- 投稿日:2020-07-14T15:44:37+09:00
React.jsでemotionを使うときはJSX Pragmaをつける必要がありまして。
普通にimportしただけだと動かない
EmotionというCSSフレームワークを使ってちょっとお試しで実装していました。
package.jsonは以下の通りとなっております。{ "dependencies": { "@emotion/core": "^10.0.28", "next": "9.4.4", "react": "16.13.1", "react-dom": "16.13.1" }, "devDependencies": { "@types/node": "^14.0.22", "@types/react": "^16.9.43", "typescript": "^3.9.6" } }スタイルを設定したいページにEmotionをimportしたのですが・・・。
import { Global, css, jsx } from "@emotion/core";これだけだとスタイルが適応されないので調査いたしました。
どうやら下記のように@jsx jsxがないとうまいことコンパイルされないようでした。/** @jsx jsx */ import { Global, css, jsx } from "@emotion/core";
jsxをコンパイルする際は、Emotionは独自のコンパイラを通す必要があり、/** @jsx jsx */というJSX Pragmaの記述をしないと動きませんでした。以下、名著「りあクト! TypeScriptで極める現場のReact開発」から引用
「Emotion はちょっと他のライブラリと違って特殊なことをしているので、使うにあたっていくつか注意事項があるのね。Emotion の文法を使って記述したJSXは通常React.createElement() ではなくEmotion が提供するコンパイラを通す必要があるの。」
「@emotion/core からインポートしてるjsx というのがそのコンパイラね。で、JSX リテラルで書いたコードをそれに渡すためにファイル冒頭で/** @jsx jsx */ の『JSX Pragma』というマジックワードを記述してあげてるの」
「えっ、言われるまで気づきませんでした。そうなんですね」
「さらに、これに起因する注意点が三つあるの。ひとつめは『親コンポーネントでJSX Pragma を使用したら、子のコンポーネントでもJSX Pragma を使わなければならない』こと」
「使わないとどうなるんですか?」
「『ReferenceError: React is not defined』って怒られてコンパイルに失敗するね。場合によっては直上の親コンポーネントにもJSX Pragma が必要なときもある。Presentational Component をインクルードしてContainer Component を作るときとか、それ自体がEmotion を使ってなくてもJSX Pragma を書かないとコンパイルが通らない」コンパイルエラーとありますが、私の環境ではエラーは出ずに、スタイルが当たらないという状況でした。
実装例
Emotionでは子コンポーネントでもJSX Pragmaの記述が必要ということで、
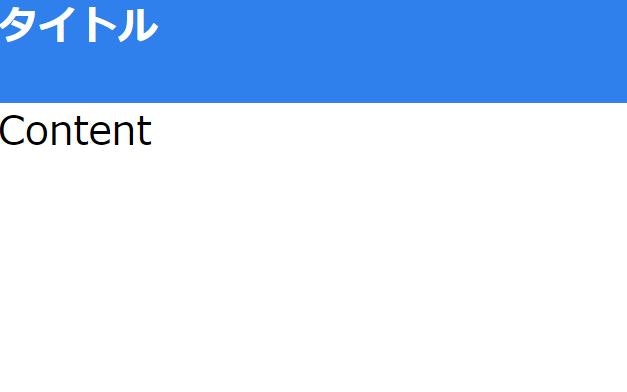
お試しとして、Indexからヘッダーを呼び出すものを実装してみました。↓こんな感じです。
src │ └─pages index.tsx header.tsxheader.tsx/** @jsx jsx */ import { Global, css, jsx } from "@emotion/core"; const globalCss = css` * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } `; const styles = { titleBase: css` height: 168px; width: 100%; `, title: css` height: 168px; width: 100%; font-family: Roboto; font-size: 64px; color: #ffffff; background: #2f80ed; `, }; interface Props { title: string; } const Header = (props: Props) => { return ( <> <Global styles={globalCss} /> <div css={styles.titleBase}> <h1 css={styles.title}>{props.title}</h1> </div> </> ); }; export default Header;index.tsximport Header from "./header"; /** @jsx jsx */ import { css, jsx } from "@emotion/core"; const styles = { content: css` height: 100%; width: 100%; font-size: 64px; `, }; export default function Index() { return ( <> <Header title="タイトル" /> <div css={styles.content}>Content</div> </> ); }Emotionをjsxで使いたい場合、JSX Pragmaを忘れずにつける必要がありました。気を付けたいですね
