- 投稿日:2020-06-25T23:44:42+09:00
【R8/ProGuard】マージ後のProGuardルールファイルを確認する方法
ライブラリ モジュールの開発に関する考慮事項 の ライブラリ モジュールには独自の ProGuard 構成ファイルを含めることができる に記載がある通り、ライブラリ側がProGuardルールファイルを内包している場合があります。(
consumerProguardFiles)そういうライブラリを使っている場合、最終的に生成されるProGuardルールファイルは、それぞれのProGuardルールファイルがマージされたものになります。
今回は、そのマージされたProGuardルールファイルを確認する方法を記載します。
printconfigurationを使う
方法は簡単で、アプリ側で使っている
proguard-rules.proに-printconfiguration proguard-rules-full.proと記述し、
minifyEnabled trueな状態でビルドするとproguard-rules-full.proというファイル名で出力することができます。参考:https://developer.android.com/studio/build/shrink-code?hl=ja#configuration-files
(おまけ)メンテナンスがしやすい

出力されたProGuardルールファイルは、単純に各ProGuardルールファイルを結合しただけのようでした。
そのため、例えばあるライブラリを使っていて、そのライブラリのルールをアプリ側に記述していたが、実はライブラリが内包しているProGuardルールファイルにそもそも記述されているので不要、といったこともわかるため、ProGuardルールファイルのメンテナンスがしやすいです。
(ProGuardルールファイルは一度書くと、なかなか変更などしないですよね。)
例えば「Glide」の場合
画像ライブラリで有名なGlideですが、GitHubのREADMEに ProGuard の記述があるため、特に調べることなく、アプリ側のProGuardルールファイルにルールをコピペしがちです。
しかしながら、 build.gradleを見てみるとconsumerProguardFiles の記述があり、 proguard-rules.txt を覗いていると、READMEに書かれているルールとほぼ同じもの 1 が書かれているため、アプリ側のProGuardルールファイルにルールを書く必要がないことがわかったりしました。
正確には
for DexGuard onlyのところがコメントアウトされていました。 ↩
- 投稿日:2020-06-25T21:56:15+09:00
[Modern Android] Jetpack Compose その4
JetNewを続いて見ながら、
Jetpack Composeを理解しようと思います。出来ればFlutterと比べながらみようと思います。
今日は
まず、DrawerButtonとtopAppBarを見てみます。
DrawerButton
- DrawerButtonはAppDrawerのComposable関数の中で使われている。
- DrawerButtonはicon、label、isSelected、actionmodifierをパラメータとしている
@Composable private fun DrawerButton( icon: VectorAsset, label: String, isSelected: Boolean, action: () -> Unit, modifier: Modifier = Modifier ) { val colors = MaterialTheme.colors val imageAlpha = if (isSelected) { 1f } else { 0.6f } val textIconColor = if (isSelected) { colors.primary } else { colors.onSurface.copy(alpha = 0.6f) } val backgroundColor = if (isSelected) { colors.primary.copy(alpha = 0.12f) } else { colors.surface } val surfaceModifier = modifier .padding(start = 8.dp, top = 8.dp, end = 8.dp) .fillMaxWidth() Surface( modifier = surfaceModifier, color = backgroundColor, shape = MaterialTheme.shapes.small ) { TextButton( onClick = action, modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth() ) { Row( horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.Start, verticalGravity = Alignment.CenterVertically, modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()) { Image( asset = icon, colorFilter = ColorFilter.tint(textIconColor), alpha = imageAlpha ) Spacer(Modifier.preferredWidth(16.dp)) Text( text = label, style = MaterialTheme.typography.body2, color = textIconColor, modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth() ) } } } }Surface Composable 関数
/** * The [Surface] is responsible for: * * 1) Clipping: Surface clips its children to the shape specified by [shape] * * 2) Elevation: Surface elevates its children on the Z axis by [elevation] pixels, * and draws the appropriate shadow. * * 3) Borders: If [shape] has a border, then it will also be drawn. * * Material surface is the central metaphor in material design. Each surface * exists at a given elevation, which influences how that piece of surface * visually relates to other surfaces and how that surface casts shadows. * * [contentColor] is the preferred color for any children inside this surface - any [Text] inside * this Surface will use this color by default. * * If no [contentColor] is set, this surface will try and match its background color to a color * defined in the theme [ColorPalette], and return the corresponding `onFoo` color. For example, * if the [color] of this surface is [ColorPalette.surface], [contentColor] will be set to * [ColorPalette.onSurface]. If [color] is not part of the theme palette, [contentColor] will keep * the same value set above this Surface. * * To modify these default style values used by text, use [ProvideTextStyle] or explicitly * pass a new [TextStyle] to your