * This is good for implementing stacks. */ static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head) { __list_add(new, head, head->next); } /** * list_add_tail - add a new entry * @new: new entry to be added * @head: list head to add it before * * Insert a new entry before the specified head. * This is useful for implementing queues. */ static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head) { __list_add(new, head->prev, head); } /* * Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries * point to each other. * * This is only for internal list manipulation where we know * the prev/next entries already! */ static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next) { next->prev = prev; prev->next = next; } /** * list_del - deletes entry from list. * @entry: the element to delete from the list. * Note: list_empty() on entry does not return true after this, the entry is * in an undefined state. */ #ifndef CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST static inline void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry) { __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next); } static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry) { __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next); entry->next = (struct list_head*)0xdeadbeef; entry->prev = (struct list_head*)0xdeadbeef; } #else extern void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry); extern void list_del(struct list_head *entry); #endif /** * list_replace - replace old entry by new one * @old : the element to be replaced * @new : the new element to insert * * If @old was empty, it will be overwritten. */ static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old, struct list_head *new) { new->next = old->next; new->next->prev = new; new->prev = old->prev; new->prev->next = new; } static inline void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old, struct list_head *new) { list_replace(old, new); INIT_LIST_HEAD(old); } /** * list_del_init - deletes entry from list and reinitialize it. * @entry: the element to delete from the list. */ static inline void list_del_init(struct list_head *entry) { __list_del_entry(entry); INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry); } /** * list_move - delete from one list and add as another's head * @list: the entry to move * @head: the head that will precede our entry */ static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) { __list_del_entry(list); list_add(list, head); } /** * list_move_tail - delete from one list and add as another's tail * @list: the entry to move * @head: the head that will follow our entry */ static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) { __list_del_entry(list); list_add_tail(list, head); } /** * list_is_last - tests whether @list is the last entry in list @head * @list: the entry to test * @head: the head of the list */ static inline int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list, const struct list_head *head) { return list->next == head; } /** * list_empty - tests whether a list is empty * @head: the list to test. */ static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head) { return head->next == head; } /** * list_empty_careful - tests whether a list is empty and not being modified * @head: the list to test * * Description: * tests whether a list is empty _and_ checks that no other CPU might be * in the process of modifying either member (next or prev) * * NOTE: using list_empty_careful() without synchronization * can only be safe if the only activity that can happen * to the list entry is list_del_init(). Eg. it cannot be used * if another CPU could re-list_add() it. */ static inline int list_empty_careful(const struct list_head *head) { struct list_head *next = head->next; return (next == head) && (next == head->prev); } /** * list_rotate_left - rotate the list to the left * @head: the head of the list */ static inline void list_rotate_left(struct list_head *head) { struct list_head *first; if (!list_empty(head)) { first = head->next; list_move_tail(first, head); } } /** * list_is_singular - tests whether a list has just one entry. * @head: the list to test. */ static inline int list_is_singular(const struct list_head *head) { return !list_empty(head) && (head->next == head->prev); } static inline void __list_cut_position(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry) { struct