- 投稿日:2020-07-14T12:52:27+09:00
styled-componentsを使ってCSS Animationを実装する方法
はじめに
styled-componentsはReactコンポーネント内で使えるCSS in JSの一種です。
スコープをコンポーネントのローカルに保てる点や、Sass記法で記述できる点などが特徴です。通常のCSSであれば
@keyframesを使ってアニメーションを記述できますが、styled-componentsではどうでしょうか。styled-componentsでのkeyframes
結論から言うと、ほぼpure CSSと同様の記述でkeyframesを実装できます。
(keyframesのimport文が必要になります)animation.jsimport styled, { keyframes } from 'styled-components'; const fadeIn = keyframes` from { opacity: 0; } to { opacity: 1; } `; const FadeIn = styled.div` animation: ${fadeIn} .5s ease-in-out; `; // JSXで<FadeIn>コンポーネントを使うとkeyframes: fadeInが適用される参考
- 投稿日:2020-07-14T12:49:41+09:00
propsの引き渡し
- 投稿日:2020-07-14T11:21:02+09:00
[Chakra UI]TypeError: Cannot use 'in' operator to search for 'green' in undefined
- 投稿日:2020-07-14T10:57:48+09:00
Next.jsで"document is not defined." "window is not defined."のエラーが出たとき
Next.jsで"document is not defined." "window is not defined."のエラーが出たとき
原因
Next.jsのSSRが原因である可能性が高いです。
SSR = Server Side Rendering
本来クライアント(ブラウザ)側でしか動かないJSフレームワークなどによるレンダリングをサーバー側で行うことによって、初期表示時の高速読み込みや検索エンジン最適化(SEO)を向上するもの。
サーバー側でJSの処理を実行しようとしているときに、ブラウザ側にしか存在しないグローバルオブジェクトの
windowやdocumentを参照しようとすると、標題のエラーが起こります。対策
1.
componentDidMount()内で処理を行う
componentDidMount()内に書いた処理は、基本的にcomponentがmountされた後にクライアント側のみで起こる処理なので、このエラーは起こらないようです。2. if文で条件分岐
React Hooksが主流の現在、こちらの方が汎用性が高いです。
ssr1.jsif (process.browser) { // windowやdocumentを使う処理を記述 }もしくはシンプルに:
ssr2.jsif (window) { // windowを使う処理を記述 }なお
undefinedを判定基準として使うことは一般的にアンチパターンとされるため、下記は避けたほうがいいと思われます。ssr3.jsif (typeof window !== "undefined") { // windowを使う処理を記述 }参考
- 投稿日:2020-07-14T10:57:48+09:00
Next.jsで"document is not defined." "window is not defined."のエラーが出たときの対処法
Next.jsで"document is not defined." "window is not defined."のエラーが出たときの対処法
原因
Next.jsのSSRが原因である可能性が高いです。
SSR = Server Side Rendering
本来クライアント(ブラウザ)側でしか動かないJSフレームワークなどによるレンダリングをサーバー側で行うことによって、初期表示時の高速読み込みや検索エンジン最適化(SEO)を向上するもの。
サーバー側でJSの処理を実行しようとしているときに、ブラウザ側にしか存在しないグローバルオブジェクトの
windowやdocumentを参照しようとすると、標題のエラーが起こります。対策
1.