text. * * To manually retrieve the content color inside a surface, use [contentColor]. * * @param modifier Modifier to be applied to the layout corresponding to the surface * @param shape Defines the surface's shape as well its shadow. A shadow is only * displayed if the [elevation] is greater than zero. * @param color The background color. Use [Color.Transparent] to have no color. * @param contentColor The preferred content color provided by this Surface to its children. * Defaults to either the matching `onFoo` color for [color], or if [color] is not a color from * the theme, this will keep the same value set above this Surface. * @param border Optional border to draw on top of the surface * @param elevation The z-coordinate at which to place this surface. This controls * the size of the shadow below the surface. */ @Composable fun Surface( modifier: Modifier = Modifier, shape: Shape = RectangleShape, color: Color = MaterialTheme.colors.surface, contentColor: Color = contentColorFor(color), border: Border? = null, elevation: Dp = 0.dp, content: @Composable () -> Unit ) { SurfaceLayout( modifier.drawShadow(elevation = elevation, shape = shape, clip = false) .zIndex(elevation.value) .plus(if (border != null) Modifier.drawBorder(border, shape) else Modifier) .drawBackground( color = getBackgroundColorForElevation(color, elevation), shape = shape ) .clip(shape) ) { Providers(ContentColorAmbient provides contentColor, children = content) } }
- surfaceの中には TextButtonー>Row->Image,Spacer,Textの感じになっている。
- TextButtonはFlutterのInkWellー>Textとか、GestureDetector->Textぽい、なぜならClickリスナーをパラメータとしている
Surface( modifier = surfaceModifier, color = backgroundColor, shape = MaterialTheme.shapes.small ) { TextButton( onClick = action, modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth() ) { Row( horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.Start, verticalGravity = Alignment.CenterVertically, modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()) { Image( asset = icon, colorFilter = ColorFilter.tint(textIconColor), alpha = imageAlpha ) Spacer(Modifier.preferredWidth(16.dp)) Text( text = label, style = MaterialTheme.typography.body2, color = textIconColor, modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth() ) } } }TextButton
- なるほど、ComposeのTextButton、これはFlutterのFlatButton Widgetですね。
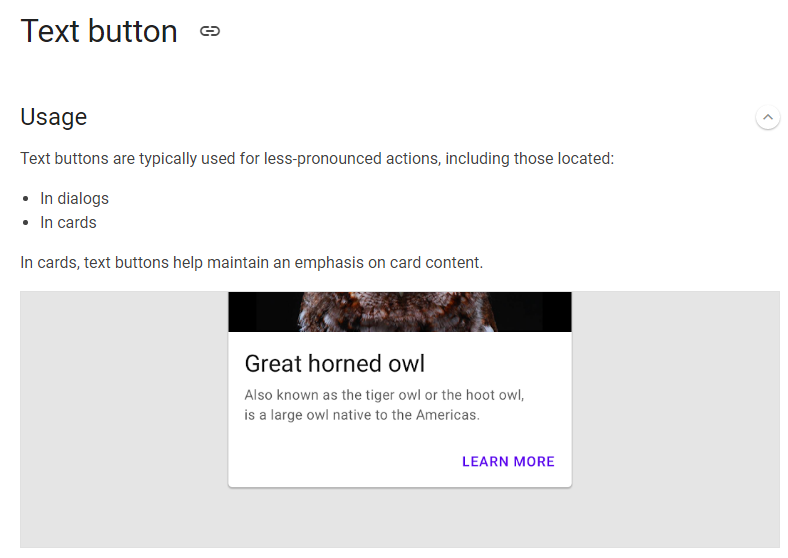
/** * Material Design implementation of a * [Material Text Button](https://material.io/design/components/buttons.html#text-button). * * Text buttons are typically used for less-pronounced actions, including those located in cards and * dialogs. * * To make a button clickable, you must provide an onClick. If no onClick is provided, this button * will display itself as disabled. * * The default text style for internal [Text] components will be set to [Typography.button]. Text * color will try to match the correlated color for the background color. For example if the * background color is set to [ColorPalette.primary] then the text will by default use * [ColorPalette.onPrimary]. * * @sample androidx.ui.material.samples.TextButtonSample * * @param onClick Will be called when the user clicks the button * @param modifier Modifier to be applied to the button * @param enabled Controls the enabled state of the button. When `false`, this button will not * be clickable * @param elevation The z-coordinate at which to place this button. This controls the size * of the shadow below the button * @param shape Defines the button's shape as well as its shadow * @param border Border to draw around the button * @param backgroundColor The background color. Use [Color.Transparent] to have no color * @param contentColor The preferred content color. Will be used by text and iconography * @param disabledContentColor The preferred content color used when [enabled] is false * @param padding The spacing values to apply internally between