list_head *new_first = entry->next; list->next = head->next; list->next->prev = list; list->prev = entry; entry->next = list; head->next = new_first; new_first->prev = head; } /** * list_cut_position - cut a list into two * @list: a new list to add all removed entries * @head: a list with entries * @entry: an entry within head, could be the head itself * and if so we won't cut the list * * This helper moves the initial part of @head, up to and * including @entry, from @head to @list. You should * pass on @entry an element you know is on @head. @list * should be an empty list or a list you do not care about * losing its data. * */ static inline void list_cut_position(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry) { if (list_empty(head)) return; if (list_is_singular(head) && (head->next != entry && head != entry)) return; if (entry == head) INIT_LIST_HEAD(list); else __list_cut_position(list, head, entry); } static inline void __list_splice(const struct list_head *list, struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next) { struct list_head *first = list->next; struct list_head *last = list->prev; first->prev = prev; prev->next = first; last->next = next; next->prev = last; } /** * list_splice - join two lists, this is designed for stacks * @list: the new list to add. * @head: the place to add it in the first list. */ static inline void list_splice(const struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) { if (!list_empty(list)) __list_splice(list, head, head->next); } /** * list_splice_tail - join two lists, each list being a queue * @list: the new list to add. * @head: the place to add it in the first list. */ static inline void list_splice_tail(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) { if (!list_empty(list)) __list_splice(list, head->prev, head); } /** * list_splice_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list. * @list: the new list to add. * @head: the place to add it in the first list. * * The list at @list is reinitialised */ static inline void list_splice_init(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) { if (!list_empty(list)) { __list_splice(list, head, head->next); INIT_LIST_HEAD(list); } } /** * list_splice_tail_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list * @list: the new list to add. * @head: the place to add it in the first list. * * Each of the lists is a queue. * The list at @list is reinitialised */ static inline void list_splice_tail_init(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) { if (!list_empty(list)) { __list_splice(list, head->prev, head); INIT_LIST_HEAD(list); } } /** * list_entry - get the struct for this entry * @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer. * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. */ #define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \ container_of(ptr, type, member) /** * list_first_entry - get the first element from a list * @ptr: the list head to take the element from. * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. * * Note, that list is expected to be not empty. */ #define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) \ list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member) /** * list_last_entry - get the last element from a list * @ptr: the list head to take the element from. * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. * * Note, that list is expected to be not empty. */ #define list_last_entry(ptr, type, member) \ list_entry((ptr)->prev, type, member) /** * list_first_entry_or_null - get the first element from a list * @ptr: the list head to take the element from. * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. * * Note that if the list is empty, it returns NULL. */ #define list_first_entry_or_null(ptr, type, member) \ (!list_empty(ptr) ? list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) : NULL) /** * list_next_entry - get the next element in list * @pos: the type * to cursor * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. */ #define list_next_entry(pos, member) \ list_entry((pos)->member.next, __typeof(*(pos)), member) /** * list_prev_entry - get the prev element in list * @pos: the type * to cursor * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. */ #define list_prev_entry(pos, member) \ list_entry((pos)->member.prev, __typeof(*(pos)), member) /** * list_for_each - iterate over a list * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. * @head: the head for your list. */ #define list_for_each(pos, head) \ for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next) /** * __list_for_each - iterate over a list * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. * @head: the head for your list. * * This variant doesn't differ from list_for_each() any more. * We don't do prefetching in either case. */ #define __list_for_each(pos, head) \ for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next) /** * list_for_each_prev - iterate over a list backwards * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. * @head: the head for your list. */ #define list_for_each_prev(pos, head) \ for (pos = (head)->prev; pos != (head); pos = pos->prev) /** * list_for_each_safe - iterate over a list safe against removal of list entry * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. * @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage * @head: the head for your list. */ #define list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \ for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head); \ pos = n, n = pos->next) /** * list_for_each_prev_safe - iterate over a list backwards safe against removal of list entry * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. * @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage * @head: the head for your list. */ #define list_for_each_prev_safe(pos, n, head) \ for (pos = (head)->prev, n = pos->prev; \ pos != (head); \ pos = n, n = pos->prev) /** * list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. * @head: the head for your list. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. */ #define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \ for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, __typeof(*pos), member); \ &pos->member != (head); \ pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, __typeof(*pos), member)) /** * list_for_each_entry_reverse - iterate backwards over list of given type. * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. * @head: the head for your list. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. */ #define list_for_each_entry_reverse(pos, head, member) \ for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, __typeof(*pos), member); \ &pos->member != (head); \ pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, __typeof(*pos), member)) /** * list_prepare_entry - prepare a pos entry for use in list_for_each_entry_continue() * @pos: the type * to use as a start point * @head: the head of the list * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. * * Prepares a pos entry for use as a start point in list_for_each_entry_continue(). */ #define list_prepare_entry(pos, head, member) \ ((pos) ? : list_entry(head, __typeof(*pos), member)) /** * list_for_each_entry_continue - continue iteration over list of given type * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. * @head: the head for your list. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. * * Continue to iterate over list of given type, continuing after * the current position. */ #define list_for_each_entry_continue(pos, head, member) \ for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, __typeof(*pos), member); \ &pos->member != (head); \ pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, __typeof(*pos), member)) /** * list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse - iterate backwards from the given point * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. * @head: the head for your list. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. * * Start to iterate over list of given type backwards, continuing after * the current position. */ #define list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse(pos, head, member) \ for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, __typeof(*pos), member); \ &pos->member != (head); \ pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, __typeof(*pos), member)) /** * list_for_each_entry_from - iterate over list of given type from the current point * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. * @head: the head for your list. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. * * Iterate over list of given type, continuing from current position. */ #define list_for_each_entry_from(pos, head, member) \ for (; &pos->member != (head); \ pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, __typeof(*pos), member)) /** * list_for_each_entry_safe - iterate over list of given type safe against removal of list entry * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. * @n: another type * to use as temporary storage * @head: the head for your list. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. */ #define list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member) \ for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, __typeof(*pos), member), \ n = list_entry(pos->member.next, __typeof(*pos), member); \ &pos->member != (head); \ pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, __typeof(*n), member)) /** * list_for_each_entry_safe_continue - continue list iteration safe against removal * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. * @n: another type * to use as temporary storage * @head: the head for your list. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. * * Iterate over list of given type, continuing after current point, * safe against removal of list entry. */ #define list_for_each_entry_safe_continue(pos, n, head, member) \ for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, __typeof(*pos), member), \ n = list_entry(pos->member.next, __typeof(*pos), member); \ &pos->member != (head); \ pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, __typeof(*n), member)) /** * list_for_each_entry_safe_from - iterate over list from current point safe against removal * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. * @n: another type * to use as temporary storage * @head: the head for your list. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. * * Iterate over list of given type from current point, safe against * removal of list entry. */ #define list_for_each_entry_safe_from(pos, n, head, member) \ for (n = list_entry(pos->member.next, __typeof(*pos), member); \ &pos->member != (head); \ pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, __typeof(*n), member)) /** * list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse - iterate backwards over list safe against removal * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. * @n: another type * to use as temporary storage * @head: the head for your list. * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. * * Iterate backwards over list of given type, safe against removal * of list entry. */ #define list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse(pos, n, head, member) \ for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, __typeof(*pos), member), \ n = list_entry(pos->member.prev, __typeof(*pos), member); \ &pos->member != (head); \ pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.prev, __typeof(*n), member)) /** * list_safe_reset_next - reset a stale list_for_each_entry_safe loop * @pos: the loop cursor used in the list_for_each_entry_safe loop * @n: temporary storage used in list_for_each_entry_safe * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. * * list_safe_reset_next is not safe to use in general if the list may be * modified concurrently (eg. the lock is dropped in the loop body). An * exception to this is if the cursor element (pos) is pinned in the list, * and list_safe_reset_next is called after re-taking the lock and before * completing the current iteration of the loop body. */ #define list_safe_reset_next(pos, n, member) \ n = list_entry(pos->member.next, __typeof(*pos), member) #endif
サンプルプログラム
リスト作成、表示、回転、削除のサンプルです。
ソースコード
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdint.h> #include <limits.h> #include <string.h> #include <stddef.h> #include "list.h" /* 海魚 */ #define FISH_SARDINE "sardine" /* イワシ */ #define FISH_MACKEREL "mackerel" /* サバ */ #define FISH_TUNA "tuna" /* マグロ */ /* 川魚 */ #define FISH_SALMON "salmon" /* サケ */ #define FISH_SEABASS "seabass" /* スズキ */ #define FISH_EEL "eel" /* ウナギ */ typedef struct { struct list_head head; uint32_t count; } fishlist_t; typedef struct { struct list_head list; uint32_t id; char name[64]; } fish_t; static fishlist_t FishSea; static fishlist_t FishRiver; /* ID発行 */ static uint32_t get_id(void) { static uint32_t id = 0; return (++id % UINT32_MAX); } /* リストの初期化 */ static void init_fish_list(void) { INIT_LIST_HEAD(&FishSea.head); FishSea.count = 0; INIT_LIST_HEAD(&FishRiver.head); FishRiver.count = 0; } /* 海魚をリストに追加 */ static void add_sea_fish_entry(void) { char *fish_name[] = { FISH_SARDINE, FISH_MACKEREL, FISH_TUNA }; fish_t *fish = NULL; for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(fish_name)/sizeof(fish_name[0]); i++) { fish = (fish_t *)malloc(sizeof(fish_t)); if (NULL != fish) { memset(fish, 0, sizeof(*fish)); snprintf(fish->name, sizeof(fish->name)-1, "%s", fish_name[i]); fish->id = get_id(); list_add_tail(&fish->list, &FishSea.head); FishSea.count++; } } } /* 川魚をリストに追加 */ static void add_river_fish_entry(void) { char *fish_name[] = { FISH_SALMON, FISH_SEABASS, FISH_EEL }; fish_t *fish = NULL; for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(fish_name)/sizeof(fish_name[0]); i++) { fish = (fish_t *)malloc(sizeof(fish_t)); if (NULL != fish) { memset(fish, 0, sizeof(*fish)); snprintf(fish->name, sizeof(fish->name)-1, "%s", fish_name[i]); fish->id = get_id(); list_add_tail(&fish->list, &FishRiver.head); FishRiver.count++; } } } /* 海魚のリストを表示 */ static void show_sea_fish_entry(void) { fish_t *fish = NULL; fish_t *n = NULL; printf("----------- show sea fish entry (cnt:%u) ------------\n", FishSea.count); list_for_each_entry_safe(fish, n, &(FishSea.head), list) { printf("id:name = %u:%s\n", fish->id, fish->name); } } /* 川魚のリストを表示 */ static void show_river_fish_entry(void) { fish_t *fish = NULL; fish_t *n = NULL; printf("----------- show river fish entry (cnt:%u) ------------\n", FishRiver.count); list_for_each_entry_safe(fish, n, &(FishRiver.head), list) { printf("id:name = %u:%s\n", fish->id, fish->name); } } /* 川魚のリストを左回転 */ static void rotate_left_sea_fish(void) { list_rotate_left(&(FishSea.head)); } /* 川魚を海魚に結合 */ static void splice_river_to_sea_fish(void) { /* FishRiverにFishSeaに結合 */ list_splice(&(FishRiver.head), &(FishSea.head)); FishSea.count += FishRiver.count; /* 以降FishRiverのリストを使ってはイケナイ */ INIT_LIST_HEAD(&(FishRiver.head)); FishRiver.count = 0; } /* 海魚リストのエントリを全削除 */ static void del_sea_fish_all(void) { fish_t *e = NULL; while(!list_empty(&(FishSea.head))) { e = list_first_entry((&FishSea.head), fish_t, list); list_del(&e->list); free(e); e = NULL; FishSea.count--; } } int main(void) { /* リストの初期化 */ init_fish_list(); /* 海魚のリスト */ add_sea_fish_entry(); show_sea_fish_entry(); /* 川魚のリスト */ add_river_fish_entry(); show_river_fish_entry(); /* リストの結合(river -> sea) */ splice_river_to_sea_fish(); show_sea_fish_entry(); /* リストの回転 */ rotate_left_sea_fish(); show_sea_fish_entry(); /* リスト削除 */ del_sea_fish_all(); show_sea_fish_entry(); return 0; }
実行結果
$ gcc list.c -std=c99 -o fish_list $ ./fish_list ----------- show sea fish entry (cnt:3) ------------ id:name = 1:sardine id:name = 2:mackerel id:name = 3:tuna ----------- show river fish entry (cnt:3) ------------ id:name = 4:salmon id:name = 5:seabass id:name = 6:eel ----------- show sea fish entry (cnt:6) ------------ id:name = 4:salmon id:name = 5:seabass id:name = 6:eel id:name = 1:sardine id:name = 2:mackerel id:name = 3:tuna ----------- show sea fish entry (cnt:6) ------------ id:name = 5:seabass id:name = 6:eel id:name = 1:sardine id:name = 2:mackerel id:name = 3:tuna id:name = 4:salmon ----------- show sea fish entry (cnt:0) ------------
queueを使ったリスト
queueはBSD系のリストを操作するマクロですが、linuxでも使うことができます。
こちらも使い方に癖がありますが、ユーザランドのアプリケーションでリストを実装する場合には便利なマクロ関数です。
ただし、linuxでは使えるリストの種類がリスト、テール (tail) キュー、循環キューの3種類です。リスト、テールは単方向、循環キューは双方向リストです。
循環キューを使って、先ほどのサンプルプログラムで使ったlist_headのマクロをCIRCLEQに置き換えてみます。
サンプルプログラム
ソースコード
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdint.h> #include <limits.h> #include <string.h> #include <stddef.h> #include <sys/queue.h> /* 海魚 */ #define FISH_SARDINE "sardine" /* イワシ */ #define FISH_MACKEREL "mackerel" /* サバ */ #define FISH_TUNA "tuna" /* マグロ */ /* 川魚 */ #define FISH_SALMON "salmon" /* サケ */ #define FISH_SEABASS "seabass" /* スズキ */ #define FISH_EEL "eel" /* ウナギ */ typedef struct { CIRCLEQ_HEAD(circleq, fish) head; uint32_t count; } fishlist_t; struct circleq *headp; /* Circular queue head. */ typedef struct fish { uint32_t id; CIRCLEQ_ENTRY(fish) list; char name[64]; } fish_t; static fishlist_t FishSea; static fishlist_t FishRiver; /* ID発行 */ static uint32_t get_id(void) { static uint32_t id = 0; return (++id % UINT32_MAX); } /* リストの初期化 */ static void init_fish_list(void) { CIRCLEQ_INIT(&FishSea.head); FishSea.count = 