componentDidMount()内で処理を行う
componentDidMount()内に書いた処理は、基本的にcomponentがmountされた後にクライアント側のみで起こる処理なので、このエラーは起こらないようです。ただ、
componentDidMount()はクラスコンポーネントのライフサイクルメソッドなので、関数コンポーネントでは使えません。2. if文で条件分岐
React Hooksが主流の現在、こちらの方が汎用性が高いです。
ssr1.jsif (process.browser) { // windowやdocumentを使う処理を記述 }もしくはシンプルに:
ssr2.jsif (window) { // windowを使う処理を記述 }なお
undefinedを判定基準として使うことは一般的にアンチパターンとされるため、下記は避けたほうがいいと思われます。ssr3.jsif (typeof window !== "undefined") { // windowを使う処理を記述 }参考
- 投稿日:2020-07-14T09:59:29+09:00
asyncとawaitの関係性、Promiseとは?(typescript, javascript)
対象
async, awaitがさっぱりわからない方
aysncとは
async「非同期処理」↔︎ sync「同期処理」
そもそも同期処理って?
同期処理とは日々我々が書いている普通のコードです。
同期処理 = コードの上から順に読まれること
重たい処理だと表示に時間がかかるため、ユーザーがイライラしてしまう。じゃあ非同期処理(async)は?
非同期処理 = 重い(時間のかかる)処理の結果を待たずに次の行のコードを読み始める処理
AwaitとPromiseとの関係性
await → Promiseの値が取り出されるまで待つ。
async → awaitキーワードを使っている関数のあたまに付ける必要がある。//Aは非同期処理 function A() { return Promise.resolve(1) } async function main() { console.log(1 + A()) // 1が出力 console.log(1 + await A()) // 2が出力 } main()まだPromiseについてはっきりしないので理解出来次第また更新します。
基礎イメージが掴めたらこちらへ(さらに詳しく)
- 投稿日:2020-07-14T08:22:29+09:00
React + TypeScript 環境構築 + ビルド環境を Flavor で切り替える (not create-react-app)
はじめに
この記事は
React+TypeScriptな環境を作成し、Flavorを設定してビルド環境(Development,Staging,Production)を切り替えられるようなProjectを作成することを目的としています。React + TypeScript 環境の構築
初期設定
サックっと初期設定してしまいましょう。
$ mkdir react-flavor-example $ cd react-flavor-example $ npm init色々聞かれるので、適当に質問に答えましょう。
package name: (app) react-flavor-example version: (1.0.0) description: entry point: (main.tsx) webpack.config.js test command: git repository: keywords: author: yukitaka13-1110 license: (ISC) About to write to /app/package.json:Dependency の追加
React 系
$ npm i -D react react-dom @types/react @types/react-domWebpack 系
$ npm i -D webpack webpack-cli webpack-dev-server html-webpack-pluginTypeScript 系
$ npm i -D typescript ts-loader
tsconfig.jsonの作成tsconfig.json{ "compilerOptions": { "sourceMap": true, "module": "commonjs", "esModuleInterop": true, "resolveJsonModule": true, "experimentalDecorators": true, "target": "es5", "jsx": "react", "lib": [ "dom", "es6" ] }, "include": [ "src" ], "compileOnSave": true }