the container and the content */ @Composable inline fun TextButton( noinline onClick: () -> Unit, modifier: Modifier = Modifier, enabled: Boolean = true, elevation: Dp = 0.dp, shape: Shape = MaterialTheme.shapes.small, border: Border? = null, backgroundColor: Color = Color.Transparent, contentColor: Color = MaterialTheme.colors.primary, disabledContentColor: Color = Button.defaultDisabledContentColor, padding: InnerPadding = TextButton.DefaultInnerPadding, noinline text: @Composable () -> Unit ) = Button( modifier = modifier, onClick = onClick, enabled = enabled, elevation = elevation, disabledElevation = 0.dp, shape = shape, border = border, backgroundColor = backgroundColor, disabledBackgroundColor = backgroundColor, contentColor = contentColor, disabledContentColor = disabledContentColor, padding = padding, text = text )Row
- ComposeのRowはComposable関数です。
- package androidx.ui.layout
- horizontalArrangementはFlutterのMainAxisAlignmentです。
- verticalGravityはFlutterのCrossAxisAlignmentです。
- Arrangementを使ってます。
/** * A layout composable that places its children in a horizontal sequence. For a layout composable * that places its children in a vertical sequence, see [Column]. * * The layout model is able to assign children widths according to their weights provided * using the [RowScope.weight] modifier. If a child is not provided a weight, it will be * asked for its preferred width before the sizes of the children with weights are calculated * proportionally to their weight based on the remaining available space. * * When none of its children have weights, a [Row] will be as small as possible to fit its * children one next to the other. In order to change the width of the [Row], use the * [Modifier.width] modifiers; e.g. to make it fill the available width [Modifier.fillMaxWidth] * can be used. If at least one child of a [Row] has a [weight][RowScope.weight], the [Row] will * fill the available width, so there is no need for [Modifier.fillMaxWidth]. However, if [Row]'s * size should be limited, the [Modifier.width] or [Modifier.size] layout modifiers should be * applied. * * When the size of the [Row] is larger than the sum of its children sizes, a * [horizontalArrangement] can be specified to define the positioning of the children inside * the [Row]. See [Arrangement] for available positioning behaviors; a custom arrangement can * also be defined using the constructor of [Arrangement]. * * Example usage: * * @sample androidx.ui.layout.samples.SimpleRow * * @param modifier The modifier to be applied to the Row. * @param horizontalArrangement The horizontal arrangement of the layout's children. * @param verticalGravity The vertical gravity of the layout's children. * * @see Column */ @Composable fun Row( modifier: Modifier = Modifier, horizontalArrangement: Arrangement.Horizontal = Arrangement.Start, verticalGravity: Alignment.Vertical = Alignment.Top, children: @Composable RowScope.() -> Unit ) { RowColumnImpl( orientation = LayoutOrientation.Horizontal, modifier = modifier, arrangement = horizontalArrangement, crossAxisAlignment = verticalGravity, crossAxisSize = SizeMode.Wrap, children = { RowScope.children() } ) }コードを理解する
- DrawerButtonの構成をみた。
- label はText Composable関数で使う。
- actionはTextButtonで使うCallback関数です。
- navigateTo(Screen.Interests)でStateを変えて画面を変化します。
DrawerButton( icon = Icons.Filled.ListAlt, label = "Interests", isSelected = currentScreen == Screen.Interests, action = { navigateTo(Screen.Interests) closeDrawer() } )TopAppBar
topAppBar = { TopAppBar( title = { Text(text = "Jetnews") }, navigationIcon = { IconButton(onClick = { scaffoldState.drawerState = DrawerState.Opened }) { Icon(vectorResource(R.drawable.ic_jetnews_logo)) } } ) },
- FlutterのAppbarとほぼ同じです。