0; CIRCLEQ_INIT(&FishRiver.head); FishRiver.count = 0; } /* 海魚をリストに追加 */ static void add_sea_fish_entry(void) { char *fish_name[] = { FISH_SARDINE, FISH_MACKEREL, FISH_TUNA }; fish_t *fish = NULL; for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(fish_name)/sizeof(fish_name[0]); i++) { fish = (fish_t *)malloc(sizeof(fish_t)); if (NULL != fish) { memset(fish, 0, sizeof(*fish)); snprintf(fish->name, sizeof(fish->name)-1, "%s", fish_name[i]); fish->id = get_id(); CIRCLEQ_INSERT_TAIL(&FishSea.head, fish, list); FishSea.count++; } } } /* 川魚をリストに追加 */ static void add_river_fish_entry(void) { char *fish_name[] = { FISH_SALMON, FISH_SEABASS, FISH_EEL }; fish_t *fish = NULL; for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(fish_name)/sizeof(fish_name[0]); i++) { fish = (fish_t *)malloc(sizeof(fish_t)); if (NULL != fish) { memset(fish, 0, sizeof(*fish)); snprintf(fish->name, sizeof(fish->name)-1, "%s", fish_name[i]); fish->id = get_id(); CIRCLEQ_INSERT_TAIL(&FishRiver.head, fish, list); FishRiver.count++; } } } /* 海魚のリストを表示 */ static void show_sea_fish_entry(void) { fish_t *fish = NULL; fish_t *n = NULL; printf("----------- show sea fish entry (cnt:%u) ------------\n", FishSea.count); for (fish = (fish_t *)FishSea.head.cqh_first; fish != (void *)&FishSea.head; fish = (fish_t *)fish->list.cqe_next) { printf("id:name = %u:%s\n", fish->id, fish->name); } } /* 川魚のリストを表示 */ static void show_river_fish_entry(void) { fish_t *fish = NULL; fish_t *n = NULL; printf("----------- show river fish entry (cnt:%u) ------------\n", FishRiver.count); for (fish = (fish_t *)FishRiver.head.cqh_first; fish != (void *)&FishRiver.head; fish = (fish_t *)fish->list.cqe_next) { printf("id:name = %u:%s\n", fish->id, fish->name); } } /* 川魚のリストを左回転 */ static void rotate_left_sea_fish(void) { fish_t *first = (fish_t *)FishSea.head.cqh_first; CIRCLEQ_REMOVE(&FishSea.head, first, list); CIRCLEQ_INSERT_TAIL(&FishSea.head, first, list); } /* 川魚を海魚に結合 */ static void splice_river_to_sea_fish(void) { fish_t *fish = NULL; /* FishRiverにFishSeaに結合 */ while (FishRiver.head.cqh_first != (void *)&FishRiver.head) { fish = (fish_t *)FishRiver.head.cqh_last; CIRCLEQ_REMOVE(&FishRiver.head, fish, list); CIRCLEQ_INSERT_HEAD(&FishSea.head, fish, list); } FishSea.count += FishRiver.count; FishRiver.count = 0; } /* 海魚リストのエントリを全削除 */ static void del_sea_fish_all(void) { fish_t *fish = NULL; while (FishSea.head.cqh_first != (void *)&FishSea.head) { fish = FishSea.head.cqh_first; CIRCLEQ_REMOVE(&FishSea.head, fish, list); free(fish); fish = NULL; FishSea.count--; } } int main(void) { /* リストの初期化 */ init_fish_list(); /* 海魚のリスト */ add_sea_fish_entry(); show_sea_fish_entry(); /* 川魚のリスト */ add_river_fish_entry(); show_river_fish_entry(); /* リストの結合(river -> sea) */ splice_river_to_sea_fish(); show_sea_fish_entry(); /* リストの回転 */ rotate_left_sea_fish(); show_sea_fish_entry(); /* リスト削除 */ del_sea_fish_all(); show_sea_fish_entry(); return 0; }
実行結果
$ gcc queue.c -std=c99 -o fish_queue $ ./fish_queue ----------- show sea fish entry (cnt:3) ------------ id:name = 1:sardine id:name = 2:mackerel id:name = 3:tuna ----------- show river fish entry (cnt:3) ------------ id:name = 4:salmon id:name = 5:seabass id:name = 6:eel ----------- show sea fish entry (cnt:6) ------------ id:name = 4:salmon id:name = 5:seabass id:name = 6:eel id:name = 1:sardine id:name = 2:mackerel id:name = 3:tuna ----------- show sea fish entry (cnt:6) ------------ id:name = 5:seabass id:name = 6:eel id:name = 1:sardine id:name = 2:mackerel id:name = 3:tuna id:name = 4:salmon ----------- show sea fish entry (cnt:0) ------------
参考
[小ネタ]CでListとかデータ構造をどうにかして簡単に使いたい
https://qiita.com/chromabox/items/ea9720422d7a974f6cedlist_headの小さなサンプルメモ
https://qiita.com/kure/items/71057470322b1b636c57inuxカーネルが提供するリストの使い方について
http://d.hatena.ne.jp/mmitou/20120626/1340731801
- 投稿日:2019-03-05T00:15:42+09:00
めんどくさいことはWSLにやらせよう
はじめに
本記事は、Windows端末を使用して、Excelでちょっとしたデータ抽出や集計を行っている場合、劇的に時短を行うためのTipsになります。
ITエンジニアとして仕事をしていると、システムから採取した何らかのログ等を使用して、集計を行ったりすることがあると思います。SIer業界で働くITエンジニアの場合、基本的に作業端末はWindowsを使用している方が多いのではないでしょうか。
実際の業務として、何らかの集計を行う場合、Excelを使用している方がほとんどだと思いますが、WSLを活用することで時短ができます。マクロは不要です。
シチュエーション
例えば、とあるシステムがあったとして、日時で何らかのログ(CSVのデータ)が出力されているとします。このログを1ヶ月分採取して、特定のエラーメッセージが日に何件出力されているか、また月の合計を求めることになった場合、どうしましょう。1個ずつCSVファイル開いて、中身をコピーして別ファイルに保存しますか?それとも、マクロ書きますか?
また、圧縮などが行われて、各フォルダ配下にファイルが生成されていたりすると、めんどくさいですね。。
そんな時は、WSLを使いましょう!