webpack.config.jsの作成webpack.config.jsconst HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin'); module.exports = { mode: 'development', entry: './src/main.tsx', plugins: [ new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'public/index.html', }), ], module: { rules: [ { test: /\.tsx?$/, use: 'ts-loader', }, ], }, resolve: { extensions: [ '.ts', '.js', 'tsx', ], }, };
index.htmlの作成
public/以下にindex.htmlを作成します。public/index.html<html lang="ja"> <body> <div id="root" /> </body> </html>
main.tsxの作成
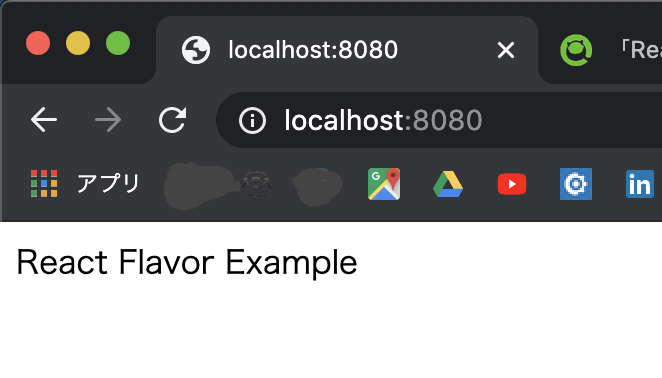
src/以下にmain.tsxを作成します。src/main.tsximport * as React from "react"; import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom"; const App: React.FC = () => { return <div>React Flavor Example</div> }; ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById("root"));この時点でディレクトリ構造が以下のようになっていればOKです。
$ tree ./ -L 2 ./ ├── node_modules ├── package-lock.json ├── package.json ├── public │ └── index.html ├── src │ └── main.tsx ├── tsconfig.json └── webpack.config.js
package.jsonのscriptsにコマンドを追加します。package.json{ ... "scripts": { "start": "webpack-dev-server", "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1" }, ... }
npm run startで起動してhttp://localhost:8080/へアクセスしてReact Flavor Exampleという文字が表示されることを確認Flavor の設定
ここからが本題です。
アプリで利用する環境変数を切り替えたいということは良くあることだと思います。
node.jsではprocess.env.NODE_ENVという環境変数を利用することでアプリで利用する環境変数を切り替えることができるようです。
しかし、process.env.NODE_ENVがstagingを受け取ることができません。型定義を見る感じは受け取れそうですが、どうやらdevelopment|production|test以外は受け付けないようにないっているみたい...。(良く分かっていない)@types/nodeinterface ProcessEnv { [key: string]: string | undefined; }そもそも型定義も貧弱なのでそこも含めて解決します。
process.envの型を上書きする
process.envの型を上書きするには、プロジェクト内のどこかにglobal.d.tsファイルを作成し、以下のように書くことで可能です。src/types/global/global.d.ts/// <reference types="node" /> declare namespace NodeJS { interface ProcessEnv { readonly NODE_ENV: 'development' | 'production' | 'test'; readonly FLAVOR: 'development' | 'staging' | 'production'; } }
NODE_ENVは触っちゃいけない気がしたので以下のようにFLAVORを生やしてみました。その後、
package.jsonでFLAVORを渡すscriptsを追加します。package.json{ "scripts": { "start": "webpack-dev-server", + "dev": "FLAVOR=\"development\" webpack-dev-server", + "stg": "FLAVOR=\"staging\" webpack-dev-server", + "prod": "FLAVOR=\"production\" webpack-dev-server", "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1" }, }渡しただけではアプリ側では受け取れないので、