/** * A TopAppBar displays information and actions relating to the current screen and is placed at the * top of the screen. * * This TopAppBar has slots for a title, navigation icon, and actions. Use the other TopAppBar * overload for a generic TopAppBar with no restriction on content. * * @sample androidx.ui.material.samples.SimpleTopAppBar * * @param title The title to be displayed in the center of the TopAppBar * @param navigationIcon The navigation icon displayed at the start of the TopAppBar. This should * typically be an [IconButton] or [IconToggleButton]. * @param actions The actions displayed at the end of the TopAppBar. This should typically be * [IconButton]s. The default layout here is a [Row], so icons inside will be placed horizontally. * @param backgroundColor The background color for the TopAppBar. Use [Color.Transparent] to have * no color. * @param contentColor The preferred content color provided by this TopAppBar to its children. * Defaults to either the matching `onFoo` color for [backgroundColor], or if [backgroundColor] * is not a color from the theme, this will keep the same value set above this TopAppBar. * @param elevation the elevation of this TopAppBar. */ @Composable fun TopAppBar( title: @Composable () -> Unit, modifier: Modifier = Modifier, navigationIcon: @Composable (() -> Unit)? = null, actions: @Composable RowScope.() -> Unit = {}, backgroundColor: Color = MaterialTheme.colors.primarySurface, contentColor: Color = contentColorFor(backgroundColor), elevation: Dp = TopAppBarElevation ) { AppBar(backgroundColor, contentColor, elevation, RectangleShape, modifier) { val emphasisLevels = EmphasisAmbient.current if (navigationIcon == null) { Spacer(TitleInsetWithoutIcon) } else { Row(TitleIconModifier, verticalGravity = ContentGravity.CenterVertically) { ProvideEmphasis(emphasisLevels.high, navigationIcon) } } Box(Modifier.fillMaxHeight().weight(1f), gravity = ContentGravity.BottomStart) { Semantics(container = true) { ProvideTextStyle(value = MaterialTheme.typography.h6) { val baselineOffset = with(DensityAmbient.current) { TitleBaselineOffset.toDp() } Row(Modifier.relativePaddingFrom(LastBaseline, after = baselineOffset)) { ProvideEmphasis(emphasisLevels.high, title) } } } } ProvideEmphasis(emphasisLevels.medium) { Row( Modifier.fillMaxHeight(), horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.End, verticalGravity = ContentGravity.CenterVertically, children = actions ) } } }
- navigationIconでDrawerを開けます。
navigationIcon: @Composable (() -> Unit)? = null
- 関数とパラメータをして受け取ります。
- 使う方見ればIconButtonが使われているんですね
- IconButtonはFlutterと同じです。
navigationIcon = { IconButton(onClick = { scaffoldState.drawerState = DrawerState.Opened }) { Icon(vectorResource(R.drawable.ic_jetnews_logo)) } }IconButton
- ボタンのサイズはMaterial Designの48dpですね。
- FlutterもIconは24dpでIconButtonWidgetは48dpになっております。
/** * IconButton is a clickable icon, used to represent actions. An IconButton has an overall minimum * touch target size of 48 x 48dp, to meet accessibility guidelines. [icon] is centered * inside the IconButton. * * This component is typically used inside an App Bar for the navigation icon / actions. See App * Bar documentation for samples of this. * * [icon] should typically be an [androidx.ui.foundation.Icon], using an icon from * [androidx.ui.material.icons.Icons]. If using a custom icon, note that the typical size for the * internal icon is 24 x 24 dp. * * @sample androidx.ui.material.samples.IconButtonSample * * @param onClick the lambda to be invoked when this icon is pressed * @param modifier optional [Modifier] for this IconButton * @param icon the content (icon) to be drawn inside the IconButton. This is typically an * [androidx.ui.foundation.Icon]. */ @Composable fun IconButton( onClick: () -> Unit, modifier: Modifier = Modifier, icon: @Composable () -> Unit ) { Box( modifier = modifier .clickable( onClick = onClick, indication = RippleIndication(bounded = false, radius = RippleRadius) ) .plus(IconButtonSizeModifier), gravity = ContentGravity.Center, children = icon ) }終わりに
今回はここまでメモします。
つづく。