WSLって何?という人は、以前、書いたWSL(Windows Subsystem for Linux)を使ってみたを参考に、インストールしてください。
以下は、上記シチュエーションを解決するためのシェルです。
Windows端末上のWSLにログインし、集計データがあるディレクトリに移動して、当シェル実行すれば一発で終わります。
- totaling.sh
#!/bin/bash ## 検索対象とするファイルを設定し、配列に追加 target_file=^201902.*csv$ list=() for i in `ls | grep ${target_file}`;do list+=(${i}); done length=${#list[@]} if [ ${length} -eq 0 ]; then echo ' *---------------------------------------------------------*' echo ' * 検索対象のファイルが存在しないため、処理を中止します *' echo ' *---------------------------------------------------------*' echo '' exit 1 else echo ' *---------------------------------------------------------*' echo ' * 以下のファイルが検索対象になります *' echo ' *---------------------------------------------------------*' echo '' for i in ${list[@]};do echo ${i}; done fi ## 出力用ファイルを設定 output_file=test.csv ## 検索するキーワードを設定 keyword="err" ## 複数条件 orで検索したい場合 #keyword='キー\|キー' log_search() { for i in ${list[@]} do grep -r "${keyword}" ./${i} --exclude=${output_file} >> ${output_file} done } if [ ! -e ${output_file} ]; then log_search else echo ' *---------------------------------------------------------*' echo ' * ファイルが存在するため、処理を中止します *' echo ' *---------------------------------------------------------*' echo '' exit 2 fi ## 集計するためにcsvから取り出すフィールドをcountに設定 count=2 echo ' *---------------------------------------------------------*' echo ' * 集計処理を行います *' echo ' *---------------------------------------------------------*' echo '' cat ${output_file} | cut -d "," -f ${count} | uniq -c実践
例として、以下のようなCSVファイルがあるとします。
このCSVファイルは"番号","日","時間", "メッセージ"が出力されています。それぞれのCSVファイルに出力された、日毎に発生した特定のエラーメッセージを、時系列に1ファイルに出力して、集計処理の結果を出力します。
2月27日は1件、2月28日は6件のエラーメッセージが確認できました。
また、出力されたtest.csvファイルには、日毎に発生した特定のエラーメッセージが、時系列に1ファイルに出力されたのがcatコマンドで確認できます。おわりに
今回は例として、2個のファイルで集計しました。これぐらいだったらExcelと大差ありませんが、対象ファイルの数が多い場合は効果を発揮します。また、集計処理は、cutコマンドを使用していますが、awkコマンドでも同じことできます。ただ、実際に業務で扱うデータというのは、データ抽出しにくい状況があるので、そういったときは、wcコマンドなどを上手く使うとよいでしょう。
重要なのは、Windows端末なのでExcelで作業するという固定観念を破壊して、新しいやり方を見出すことです。WSLが使用できるということは、Windows端末でLinuxのコマンドが実行できるということです。ファイルを検索する場合も、findコマンドで探したりすることができます。
本記事が、Windows端末で業務を行うITエンジニアの役にたてれば幸いです。
- 投稿日:2019-03-05T00:11:52+09:00
WSLでも通常のLinuxでもdockerにマウントできるカレントパスを取得する
概要
WSL上でdockerを使用する場合、docker for windowsに接続して使用する事が一般的かと思います。
ここで、一番厄介なのがボリュームのパスです。
docker for windowsはwindowsの世界で動いているので、マウントするボリュームパスとしてはwindowsのパスを指定する必要が有ります。
WSL上のshellから「カレントディレクトリの内容をdockerに食わせたい」と考えた場合、パスの形式が違うので一度変換する必要が有ります。
スクリプト等でこれをやろうとする、WSLと普通のlinuxで書き方が変わってしまってややこしいので変換関数を作りました。変換補助関数
以下が今回作成した補助関数です。
これを使うと、WSLの場合は、現在のパスがwindowsのパスとして取得されます。function getPWD(){ local t_PWD=`pwd` if [ -f /proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc/WSLInterop ]; then echo `wslpath -w $t_PWD`; else echo $t_PWD fi }使用イメージ
カレントディレクトリをlocalにマウントする
pwd=`getPWD` docker run --rm -v ${pwd}:/local ${DOCKER_IMAGE}





