webpack.config.jsで工夫します。webpack.config.jsconst HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin'); + const webpack = require('webpack'); + const flavor = process.env.FLAVOR || 'development'; module.exports = { mode: 'development', entry: './src/main.tsx', plugins: [ new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'public/index.html', }), + new webpack.DefinePlugin({ + 'process.env.FLAVOR': JSON.stringify(flavor), + }) ], }
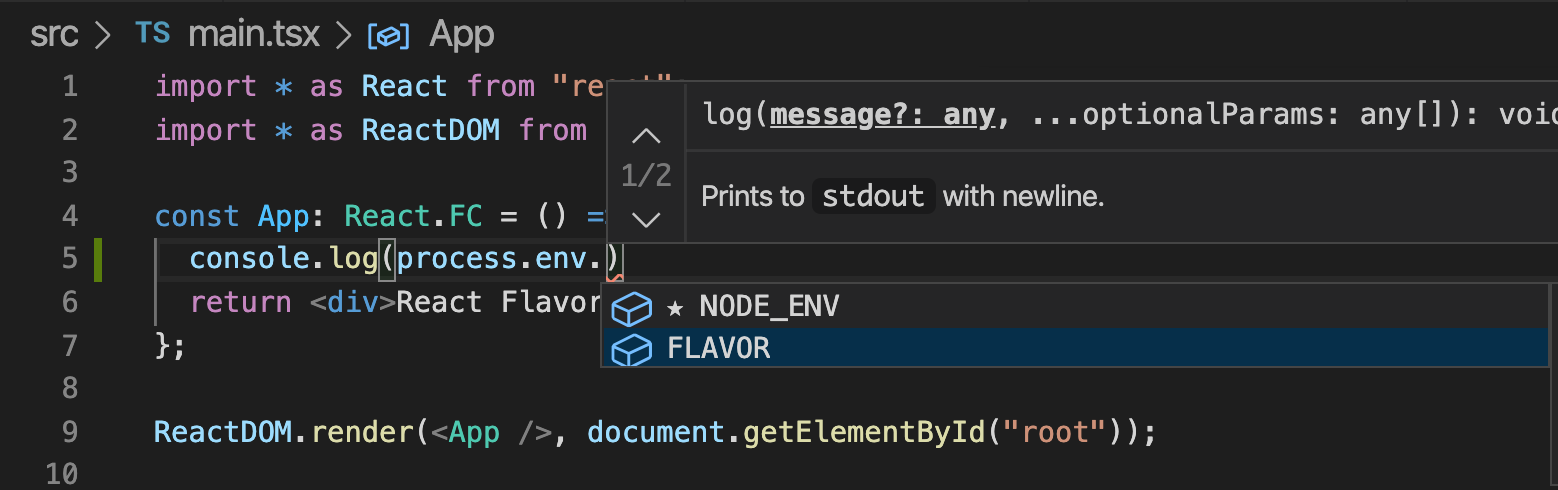
main.tsxにconsole.log()を追加してみましょう。
先程、型定義を上書きしたので補完が効くようになっています。試しに
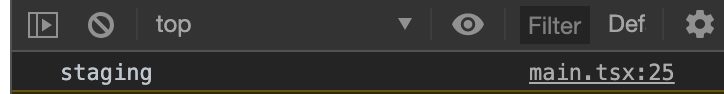
npm run stgを実行してみましょう。
ちゃんと値を受け取れています。後は適当に環境毎に変数を定義して
process.env.FLAVORを使って分岐するだけです。
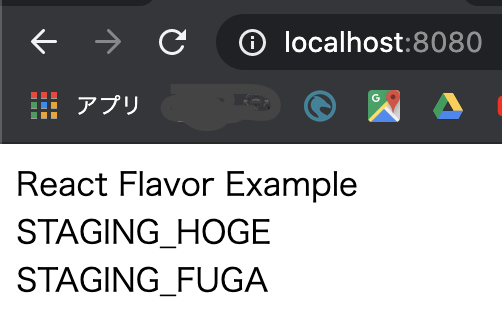
例えば以下のようなconfigディレクトリを用意しておけば良いでしょう。./src/config ├── development │ └── index.ts ├── index.ts ├── production │ └── index.ts └── staging └── index.tsstaging/index.tsimport { EnvVariables } from '../'; const stgVariables: EnvVariables = { HOGE: 'STAGING_HOGE', FUGA: 'STAGING_FUGA', }; export default stgVariables;index.tsimport devVariables from './development'; import stgVariables from './staging'; import prodVariables from './production'; export type EnvVariables = { HOGE: string; FUGA: string; }; const envVariables = (): EnvVariables => { if (process.env.FLAVOR === 'production') { return prodVariables; } if (process.env.FLAVOR === 'staging') { return stgVariables; } return devVariables; }; export default envVariables();src/main.tsximport * as React from "react"; import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom"; import envVariables from './config' // Add import; const App: React.FC = () => { return ( <div> <div>React Flavor Example</div> <div>{envVariables.HOGE}</div> <div>{envVariables.FUGA}</div> </div> ); }; ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById("root"));
npm run stgを実行してhttp://localhost:8080/にアクセスします。ちゃんと値を表示することができました。
終わりに
今回使用したコードはこちらに載せています。
https://github.com/yukitaka13-1110/react-flavor-example現在、QUANDO では iOS, Android, Flutter エンジニア募集中です。
- 投稿日:2020-07-14T03:15:56+09:00
react Hooks useState 使ってみた
useStateを実際に使おう
useStateとは?
Returns a stateful value, and a function to update it.
During the initial render, the returned state (state) is the same as the value passed as the first argument (initialState).
The setState function is used to update the state. It accepts a new state value and enqueues a re-render of the component.
(react 公式サイトuseStateより引用)
React公式サイトにはこのように書いています。
ん?わからない。
なので実際に簡単なコードを書いてみました。
※これはReact Application上で書きました
コード1
const example = useState(0) console.log({example})この場合のconsole.logの出力は次のようになります。
example: Array(2)これの中身を見るとこのようになっています。
0: 0 1: f()つまりexampleは配列になっています。
1番目には初期値である0が
2番目には関数が入ります。コード2
useState()の括弧の中が
本当に初期値なのかと疑問に思ったので
console.logしてみました。const example = useState(500) console.log({example})この場合のexampleの配列の中身は次のようになります。
0: 500 1: f()ちゃんと初期値になってます!
コード3
この配列には2つの要素が入ることがわかりました。
ここでjavascriptの分割代入を使って
それぞれの要素を受け取るようにします。const [count, setCount] = useState(0); const up =() => setCount(count +1)ここでupはcountを+1します。
countの状態を変えるために
setCountをこのように使います。
これによりcountの値を+1していくことができます。実際に書いたコード
import react, {useState} from 'react'; const App = () => { const [count, setCount] = useState(0); const up =() => setCount(count +1) const down =() => setCount(count -1) return ( <> <div>count: {count}</div> <div> <button onClick={up}>+1</button> <button onClick={down}>-1</button> </div> </> ); } export default App;学習したことを応用して
簡単なカウンターを作ってみました。buttonタグでボタンを表示し
onClickはボタンを押したときの処理です。
こうすることでボタンを押して
+1,-1できるカウンターの出来上がりです!
- 投稿日:2020-07-14T00:15:57+09:00
【メモ】react-native にて FontAwesome を急に読み込めなくなった問題
react-native にて FontAwesome を急に読み込めなくなった問題
業務で
react-nativeを扱うことになり、 udemy で講座を購入し、勉強していたのですが急にFontAwesomeが読み込めなくなりました。
とりあえず解決できたので、メモがてら記録に残しておきます。環境
- MacOS: Catalina 10.15.3
- react: 16.9.0
- expo-font: 8.1.1
- expo: 37.0.0
エラーメッセージ
console.error: "fontFamily "FontAwesome" is not a system font and has not been loaded through Font.loadAsync. - If you intended to use a system font, make sure you typed the name correctly and that it is supported by your device operating system. - If this is a custom font, be sure to load it with Font.loadAsync."カスタムフォントを使うなら、
Font.loadAsyncを用いてそのフォントを読み込んでね!ってことでしょうか。ソースコード
button.jsimport React from 'react'; import { StyleSheet, View, TouchableHighlight } from 'react-native'; import * as Font from 'expo-font'; import { createIconSet } from '@expo/vector-icons'; import fontAwsome from '../../assets/fonts/fa-solid-900.ttf'; const CustomIcon = createIconSet({ pencil: '\uf303', plus: '\uf067', check: '\uf00c', }, 'FontAwesome'); class CircleButton extends React.Component { state = { fontLoaded: false, }; async componentDidMount() { await Font.loadAsync({ FontAwesome: fontAwsome, }); this.setState({ fontLoaded: true }); } //以下中略 ); } }こんな感じで読み込んでいたのですが、うまいこと読み込んでくれませんでした。
解決
expo をアップデートすることで解決しました。
npm i -g expo-cli expo upgrade参考